Designing an Internet of Things solution for monitoring vital signs
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.300745Keywords:
vital signs monitoring, client-server architecture, information system, Internet of Things, IoTAbstract
The object of study is the process of monitoring vital signs using an automated system based on an Internet of Things (IoT) solution. The study investigates and analyses the best existing solutions for continuous monitoring of human health. The research is important in the context of a possible pandemic and general health monitoring.
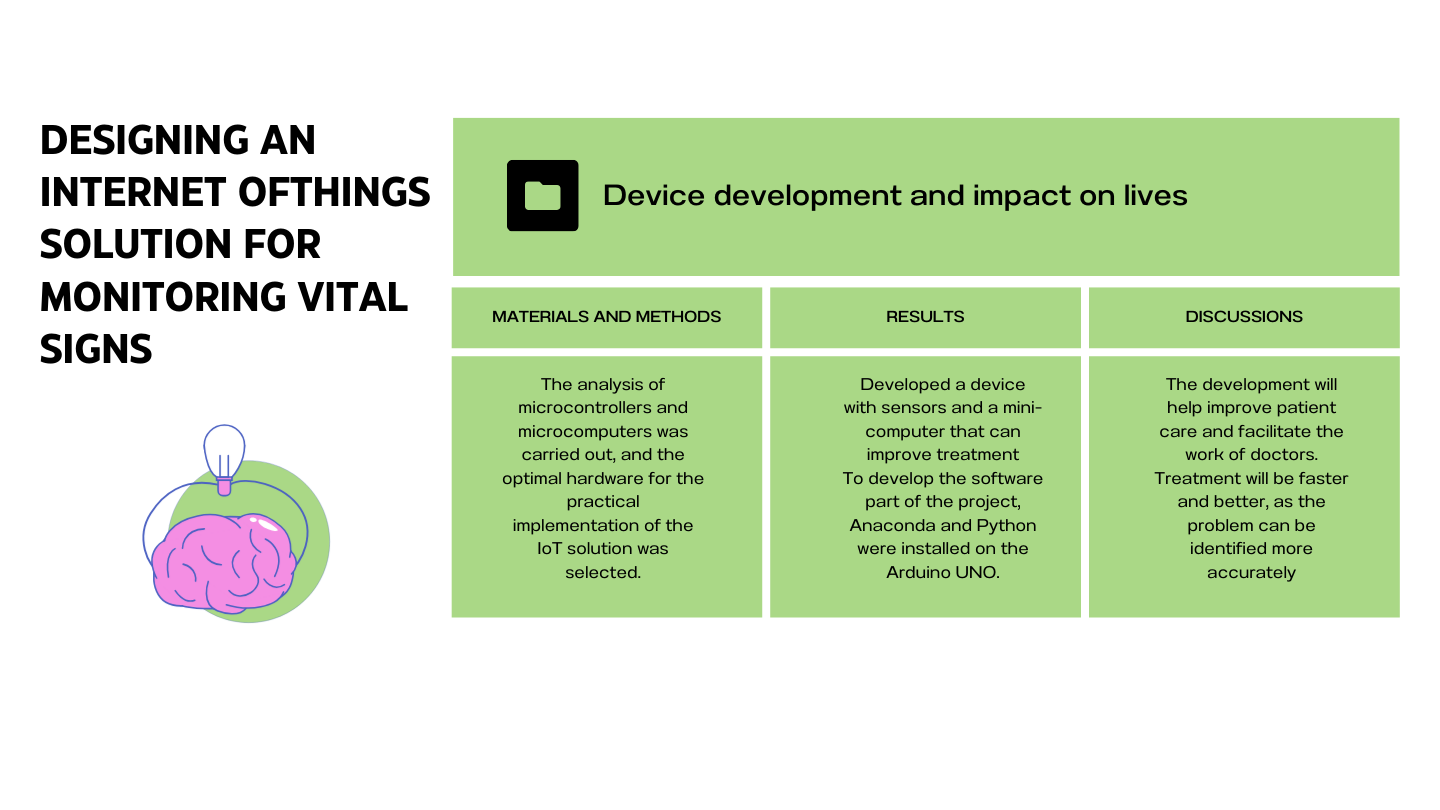
An IoT model of a solution for monitoring and analyzing vital signs in patients is proposed. The project involves the creation of hardware and software for tracking vital signs. The interaction of the two parts will ensure that the main task is to obtain the result and analyze the indicators of vital functions of the human body. The hardware is implemented using devices for scanning data on heart rate, temperature, saturation, and the ability to track electrocardiograms. It is possible to transmit data on the state of the body. The position of the sensors attached to the body is taken into account in case they come off. The device itself should be placed on the human body in the area of the front chest wall, wrists, and ankles. The device is also programmed to respond to sudden changes in these values. The software implementation is based on a web-based interface. The design of the final solutions for the interaction between the local and intermediate server was implemented using Django and Python. The ability to administer the intermediate server of the client's time zone was written using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The use of the IoT solution allows monitoring the indicators of vital functions of the body and their analysis. A scheme of information exchange in the system for monitoring health indicators has been built.
References
- Norav medical. Available at: https://www.noravmedical.com
- Cardiomo monitoring heart health. Available at: https://www.cardiomo.com
- Shea, S. (2018). Microcomputer. Available at: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/microcomputer
- Lutkevich, B. (2019). Microcontroller. Available at: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/microcontroller
- Raspberry Pi. Available at: https://www.raspberrypi.org
- Asus Tinker Board. Available at: https://www.asus.com/networking-iot-servers
- LattePanda. Available at: https://www.lattepanda.com
- Arduino. Available at: https://www.arduino.cc
- Google Trends. Available at: https://trends.google.com/trends/
- e-Health Sensor Shield. Available at: https://www.arrow.com/en/products/10269/libelium-comunicaciones-distribuidas-sl
- The DFRobot heart rate and oximeter sensor integrates the Maxim MAX30102 chip. Available at: https://wiki.dfrobot.com/Heart_Rate_and_Oximeter_Sensor_V2_SKU_SEN0344
- Model JP403 – Medical Temperature Sensor of Adult Body Surface. Available at: https://www.medical-xprt.com/products/model-jp403-medical-temperature-sensor-of-adult-body-surface-673919
- ECG Monitoring with AD8232 ECG Sensor & Arduino. Available at: https://how2electronics.com/ecg-monitoring-with-ad8232-ecg-sensor-arduino/
- ANACONDA. Available at: https://www.anaconda.com/
- Django framework. Available at: https://www.djangoproject.com
- Arduino Software. Available at: https://www.arduino.cc/en/software/
- SQLite. Available at: https://www.sqlite.org/index.html
- Python Developer’s Guide. Available at: https://devguide.python.org/
- What is Arduino. Available at: https://www.kanda.com/what-is-arduino.php
- Microcomputer-controlled devices for human implantation. Available at: https://secwww.jhuapl.edu/techdigest/Content/techdigest/pdf/V04-N02/04-02-Fischell.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Iryna Zinko, Olha Kravchenko, Dmytro Syvoglaz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







