Analysis of the efficiency of the application of natural coagulants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.303190Keywords:
coagulation, natural coagulant, Moringa oleifera, water treatment, turbidity, synthesized coagulantsAbstract
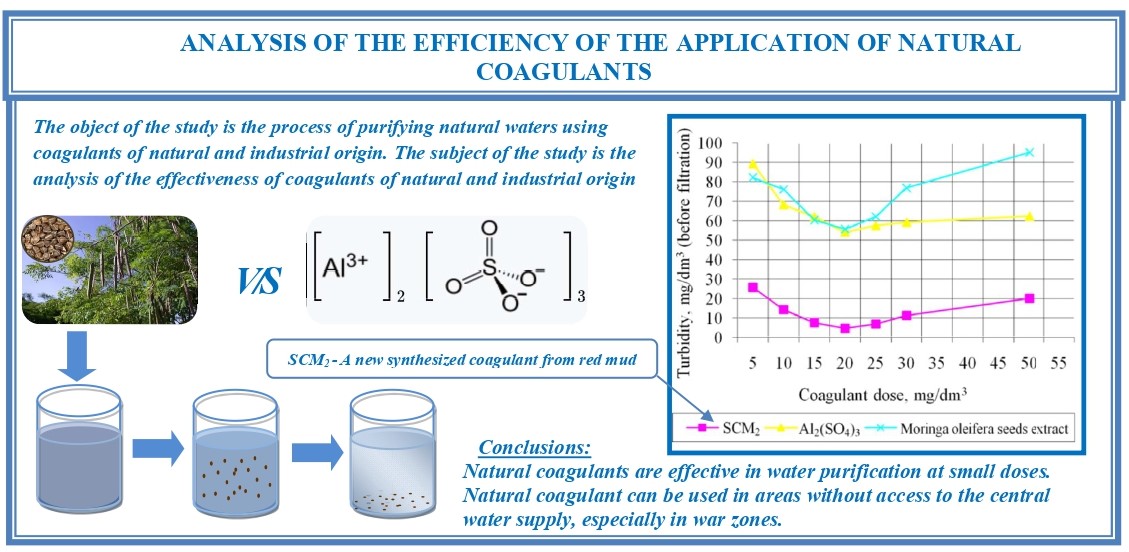
The object of the study is the process of purifying natural waters using coagulants of natural and industrial origin. The subject of the study is the analysis of the effectiveness of coagulants of natural and industrial origin.
Today, there is great interest in finding alternative methods of water purification that would be more economical and environmentally friendly. The availability of clean and safe water is especially important during times of martial law. Coagulants of natural origin can be an affordable and effective means of water purification and disinfection. One of the important advantages is availability, which indicates the possibility of becoming an alternative to chemical coagulants. Thus, there is a need to study the possibility of using natural coagulants both on an industrial scale and in emergency conditions.
This study presents a characterization of existing coagulants of natural origin, an analysis of the effectiveness of their use, comparison with chemical analogues, as well as an analysis of the effectiveness of using Moringa oleifera as a natural coagulant.
During the work, two coagulants were synthesized from red mud from aluminium production. A comparative analysis of coagulants synthesized from red mud, Moringa oleifera, aquatone and aluminium sulphate was carried out. All reagents were used to remove turbidity and other impurities. The studies were carried out 3 times in different seasons of the year. All results were compared to determine the most effective coagulant and its dose.
As a result, it was found that all of these coagulants can be used and reduce water treatment costs at local water treatment plants. The natural coagulant can be used in areas where there is no access to a central water supply, especially in war zones.
References
- Yongabi, K. A. (2010). Biocoagulants for Water and Waste Water Purification: a Review. International Review of Chemical Engineering, 2 (3), 444–458.
- Atreya, K., Kattel, K., Tiwari, K. R., Baral, S., Adhikari, R., Kalwar, O. P. (2023). Nutritional, ecological and livelihood significance of Moringa oleifera: A review. Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 8 (3), 452–461. doi: https://doi.org/10.26832/24566632.2023.0803025
- Abd El-Mageed, T. A., Semida, W. M., Rady, M. M. (2017). Moringa leaf extract as biostimulant improves water use efficiency, physio-biochemical attributes of squash plants under deficit irrigation. Agricultural Water Management, 193, 46–54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.08.004
- Baptista, A. T. A., Silva, M. O., Gomes, R. G., Bergamasco, R., Vieira, M. F., Vieira, A. M. S. (2017). Protein fractionation of seeds of Moringa oleifera lam and its application in superficial water treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 180, 114–124. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.02.040
- Camacho, F. P., Sousa, V. S., Bergamasco, R., Ribau Teixeira, M. (2017). The use of Moringa oleifera as a natural coagulant in surface water treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 313, 226–237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.031
- Anzano, A., de Falco, B., Ammar, M., Ricciardelli, A., Grauso, L., Sabbah, M. et al. (2022). Chemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves and Seeds. Molecules, 27 (24), 8920. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248920
- Abdel Shakour, Z. T., El-Akad, R. H., Elshamy, A. I., El Gendy, A. E.-N. G., Wessjohann, L. A., Farag, M. A. (2023). Dissection of Moringa oleifera leaf metabolome in context of its different extracts, origin and in relationship to its biological effects as analysed using molecular networking and chemometrics. Food Chemistry, 399, 133948. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133948
- Xu, Y., Chen, G., Guo, M. (2020). Correlations between phytochemical fingerprints of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts and their antioxidant activities revealed by chemometric analysis. Phytochemical Analysis, 32 (5), 698–709. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.3016
- Yin, C.-Y. (2010). Emerging usage of plant-based coagulants for water and wastewater treatment. Process Biochemistry, 45 (9), 1437–1444. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.05.030
- Ueda Yamaguchi, N., Cusioli, L. F., Quesada, H. B., Camargo Ferreira, M. E., Fagundes-Klen, M. R., Salcedo Vieira, A. M. et al. (2021). A review of Moringa oleifera seeds in water treatment: Trends and future challenges. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 147, 405–420. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.09.044
- Camacho, F. P., Sousa, V. S., Bergamasco, R., Ribau Teixeira, M. (2017). The use of Moringa oleifera as a natural coagulant in surface water treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 313, 226–237. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.031
- Pritchard, M., Craven, T., Mkandawire, T., Edmondson, A. S., O’Neill, J. G. (2010). A comparison between Moringa oleifera and chemical coagulants in the purification of drinking water – An alternative sustainable solution for developing countries. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 35 (13-14), 798–805. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2010.07.014
- Antov, M. G., Šćiban, M. B., Petrović, N. J. (2010). Proteins from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) seed as a natural coagulant for potential application in water turbidity removal. Bioresource Technology, 101 (7), 2167–2172. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.020
- Trokhymenko, G. G., Chestnykh, Yu. V. (2023). Analysis of the effectiveness of coagulants of natural origin. Problems of ecology and energy saving. Mykolaiv: V. V. Torubara Publisher, 68–70.
- Mogbo, O. N., Iorwua, M. B., Duweni, E. C., Tiza, M. T. (2020). A study on the efficacy of bio-coagulants for turbid and waste water treatment. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7 (18), 1307–1315.
- Vyverets, A. O., Trokhymenko, G. G., Gomelya, M. D. (2016). Analysis of the efficiency of using Moringa oleifera seed powder and sludge from alumina production as coagulants for water purification. Problems of water supply, drainage and hydraulics: scientific and technical collection, 27, 39–47.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ganna Trokhymenko, Yuliia Chestnykh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







