Investigation of physicochemical characterization and magnetic enrichment of iron ore from Sidi Maarouf deposit
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.297846Keywords:
iron oxide, characterization, steel industry, magnetic separation, washing, Jijel region, eastern AlgeriaAbstract
The establishment of a new metallurgical complex in Bellara, located in El-Milia in the Jijel region, is geographically advantageous due to its proximity to the Sidi Maarouf deposit (Algeria). This proximity has been a fundamental motivation for the completion of the current study. The object of research is the quality of iron products from Sidi Maarouf. The research is aimed at developing a treatment process aimed at improving the quality of iron products from Sidi Maarouf, while reducing the impurities of quartz and clay present in this ore. This approach will be based on an approved technological treatment scheme, implemented through an experimental approach to ensure reliable results that meet the requirements of the steel industry. The problem issue revolves around the difficulties encountered in the production of steels due to the natural characteristics of the raw material.
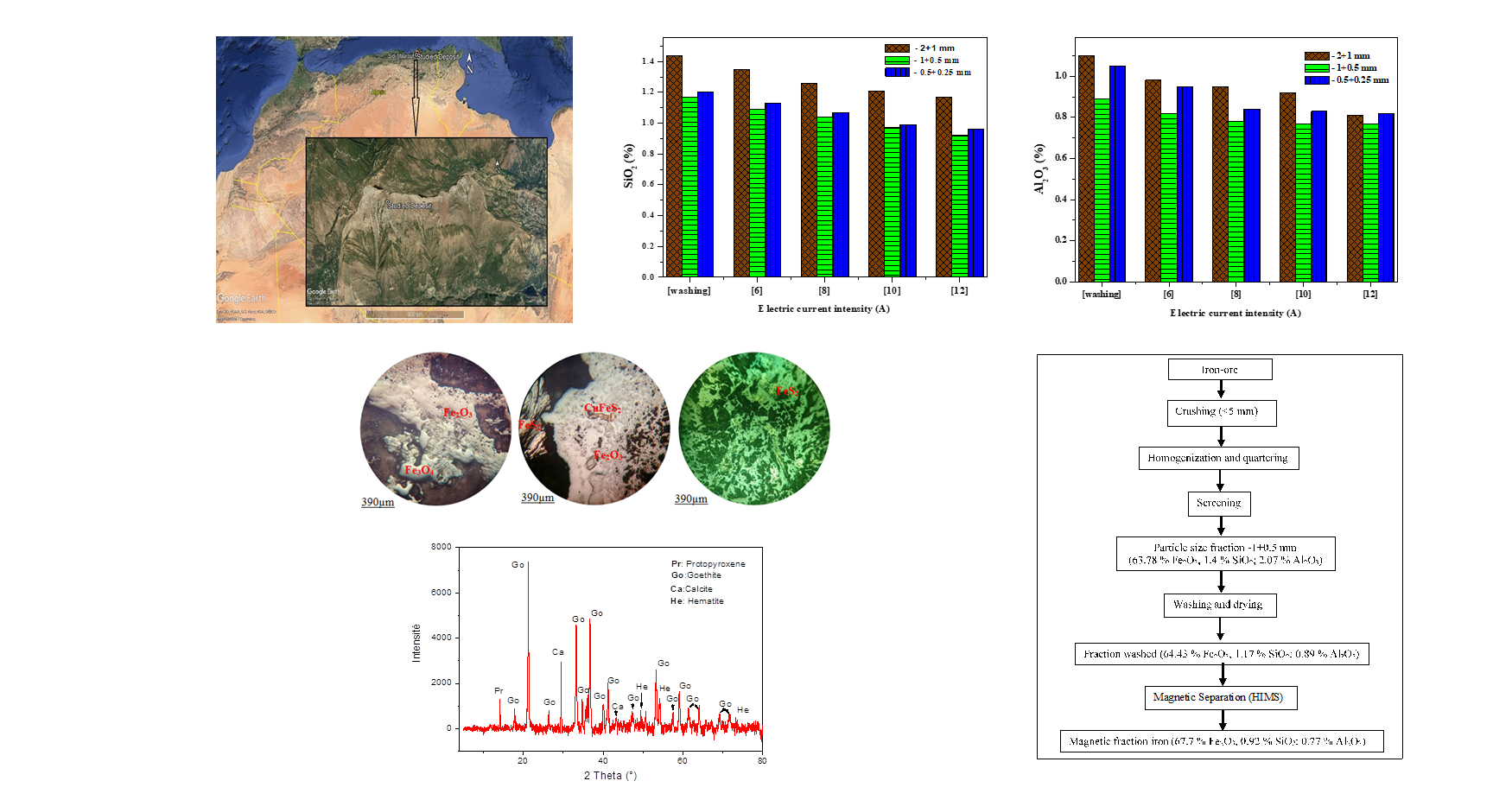
In the absence of a physico-chemical characterization of the Sidi Maarouf iron ore deposit, samples taken undergo a series of thorough analyses, including microscopic examinations, X-ray diffraction (XRD), as well as additional chemical analyses using X-ray fluorescence (XRF). The identified minerals are predominantly composed of hematite in terms of iron. As for the gangue, it is mainly composed of calcite and quartz. Through to the pre-treatment process involving washing, we have successfully removed lightweight particles, resulting in a concentrate containing dense particles. This approach was crucial in achieving satisfactory results during the high-intensity dry magnetic separation. As a result of the research it is shown that the enrichment of the Sidi Maarouf iron ore through high-intensity dry magnetic separation, a final concentrate was obtained with a Fe2O3 content exceeding 67 %, along with a significant reduction in silica impurities to 0.92 % and alumina to 0.77 %. It was concluded that this concentrate, derived from the -1+0.5 mm fraction and obtained under a current intensity of 12 A, meets the requirements of the steel industry.
Following the work carried out, it is found that the methods of valorization of iron ore through mineralogical processes consistently require a high level of efficiency and performance in terms of equipment and characterization of the products obtained. In the future, iron ore processing will be conducted using innovative methods, integrating advanced technologies to enhance its characteristics while adopting environmentally friendly practices.
References
- Zerzour, O., Gadri, L., Hadji, R., Mebrouk, F., Hamed, Y. (2020). Semi-variograms and kriging techniques in iron ore reserve categorization: application at Jebel Wenza deposit. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13 (16). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05858-x
- Filippov, L. O., Severov, V. V., Filippova, I. V. (2014). An overview of the beneficiation of iron ores via reverse cationic flotation. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 127, 62–69. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2014.01.002
- Selim, K. A., Rostom, M. (2018). Bioflocculation of (Iron oxide – Silica) system using Bacillus cereus bacteria isolated from Egyptian iron ore surface. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 27 (2), 235–240. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2017.07.002
- Xiong, D., Lu, L., Holmes, R. J. (2015). Developments in the physical separation of iron ore: magnetic separation. Iron ore. Woodhead Publishing, 283–307.
- Suthers, S. P., Nunna, V., Tripathi, A., Douglas, J., Hapugoda, S. (2014). Experimental study on the beneficiation of low-grade iron ore fines using hydrocyclone desliming, reduction roasting and magnetic separation. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 123 (4), 212–227. doi: https://doi.org/10.1179/1743285514y.0000000067
- Nadir, D. E. G. H. F. E. L., Chouki, F. A. R. S. I., Azzedine, B. E. N. Y. A. H. I. A., Moussa, Z. A. O. U. I. (2021). Evaluation of materials from the excavation of the Ouenza hematite deposit (North-East Algeria) by gravimetric enrichment. Natural Volatiles & Essential Oils, 8 (4), 11529–11537.
- Zhang, X., Gu, X., Han, Y., Parra-Álvarez, N., Claremboux, V., Kawatra, S. K. (2019). Flotation of Iron Ores: A Review. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 42 (3), 184–212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2019.1689494
- Rath, S. S., Sahoo, H. (2020). A Review on the Application of Starch as Depressant in Iron Ore Flotation. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 43 (1), 122–135. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2020.1843028
- Sis, H., Karaağaç, T., Birinci, M., Kiyak, T. (2021). Düşük tenörlü manyetit cevherinin manyetik ayirma ve yerçekimi ile zenginleştirilmesi: tane boyu etkisi. Bilimsel Madencilik Dergisi, 60 (1), 31–39. doi: https://doi.org/10.30797/madencilik.796806
- Akbari, H., Noaparast, M., Shafaei, S. Z., Hajati, A., Aghazadeh, S., Akbari, H. (2018). A Beneficiation Study on a Low Grade Iron Ore by Gravity and Magnetic Separation. Russian Journal of Non-Ferrous Metals, 59 (4), 353–363. doi: https://doi.org/10.3103/s1067821218040028
- Siame, M., Kaoma, J., Shibayama, A. (2021). Development of impurities removal process for low-grade Sanje iron ore using mineral processing technologies. Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences, 3 (1), 36–52. doi: https://doi.org/10.53974/unza.jonas.3.1.460
- Nameni, A., Nazari, M., Shahmardan, M. M., Nazari, M., Mashayekhi, V. (2022). Separation and trapping of magnetic particles by insertion of ferromagnetic wires inside a microchip: Proposing a novel geometry in magnetophoresis. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 560, 169424. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169424
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Abdeslam Chaib, Soufiane Bouabdallah, Meriem Ferfar, Aissa Benselhoub, Nadiia Dovbash, Stefano Bellucci

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







