Development of a microwave resonant waveguide slot antenna with in-phase slot excitation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2023.274990Keywords:
resonant antenna, waveguide-slot antenna, frequency range, voltage standing wave ratio, radiation patternAbstract
The object of research in the work is the process of radiation of electromagnetic waves of a resonant waveguide-slot antenna with in-phase excitation of slots. The subject of research is the wave parameters and directional properties of a resonant slotted waveguide antenna with in-phase slot excitation. The existing problem is that it is necessary to ensure highly directional properties of the antenna with electrical control of its wave parameters at high transmitter power. This problem is due to the fact that to solve the problem of developing equipment for radio control, and radar of aircraft, highly directional antennas of small sizes are required. To solve this problem, the paper proposes the design of a simple and cheap version of a microwave resonant waveguide-slot antenna with in-phase slot excitation.
As a basis for developing a resonant slotted waveguide antenna, the authors chose a standard R48 rectangular waveguide, which is a classic in the theory of directional systems in the microwave range. This is due to the fact that in order to calculate and study a microwave resonant waveguide-slot antenna with in-phase excitation of slots, the authors used well-known elements of the theory of aperture antennas. The design of a resonant slotted waveguide antenna consists of a rectangular waveguide, an exciter, and a feeder. The radiation surface of the antenna is a wide wall of a standard R48 rectangular waveguide along the central axis, of which slots are symmetrically cut in a checkerboard pattern. The exciter is made in the form of a metal pin inside a rectangular waveguide near the short-circuited wall. This pin acts as an asymmetric vertical vibrator that excites electromagnetic waves in a rectangular waveguide. The antenna is tuned to the maximum radiation power mechanically by moving the short-circuited wall of the rectangular waveguide. The pin feeds a feeder based on a coaxial cable with a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms.
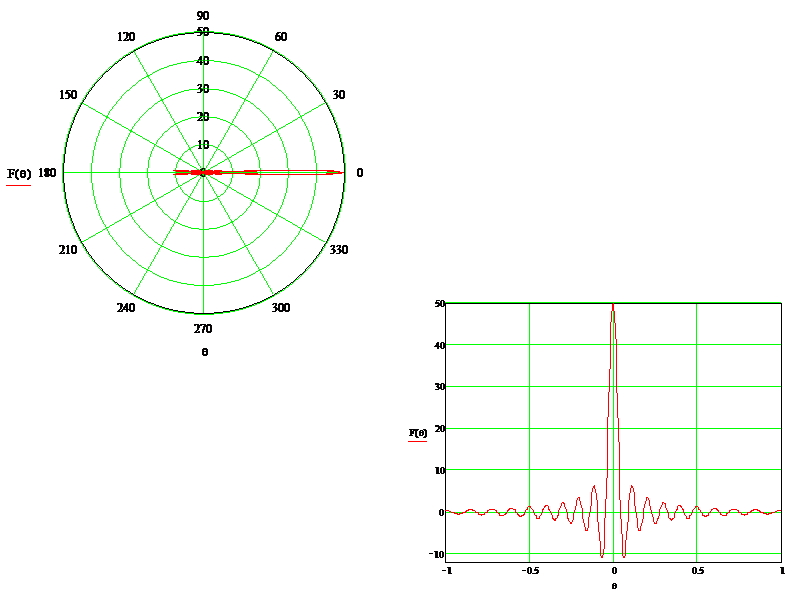
The developed resonant waveguide-slot antenna with in-phase excitation of slots operates in the frequency range of 4.0–6.0 GHz. In the frequency range of 4.0–5.45 GHz, the value of Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) varies from 1.08 to 2.1. In the frequency range of 5.45–6.0 GHz, the Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) value varies from 2.1 to 6.55. The directivity of the antenna in the operating frequency range is not less than 90. The width of the main lobe of the antenna pattern in the horizontal plane is not more than 3.1°. The antenna gain in the operating frequency band is at least 100. The efficiency is at least 90 % with a maximum generator signal power of 10 kW.
Supporting Agency
- Presentation of research in the form of publication through financial support in the form of a grant from SUES (Support to Ukrainian Editorial Staff).
References
- Liao, S., Chen, Y., Wei, J., Xu, J. (2010). Unequally Spaced Resonant Slotted-Waveguide Antenna Array Based on the Infinite Wavelength Propagation Property of Composite Right/Left-Handed Waveguide. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 9, 451–454. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2010.2050132
- Taheri, M., Majedi, M. S. (2017). Resonant slotted-waveguide antenna array using open-ended SIW resonator. 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iraniancee.2017.7985396
- Coetzee, J. C., Kulkarni, A., Albannay, M. M. (2014). Compensation for higher order mode coupling between inclined coupling slots and radiating slots in planar slotted waveguide arrays. 2014 USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (Joint with AP-S Symposium). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/usnc-ursi.2014.6955442
- Dunn, D. S., Augustin, E. P., Chin Chang. (1994). Design of an eight element edge slot waveguide array antenna. Conference Record Southcon. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/southc.1994.498115
- Cao, J., Wang, H., Mou, S., Soothar, P., Zhou, J. (2019). An Air Cavity-Fed Circularly Polarized Magneto-Electric Dipole Antenna Array With Gap Waveguide Technology for mm-Wave Applications. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 67 (9), 6211–6216. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2019.2925186
- Maxum, B. (1960). Resonant slots with independent control of amplitude and phase. IRE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 8 (4), 384–389. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.1960.1144869
- He, W.-H., Liu, S.-B., Li, W., Hu, Z.-Y., Zhang, X.-W., Zhou, Z.-Y. (2021). Wideband Excitations of Higher-order Mode SIW Slot Array Antenna for X-band Applications. 2021 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/piers53385.2021.9694951
- Rao, Y., Zhang, H., Sun, G. (2020). Shared Aperture Dual-band Waveguide Slot antenna. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ieeeconf35879.2020.9330047
- Lubis, Moh. A. K. S., Yusuf, D. P., Apriono, C., Rahardjo, E. T. (2017). The effect of flange connectors on the radiation performance of narrow wall slotted waveguide antenna at X-band frequency. 2017 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/isanp.2017.8228980
- Zhang, J.-P., Li, B., Zhou, Z.-P. (2018). A substrate integrated waveguide slot antenna for 79-GHz applications. 2018 International Workshop on Antenna Technology (IWAT). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iwat.2018.8379184
- Balanis, C. A. (2016). Antenna Theory. Analysis and Design. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1072.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Andriy Semenov, Olena Semenova, Natalia Kryvinska, Andrii Krystoforov, Pavlo Kurovskyi, Oleh Kaplychnyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







