Development of a fuzzy production model for assessing the degree of information security in international cooperation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.318446Keywords:
fuzzy production model, information security, international cooperation, potential risks, influence coefficients, risk categoriesAbstract
The object of research is the methods of assessing the information security indicator in the process of international cooperation.
The problem of unification and simplification of the processes of assessing the degree of information security is considered in order to reduce the involvement of human and material resources in them, using the apparatus of fuzzy set theory to take into account the conclusions of competent experts.
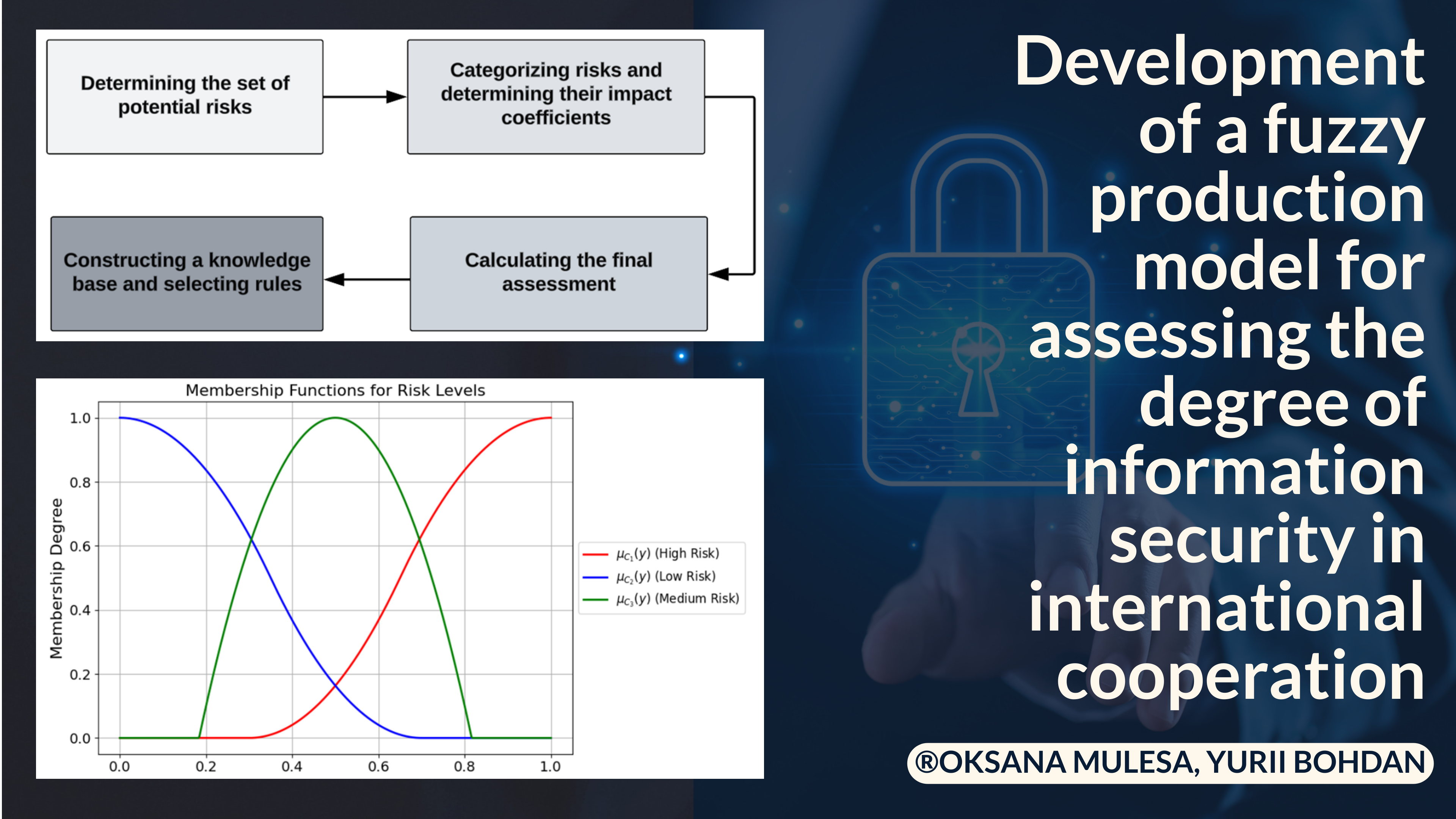
A fuzzy production model of assessing the degree of information security is developed, which is based on the use of expert knowledge and fuzzy logic methods. A step-by-step approach is proposed for identifying potential risks, classifying them by categories and calculating influence coefficients. An iterative assessment method is created, which allows obtaining a numerical indicator of the degree of information security. Heuristic rules for determining the effective assessment of the degree of information security are developed, taking into account the criticality factor and influence coefficients of different risk categories.
A classification of potential information security risks in international IT projects is proposed. An example of constructing production rules for a fuzzy knowledge base is demonstrated.
The results are explained by the use of systems analysis to take into account the relationships between different risk categories and the use of fuzzy logic to work with uncertain and incomplete data. The model is based on production rules that integrate expert judgment and allow for adaptive analysis in changing conditions of international cooperation.
The developed model can be used to assess information security in small and medium-sized international projects, where it is necessary to provide a quick and effective assessment of the level of security without involving significant resources. The model is especially useful in conditions where the data is fuzzy or incomplete, and the risks vary depending on the specifics of cooperation between different countries and organizations.
Supporting Agency
- The study was conducted within the framework of the implementation of the state budget topic DB-921M “Information security protection in the management of international cooperation projects on the basis of ensuring the national security of Ukraine” with the support of the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine.
References
- Mulesa, O., Yakob, E., Valko, P., Sviezhentseva, O., Marhitych, D. (2024). Development of decision-making technology for the provision of services in project implementation. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 2 (2 (76)), 13–17. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.301317
- Mulesa, O., Horvat, P., Radivilova, T., Sabadosh, V., Baranovskyi, O., Duran, S. (2023). Design of mechanisms for ensuring the execution of tasks in project planning. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2 (4 (122)), 16–22. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.277585
- Vedadi, A., Warkentin, M., Dennis, A. (2021). Herd behavior in information security decision-making. Information & Management, 58 (8), 103526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2021.103526
- Georg-Schaffner, L., Prinz, E. (2021). Corporate management boards’ information security orientation: an analysis of cybersecurity incidents in DAX 30 companies. Journal of Management and Governance, 26 (4), 1375–1408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10997-021-09588-4
- Banitalebi Dehkordi, A., Soltanaghaei, M., Boroujeni, F. Z. (2020). The DDoS attacks detection through machine learning and statistical methods in SDN. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77 (3), 2383–2415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03323-w
- Ashok, K., Gopikrishnan, S. (2023). Statistical Analysis of Remote Health Monitoring Based IoT Security Models & Deployments From a Pragmatic Perspective. IEEE Access, 11, 2621–2651. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3234632
- Radivilova, T., Kirichenko, L., Alghawli, A. S., Ageyev, D., Mulesa, O., Baranovskyi, O. et al.; Oliynykov, R., Kuznetsov, O., Lemeshko, O., Radivilova, T. (Eds.) (2022). Statistical and Signature Analysis Methods of Intrusion Detection. Information Security Technologies in the Decentralized Distributed Networks. Vol. 115. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 115–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-95161-0_5
- Viktoriia, H., Hnatienko, H., Babenko, T. (2021). An intelligent model to assess information systems security level. 2021 Fifth World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems Security and Sustainability (WorldS4). London, 128–133. https://doi.org/10.1109/worlds451998.2021.9514019
- Ganguli, C., Shandilya, S. K., Izonin, I. (2023). Design and implementation of adaptive network stabilization based on artificial bees colony optimization for nature inspired cyber security. Journal of King Saud University – Science, 35 (5), 102713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102713
- Jin, X., Lü, S., Qin, J., Zheng, W. X., Liu, Q. (2023). Adaptive ELM-Based Security Control for a Class of Nonlinear-Interconnected Systems With DoS Attacks. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 53 (8), 5000–5012. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2023.3257133
- Chen, H., Galteland, Y. J., Liang, K.; Guo, J., Steinfeld, R. (Eds.) (2023). CCA-1 Secure Updatable Encryption with Adaptive Security. Advances in Cryptology – ASIACRYPT 2023. Vol. 14442. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 374–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8733-7_12
- Lizunov, P., Biloshchytskyi, A., Kuchansky, A., Andrashko, Y., Biloshchytska, S. (2019). Improvement of the method for scientific publications clustering based on n-gram analysis and fuzzy method for selecting research partners. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4 (4 (100)), 6–14. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.175139
- Saatchi, R. (2024). Fuzzy Logic Concepts, Developments and Implementation. Information, 15 (10), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15100656
- Kerimkhulle, S., Dildebayeva, Z., Tokhmetov, A., Amirova, A., Tussupov, J., Makhazhanova, U., Adalbek, A., Taberkhan, R., Zakirova, A., Salykbayeva, A. (2023). Fuzzy Logic and Its Application in the Assessment of Information Security Risk of Industrial Internet of Things. Symmetry, 15 (10), 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15101958
- Vaidya, O. S., Kumar, S. (2006). Analytic hierarchy process: An overview of applications. European Journal of Operational Research, 169 (1), 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.04.028
- Paz, F., Moquillaza, A., Lecaros, A., Falconi, F., Aguirre, J., Ramos, C. (2023). Applying Heuristic Evaluation with Different Evaluator Profiles: A Comparative Study Between Novice and Expert Specialists. Proceedings of the XI Latin American Conference on Human Computer Interaction. Puebla: ACM, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1145/3630970.3631063
- Zhu, Y., Tian, D., Yan, F. (2020). Effectiveness of Entropy Weight Method in Decision-Making. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3564835
- Božanić, D., Pamučar, D., Milić, A., Marinković, D., Komazec, N. (2022). Modification of the Logarithm Methodology of Additive Weights (LMAW) by a Triangular Fuzzy Number and Its Application in Multi-Criteria Decision Making. Axioms, 11 (3), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/axioms11030089
- Balboa, A., Cuesta, A., González-Villa, J., Ortiz, G., Alvear, D. (2024). Logistic regression vs machine learning to predict evacuation decisions in fire alarm situations. Safety Science, 174, 106485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2024.106485
- Herrera-Viedma, E., Palomares, I., Li, C.-C., Cabrerizo, F. J., Dong, Y., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F. (2021). Revisiting Fuzzy and Linguistic Decision Making: Scenarios and Challenges for Making Wiser Decisions in a Better Way. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 51 (1), 191–208. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.2020.3043016
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oksana Mulesa, Yurii Bohdan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







