Development of white organic light emitting diodes based on carbazole-derived compounds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.301770Keywords:
organic light emitting diodes, OLED, electroplex, carbazole-derived compounds, thermogravimetry, differential scanning calorimetry, electroluminescenceAbstract
The object of research is the thermal, photophysical, and electrophysical properties of newly synthesized carbazole-derived compounds and organic light-emitting structures based on them. The problem consists in the comprehensive solution of scientific and technical problems of improving the characteristics of white organic light-emitting diodes (OLED), expanding their emission spectrum, improving color and energy characteristics.
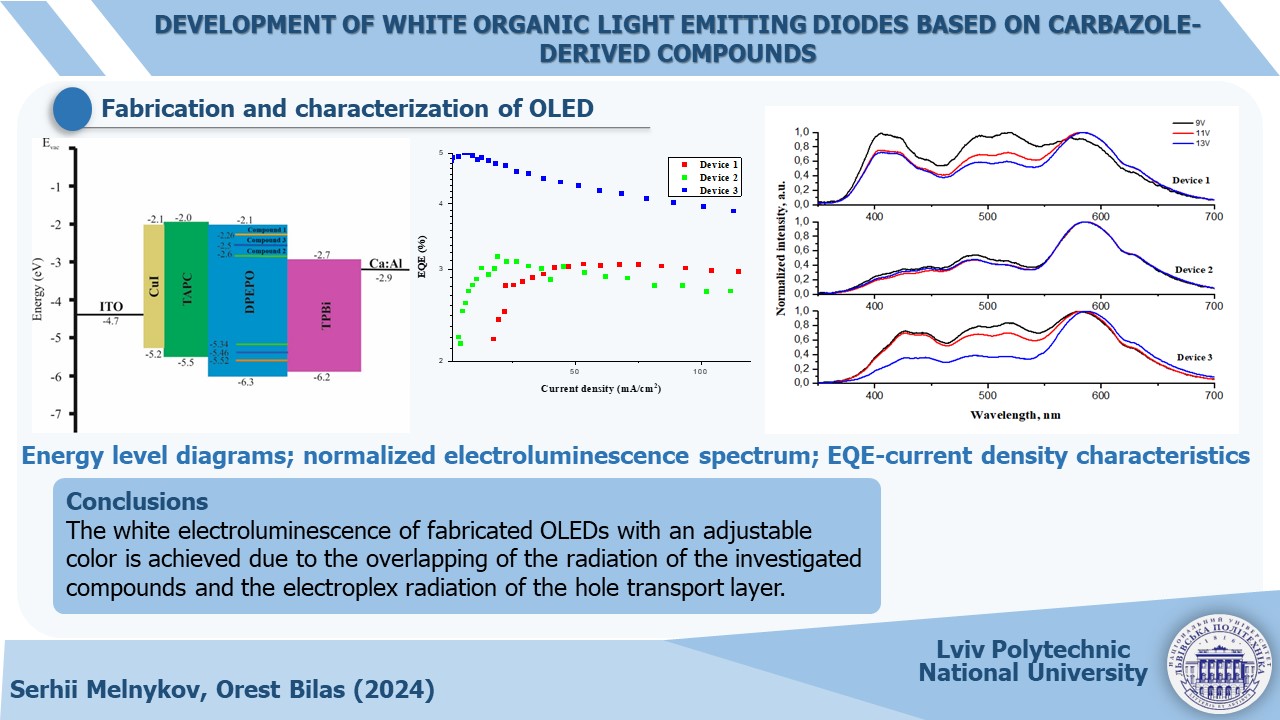
The results of the thermal, electrophysical and photophysical properties of the investigated carbazole compounds were obtained. They demonstrated good thermal stability. Absorption spectra in solid films were recorded in the range of 300–350 nm. Photoluminescence spectra were observed at a wavelength of 407 nm for the first and second compounds and 430 nm for the third. The quantum yield of photoluminescence in films for compounds 1, 2, and 3 was 16 %, 7 %, and 7 %, respectively.
Organic light-emitting structures of white emission color with color coordinates (0.31, 0.35), (0.32, 0.34) and (0.38, 0.34) close to natural white light (0.33, 0.33) were formed using the thermovacuum sputtering method. The turn-on voltage of the white OLED is 6 V, the maximum brightness of the light-emitting structures was 10,000 cd/m2. The devices demonstrated a sufficiently high external quantum efficiency of 5 % to 7 %.
The obtained results are explained by the mixing of different types of electroluminescence, namely excitonic and electromeric. Electromeric radiation is obtained due to transport layers. This approach improves such an important parameter of white light as its quality, which includes color coordinates and color rendering index.
Due to their color characteristics, white light-emitting diodes based on carbazole-derived compounds are promising candidates for use in modern lighting systems. A separate advantage of these light-emitting structures is the dependence of the color gamut of their radiation on the applied voltage. In addition, organic LEDs based on carbazole-derived compounds have low energy consumption and are environmentally friendly due to the absence of toxic substances in their design, which creates prerequisites for both global energy savings and a reduction of the industrial burden on the environment.
References
- Zhang, Q., Li, B., Huang, S., Nomura, H., Tanaka, H., Adachi, C. (2014). Efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes employing thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Nature Photonics, 8 (4), 326–332. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.12
- Ledwon, P. (2019). Recent advances of donor-acceptor type carbazole-based molecules for light emitting applications. Organic Electronics, 75, 105422. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2019.105422
- Zhang, X., Pan, T., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Xie, W. (2019). Color-Tunable, Spectra-Stable Flexible White Top-Emitting Organic Light-Emitting Devices Based on Alternating Current Driven and Dual-Microcavity Technology. ACS Photonics, 6 (9), 2350–2357. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.9b00900
- Joo, C. W., Moon, J., Han, J.-H., Huh, J. W., Lee, J., Cho, N. S. et al. (2014). Color temperature tunable white organic light-emitting diodes. Organic Electronics, 15 (1), 189–195. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2013.10.005
- Yang, S.-H., Shih, P.-J., Wu, W.-J., Huang, Y.-H. (2013). Color-tunable and stable-efficiency white organic light-emitting diode fabricated with fluorescent-phosphorescent emission layers. Journal of Luminescence, 142, 86–91. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.03.060
- Wong, K.-T., Chen, Y.-M., Lin, Y.-T., Su, H.-C., Wu, C. (2005). Nonconjugated Hybrid of Carbazole and Fluorene: A Novel Host Material for Highly Efficient Green and Red Phosphorescent OLEDs. Organic Letters, 7 (24), 5361–5364. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ol051977h
- Danyliv, Y., Ivaniuk, K., Danyliv, I., Bezvikonnyi, O., Volyniuk, D., Galyna, S. et al. (2023). Carbazole-σ-sulfobenzimide derivative exhibiting mechanochromic thermally activated delayed fluorescence as emitter for flexible OLEDs: Theoretical and experimental insights. Dyes and Pigments, 208, 110841. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2022.110841
- Li, W., Liu, D., Shen, F., Ma, D., Wang, Z., Feng, T. et al. (2012). A Twisting Donor‐Acceptor Molecule with an Intercrossed Excited State for Highly Efficient, Deep‐Blue Electroluminescence. Advanced Functional Materials, 22 (13), 2797–2803. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201200116
- Kalinowski, J., Giro, G., Cocchi, M., Fattori, V., Di Marco, P. (2000). Unusual disparity in electroluminescence and photoluminescence spectra of vacuum-evaporated films of 1,1-bis ((di-4-tolylamino) phenyl) cyclohexane. Applied Physics Letters, 76 (17), 2352–2354. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.126343
- Shan, M., Jiang, H., Guan, Y., Sun, D., Wang, Y., Hua, J., Wang, J. (2017). Enhanced hole injection in organic light-emitting diodes utilizing a copper iodide-doped hole injection layer. RSC Advances, 7 (22), 13584–13589. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra28644e
- Miwa, T., Kubo, S., Shizu, K., Komino, T., Adachi, C., Kaji, H. (2017). Blue organic light-emitting diodes realizing external quantum efficiency over 25 % using thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters. Scientific Reports, 7 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00368-5
- Xu, H., Wang, L.-H., Zhu, X.-H., Yin, K., Zhong, G.-Y., Hou, X.-Y., Huang, W. (2006). Application of Chelate Phosphine Oxide Ligand in EuIII Complex with Mezzo Triplet Energy Level, Highly Efficient Photoluminescent, and Electroluminescent Performances. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 110 (7), 3023–3029. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp055355p
- Stavrou, K., Danos, A., Hama, T., Hatakeyama, T., Monkman, A. (2021). Hot Vibrational States in a High-Performance Multiple Resonance Emitter and the Effect of Excimer Quenching on Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (7), 8643–8655. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c20619
- Wei, M., Gui, G., Chung, Y.-H., Xiao, L., Qu, B., Chen, Z. (2015). Micromechanism of electroplex formation. Physica Status Solidi (b), 252 (8), 1711–1716. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201552098
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Serhii Melnykov, Orest Bilas

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







