Optimization of technical and technological indicators of kefir added with defatted sesame flour and rice bran
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.272029Keywords:
kefir optimization, defatted sesame flour, rice bran, dietary fiber, pHAbstract
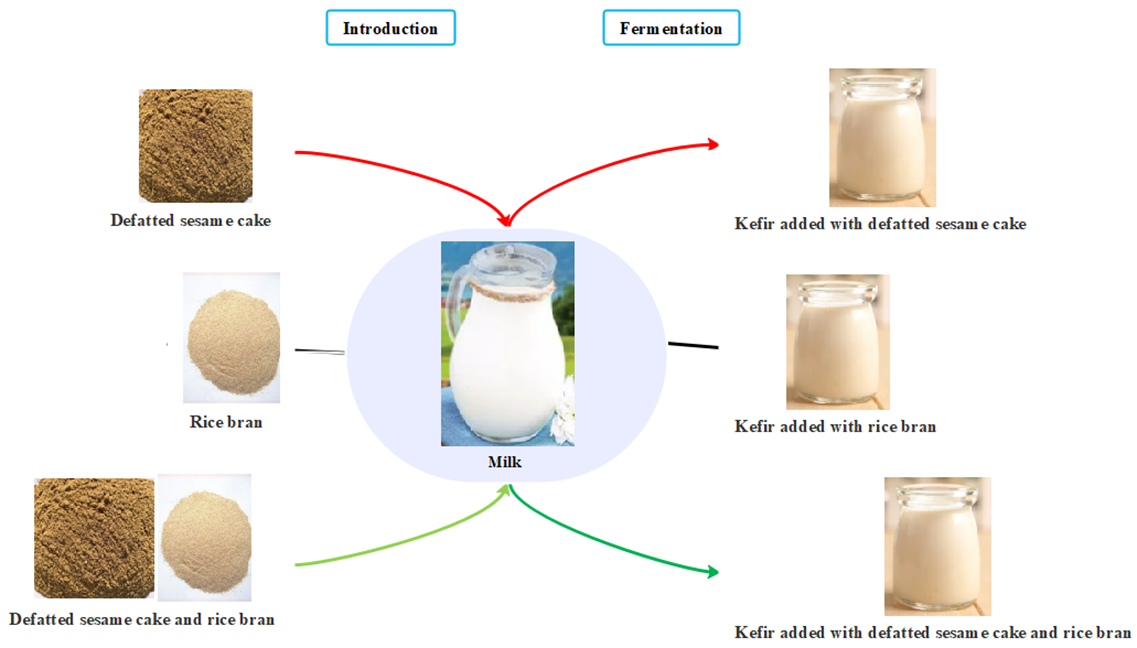
Defatted sesame cake and rice bran are all by-products of agricultural processing. The aim of the study was to optimize the recipes of kefir added with defatted sesame flour and rice bran. The previous study has yielded some results including dietary fiber content, pH values and sensory evaluation values of kefir samples added with 0, 2 %, 4 %, 6 %, 8 % DSC and 0, 0.1 %, 0.3 %, 0.5 %, 0.7 % RB, but made no optimization of kefir products. Based on these data, formulation optimization was done using a mathematical model. Two central composite designs for the two-factor analysis (x1x2 and x1x3, respectively) and one three-factor design (x1x2x3) were drawn up to predict the optimal formulation and reduce the number of future experiments. After studying the results of mathematical modeling, the optimal prescription composition corresponds to the 2 % DSC or 0.1 % rice bran content or 2 % DSC and 0.4 % RB content in the recipe. Through mathematical optimization, products with high dietary fiber content, suitable acidity and excellent sensory quality can be obtained. The products meet the current social demand for healthy food and have very good research value. In practical use, three kinds of kefir can be developed:
1. DSC should be ground separately before used, 2 % DSC was introduced into cow milk (m/v), fermented at 28°C for 22 h until pH reached 4.7, then stored at 4 °C;
2. RB should be ground before used, 0.4 % RB was introduced into cow milk (m/v), fermented at 28°C for 22 h until pH reached 4.7, then stored at 4°C;
3. DSC and RB should be ground before used, 2 % DSC and 0.4 % RB were introduced into cow milk (m/v), fermented at 28 °C for 22 h until pH reached 4.7, then stored at 4 °C
Supporting Agency
- The article was f und by school level project, Hezhou University, project name: A series of food made by water chestnut with low GI, project number: 209200004.
References
- Worsley, T. (2020). Nutrition Promotion. Routledge, 448. doi: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003116608
- Park, S. H., Chung, S., Chung, M.-Y., Choi, H.-K., Hwang, J.-T., Park, J. H. (2022). Effects of Panax ginseng on hyperglycemia, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Ginseng Research, 46 (2), 188–205. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.10.002
- Nan, H., Stepanova, T. M., Kondratiuk, N. V., Nie, Y., Li, B. (2022). Effects of Agaricus bisporus on gel properties of chicken myofibrillar protein. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 57 (8), 5532–5541. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15898
- Hertzler, S. R., Clancy, S. M. (2003). Kefir improves lactose digestion and tolerance in adults with lactose maldigestion. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 103 (5), 582–587. doi: https://doi.org/10.1053/jada.2003.50111
- Erdogan, F. S., Ozarslan, S., Guzel-Seydim, Z. B., Kök Taş, T. (2019). The effect of kefir produced from natural kefir grains on the intestinal microbial populations and antioxidant capacities of Balb/c mice. Food Research International, 115, 408–413. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.10.080
- Huang, Y. Y., She, Z. Y., Shu, M. Y. (2015). Antibacterial activity of foods additives against two strains of lactic acid bacteria. China Dairy Industry, 43 (08), 16–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-2230.2015.08.004
- Liu, S. J., Hou, L. Y., Peng, Z. Y. (2018). Effects of Food Additives on the Activity of Lactic in Probiotic Drink. Journal of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology, 32 (03), 35–39. doi: https://doi.org/10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-7983.2018.03.007
- Micka, A., Siepelmeyer, A., Holz, A., Theis, S., Schön, C. (2016). Effect of consumption of chicory inulin on bowel function in healthy subjects with constipation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 68 (1), 82–89. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09637486.2016.1212819
- Fernández, J., Ledesma, E., Monte, J., Millán, E., Costa, P., de la Fuente, V. G. et al. (2019). Traditional Processed Meat Products Re-designed Towards Inulin-rich Functional Foods Reduce Polyps in Two Colorectal Cancer Animal Models. Scientific Reports, 9 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51437-w
- Li, L., Pan, M., Pan, S., Li, W., Zhong, Y., Hu, J., Nie, S. (2020). Effects of insoluble and soluble fibers isolated from barley on blood glucose, serum lipids, liver function and caecal short-chain fatty acids in type 2 diabetic and normal rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 135, 110937. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2019.110937
- Goncu, B. (2017). Some properties of kefir enriched with apple and lemon fiber. Mljekarstvo, 208–216. doi: https://doi.org/10.15567/mljekarstvo.2017.0305
- Irvine, S. L., Hekmat, S. (2011). Evaluation of Sensory Properties of Probiotic Yogurt Containing Food Products with Prebiotic Fibresin Mwanza, Tanzania. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 02 (05), 434–439. doi: https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2011.25061
- Qin, X., Samilyk, M., Luo, Y., Sokolenko, V. (2021). Influence of sesame flour on physicochemical properties of sour milk drinks. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (11 (111)), 6–16. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2021.234752
- Samilyk, M., Qin, X., Luo, Y. (2021). The influence of the introduction of rice bran on fermented milk drink. Scientific Messenger of LNU of Veterinary Medicine and Biotechnologies, 23 (96), 39–45. doi: https://doi.org/10.32718/nvlvet-f9608
- Dinkçi, N. D. (2015). An innovative approach: cow/oat milk based kefir. Mljekarstvo, 65 (3), 177–186. doi: https://doi.org/10.15567/mljekarstvo.2015.0304
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Xuanxuan Qin, Maryna Samilyk, Yanghe Luo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.
A license agreement is a document in which the author warrants that he/she owns all copyright for the work (manuscript, article, etc.).
The authors, signing the License Agreement with TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC, have all rights to the further use of their work, provided that they link to our edition in which the work was published.
According to the terms of the License Agreement, the Publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC does not take away your copyrights and receives permission from the authors to use and dissemination of the publication through the world's scientific resources (own electronic resources, scientometric databases, repositories, libraries, etc.).
In the absence of a signed License Agreement or in the absence of this agreement of identifiers allowing to identify the identity of the author, the editors have no right to work with the manuscript.
It is important to remember that there is another type of agreement between authors and publishers – when copyright is transferred from the authors to the publisher. In this case, the authors lose ownership of their work and may not use it in any way.









