Gut microbiota modulation by postbiotics in patients with coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4798.2024.300625Keywords:
coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, gut microbiota composition, postbiotics, propionic acid, amino acids, glycineAbstract
The aim: is to improve gut microbiota composition by the long-term postbiotics (glycine and propionic acid) supplementation in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and atrial fibrillation (AF).
Materials and methods: 40 patients were divided into 3 groups: first (CAD) – 14 patients with CAD but without arrhythmias; second (CAD+AF) – 18 patients with CAD and AF paroxysm; and the control group – 8 patients without CAD and arrhythmias. 16 patients from the II group received basic therapy, according to the latest ESC guidelines, and postbiotic supplementation: rebamipide (2-(4-chlorobenzoylamino)-3-[2(1H))-quinolon-4-yl] propionic acid) by 100 mg 3 times a day and glycine by 100 mg 3 times a day during 6 months. 16-S rRNA sequencing checked gut microbiota composition.
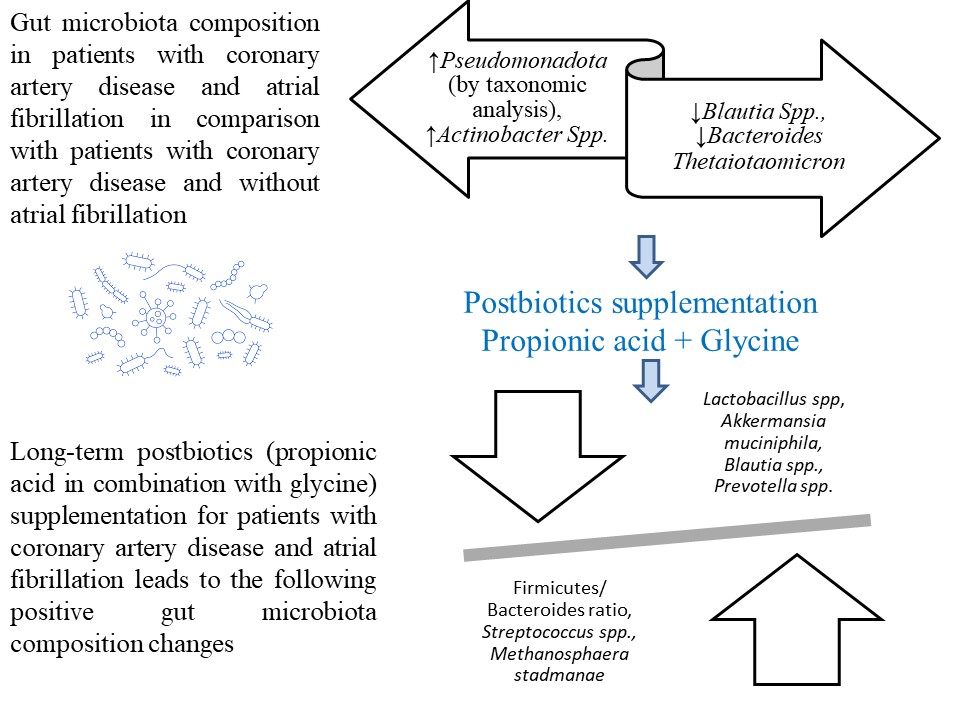
Results: The II group patients had a significant rise in Pseudomonadota (by taxonomic analysis), Actinobacter Spp. and a decrease in Blautia Spp., Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron compared with the I group, P<0.05. Long-term postbiotics supplementation for patients with coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation leads to a significant decrease in Firmicutes/ Bacteroides ratio, P<0.05; a significant rise in Verrucomicrobiota and a decrease in Firmicutes, P<0.05; a significant increase in Lactobacillus spp., Akkermansia muciniphila, Blautia spp., Prevotella spp. and a decrease in Streptococcus spp. and Methanosphaera stadmanae, P<0.05. A significantly lower F/B ratio was found in the patients with long-term postbiotics supplementation in comparison with placebo group patients, P<0.05. A significant increase in Actinomycetota was found in the patients with long-term postbiotics supplementation compared to placebo group patients, P<0.05. A significant increase in probiotic species (Akkermansia muciniphila, Blautia spp., Eubacterium Rectale, and Prevotella spp.) and a decrease in species, associated with cardiometabolic disorders (Streptococcus spp.) was found in the patients with long term postbiotics supplementation in comparison with placebo group patients, P<0.05.
Conclusion: Long-term postbiotics supplementation for patients with coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation leads to positive gut microbiota modulation
Supporting Agency
- Department's scientific research work "Changes in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in patients with coronary heart disease and arterial hypertension with heart rhythm disorders, possibilities of drug correction" 2021–2023 (state registration number 0121U108875).
References
- Adak, A., Khan, M. R. (2018). An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 76 (3), 473–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2943-4
- Gawałko, M., Agbaedeng, T. A., Saljic, A., Müller, D. N., Wilck, N., Schnabel, R. et al. (2021). Gut microbiota, dysbiosis and atrial fibrillation. Arrhythmogenic mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Cardiovascular Research, 118 (11), 2415–2427. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvab292
- Hindricks, G., Potpara, T., Dagres, N., Arbelo, E., Bax, J. J., Blomström-Lundqvist, C. et al. (2020). 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). European Heart Journal, 42 (5), 373–498. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612
- Knuuti, J., Wijns, W., Saraste, A., Capodanno, D., Barbato, E., Funck-Brentano, C. et al. (2019). 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. European Heart Journal, 41 (3), 407–477. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425
- Choroszy, M., Litwinowicz, K., Bednarz, R., Roleder, T., Lerman, A., Toya, T. et al. (2022). Human Gut Microbiota in Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Metabolites, 12 (12), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12121165
- Nataraj, B. H., Ali, S. A., Behare, P. V., Yadav, H. (2020). Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microbial Cell Factories, 19 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01426-w
- Tain, Y.-L., Hou, C.-Y., Chang-Chien, G.-P., Lin, S., Tzeng, H.-T., Lee, W.-C. et al. (2023). Reprogramming Effects of Postbiotic Butyrate and Propionate on Maternal High-Fructose Diet-Induced Offspring Hypertension. Nutrients, 15 (7), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071682
- Vrzáčková, N., Ruml, T., Zelenka, J. (2021). Postbiotics, Metabolic Signaling, and Cancer. Molecules, 26 (6), 1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061528
- Muralitharan, R. R., Jama, H. A., Xie, L., Peh, A., Snelson, M., Marques, F. Z. (2020). Microbial Peer Pressure: The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Hypertension and Its Complications. Hypertension, 76 (6), 1674–1687. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.120.14473
- Rom, O., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Wu, J., Ghrayeb, A. et al. (2020). Glycine-based treatment ameliorates NAFLD by modulating fatty acid oxidation, glutathione synthesis, and the gut microbiome. Science Translational Medicine, 12 (572). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz2841
- Yang, S., Zhao, J., Liu, X., Wang, J., Gu, M., Cai, C. et al. (2023). Metabolomics Profiling Predicts Ventricular Arrhythmia in Patients with an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 17 (1), 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-023-10413-6
- Faizi, N., Alvi, Y. (2023). Biostatistics Manual for Health Research. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2022-0-00374-3
- Hill, C., Guarner, F., Reid, G., Gibson, G. R., Merenstein, D. J., Pot, B. et al. (2014). The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 11 (8), 506–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
- Oxman, T., Shapira, M., Klein, R., Avazov, N., Rabinowitz, B. (2001). Oral Administration of Lactobacillus Induces Cardioprotection. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 7 (4), 345–354. https://doi.org/10.1089/107555301750463224
- Li, W., Li, C., Ren, C., Zhou, S., Cheng, H., Chen, Y. et al. (2023). Bidirectional effects of oral anticoagulants on gut microbiota in patients with atrial fibrillation. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1038472
- Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Han, X., Yuan, Y., Zhou, Y., Gao, Y. et al. (2022). Akkermansia muciniphila prevents cold-related atrial fibrillation in rats by modulation of TMAO induced cardiac pyroptosis. EBioMedicine, 82, 104087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104087
- Okami, Y., Arima, H., Kondo, K., Hexun, Z., Yano, Y., Kadota, A. Et al. (2024). The gut microbiota and coronary artery calcification in Japanese men. American Heart Journal, 267, 12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2023.09.009
- Tett, A., Pasolli, E., Masetti, G., Ercolini, D., Segata, N. (2021). Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19 (9), 585–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00559-y
- Fang, C., Zuo, K., Fu, Y., Zhu, X., Li, J., Zhong, J., Xu, L., Yang, X. (2022). Aggravated Gut Microbiota and Metabolomic Imbalances Are Associated with Hypertension Patients Comorbid with Atrial Fibrillation. Biomolecules, 12 (10), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12101445
- Cisek, A. A., Szymańska, E., Wierzbicka-Rucińska, A., Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk, T., Cukrowska, B. (2024). Methanogenic Archaea in the Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Relation to Disease Type and Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25 (1), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010673
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Iryna Melnychuk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.
Authors, who are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. The authors reserve the right to authorship of the work and pass the first publication right of this work to the journal under the terms of a Creative Commons CC BY, which allows others to freely distribute the published research with the obligatory reference to the authors of the original work and the first publication of the work in this journal.
2. The authors have the right to conclude separate supplement agreements that relate to non-exclusive work distribution in the form in which it has been published by the journal (for example, to upload the work to the online storage of the journal or publish it as part of a monograph), provided that the reference to the first publication of the work in this journal is included.








