Distribution of heavy metals in core sediments of Southern Iraq Waterways
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.314134Keywords:
sediments, heavy metals, atomic absorption, Southern Iraq Waterways, Shatt Al-Arab RiverAbstract
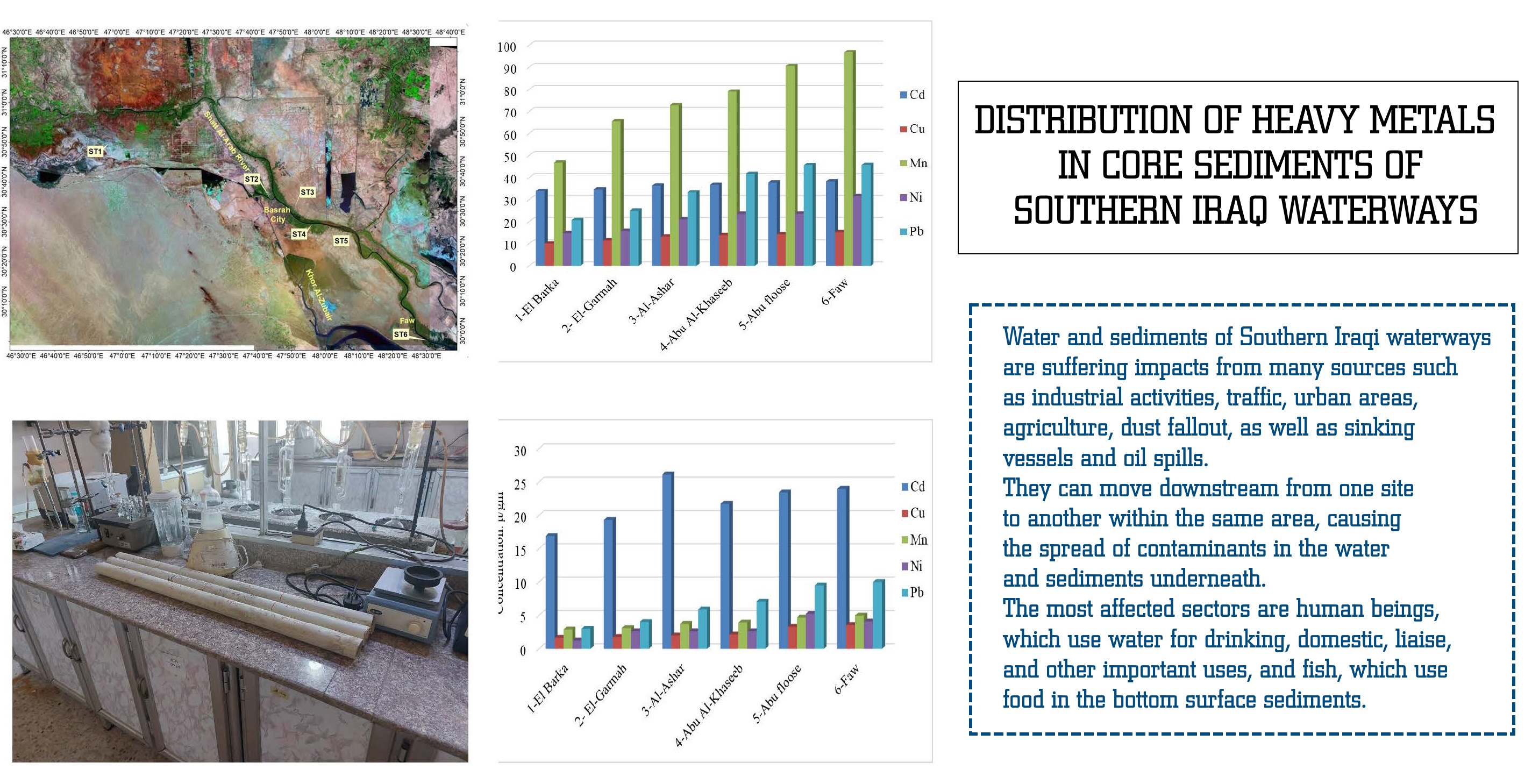
The object of the study is heavy metals in the Shatt Al-Arab River. Shatt Al-Arab River is considered one of the most important internal rivers in Iraq due to its multiple economic and social importance. In addition, this river has an important strategic location. Despite its importance mentioned above, the Shatt Al-Arab River suffers from various wastes from many and varied sources, which have directly affected the quality of its water and consequently the quality of the community of living organisms that live in it. Levels and distribution of certain heavy metals, Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, and Pb, were determined in core sediments from Southern Iraq Waterways. Six sites were investigated, two in the lower reaches of Al-Hammar Marsh, 1) El-Barka, 2) El-Garmah, and four sites along Shatt Al-Arab River, 3) Al-Ashar, 4) Abu Al-Khaseeb, 5) Abu Floos Port, and 6) Al-Faw. The results indicate that Al-Faw station was distinguished by the fact that the highest values of heavy elements were obtained at this station and all depths, except Cd at Al-Ashar station at a depth of 25 cm (26.1375 μ/gm), Cu at a core depth of 50 cm (4.9635 μ/gm), Ni at a core depth of 25 cm (5.2483 μ/gm), and surface water (2.9021 μ/gm) and Pb in surface water at Abu Floos Port station (3.5001 μ/gm). The lowest concentrations of heavy elements for Cu, Mn, and Ni are in all depths of core sediments. Other elements, Cd, Pb, and Fe, were higher; on the other hand, higher levels of concentrations for all studied heavy metals were recorded at a depth of 100 cm. Iron was the highest in all depths of core sediments.
References
- Al-Asadi, S. A. R., Al-Qurnawi, W. S., Al Hawash, A. B., Ghalib, H. B., Alkhlifa, N.-H. A. (2020). Water quality and impacting factors on heavy metals levels in Shatt Al-Arab River, Basra, Iraq. Applied Water Science, 10 (5), 103–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01196-1
- Karem, D. S., Al-Shamsi, Z. S., Saleh, S. M., Mohammed, A. H., Al-Saad, H. T. (2024). Environmental assessment of Heavy Metals in Sedi – ments of Tigris, Euphrates, Shatt Al-Arab rivers and northern west of Arabian Gulf. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 1300 (1), 012026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1300/1/012026
- Al-Saad, H. T., Al-Tein, S. H., Al-Hello, M. A. R., DouAbul, A. A. Z. (2009). Hydrocarbons and trace elements in the waters and sediments of the marshland of Southern Iraq. Mesopotamian Journal of Marine Sciences, 24 (2), 126–139.
- Mannaa, A. A., Khan, A. A., Haredy, R., Al-Zubieri, A. G. (2021). Contamination Evaluation of Heavy Metals in a Sediment Core from the Al-Salam Lagoon, Jeddah Coast, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9 (8), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9080899
- AI-Shawi, S. R. A., Kadhim, H. A. H., Al-Saad, H. T. (2022). Assessment of heavy metals in exchangeable sediments samples from Tigris – Euphrates and Shatt al-Arab rivers. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 6 (3 (68)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2022.267794
- Seifi, M., Mahvi, A. H., Hashemi, S. Y., Arfaeinia, H., Pasalari, H., Zarei, A., Changani, F. (2019). Spatial distribution, enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals in surface sediments near urban and industrial areas in the Persian Gulf. Desalination and Water Treatment, 158, 130–139. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.24238
- Al-Khuzaie, D. K. K., Hasan, W. F., Imran, R., Abdul-Nabi, Z. A. (2020). Water quality of Shatt Al-Arab River in Basra, Iraq. Heavy and trace metal concentration. Poll. Res., 39 (2), 231–236.
- Yang, G., Song, Z., Sun, X., Chen, C., Ke, S., Zhang, J. (2020). Heavy metals of sediment cores in Dachan Bay and their responses to human activities. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110764
- Moyel, M. S., Aymt, A. H., Mehdi, W. F., Khalaf, H. H. (2015). Application and evaluation of water quality pollution indeces for heavy metals contamination as a monitoring tool in Shatt Al-Arab River. Journal of International Academic Research for Multidisciplinary, 3 (4), 67–75.
- Allafta, H., Opp, C. (2020). Spatio-temporal variability and pollution sources identification of the surface sediments of Shatt Al-Arab River, Southern Iraq. Scientific Reports, 10 (1), 6974–6991. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63893-w
- Hussian, M. L., Al-Jaberi, M. H., (2020). Comparison the Bed Sediment Contamination of the Southern Part of Euphrates River with Shatt Al-Arab, Iraq. Iraqi Geological Journal, 53 (1C), 68–89. https://doi.org/10.46717/igj.53.1c.5rx-2020-04-05
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Faris Al-Imarah, Ghasan Al-Najare, Nawras Al-Faiz, Kadhim Younis

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







