Removal of methylene blue from water by NiO-modified silica gel
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.319822Keywords:
adsorption, organic dyes, modification, nickel (II) oxide, water purification, silica gelAbstract
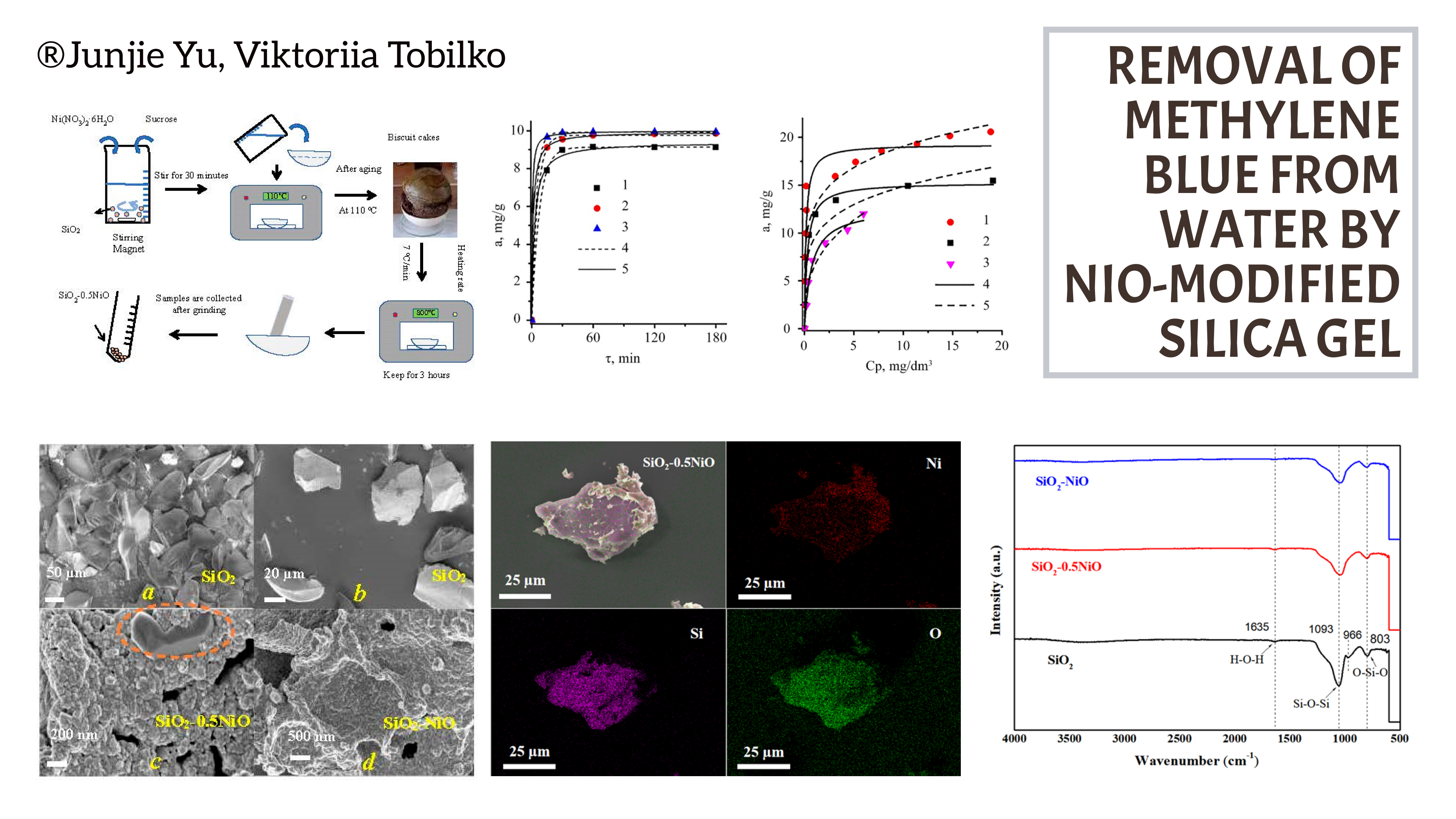
The objects of the study are sorption materials based on commercial silica gel and nickel (II) oxide with different mass ratios of NiO to SiO2: 1:1 and 0.5:1. To obtain such materials, expensive reagents and complex synthesis schemes are not required. In addition, they are distinguished by chemical stability, controlled morphology and have a significant number of reactive functional groups, which contributes to high adsorption capacity for various types of contaminants.
The morphology of composite sorbents was studied using the electron microscopy method, the presence of a crystalline phase of nickel oxide on the amorphous surface of silica gel was investigated by X-ray phase analysis, and the successful application of a layer of nickel-containing compounds was confirmed by infrared spectroscopy.
The main parameters of the mesoporous structure of the samples were determined by the method of low-temperature nitrogen adsorption/desorption. It was found that with an increase in the amount of the deposited oxide layer, the specific surface area and pore volume of the obtained sorbents decrease by 1.5–2 times compared to the original silica gel.
The physicochemical features of the extraction of methylene blue dye by nickel-containing composites based on silica gel were studied. It was found that modification of the SiO2 surface with nickel (II) oxide leads to an increase in the sorption capacity of materials in relation to cationic dyes. It was shown that the highest sorption capacity is possessed by a sample with a mass ratio of NiO to SiO2 equal to 0.5:1. The maximum sorption value is 21 mg/g, which is almost 2 times higher than that for the original silica gel. The adsorption kinetics is adequately described by pseudo-first and pseudo-second order models, which indicates a high affinity of methylene blue with the surface of such samples.
The results obtained indicate that the obtained sorption materials based on commercial silica gel and nickel (II) oxide can be used in the purification of water contaminated with organic cationic dyes.
References
- Natarajan, S., Bajaj, H. C., Tayade, R. J. (2018). Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 65, 201–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.03.011
- Saruchi, Kumar, V., Dhami, J. K., Rehani, V., Singh, M. (2022). Synthesis and characterization of Aloe-vera-poly(acrylic acid)-Cu-Ni-bionanocomposite: its evaluation as removal of carcinogenic dye malachite green. Journal of Polymer Research, 29 (2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-02898-7
- Verma, N., Chundawat, T. S., Chandra, H., Vaya, D. (2023). An efficient time reductive photocatalytic degradation of carcinogenic dyes by TiO2-GO nanocomposite. Materials Research Bulletin, 158, 112043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.112043
- Kyzas, G., Fu, J., Matis, K. (2013). The Change from Past to Future for Adsorbent Materials in Treatment of Dyeing Wastewaters. Materials, 6 (11), 5131–5158. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115131
- Ahmad, A., Mohd-Setapar, S. H., Chuong, C. S., Khatoon, A., Wani, W. A., Kumar, R., Rafatullah, M. (2015). Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Advances, 5 (39), 30801–30818. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra16959j
- Yagub, M. T., Sen, T. K., Afroze, S., Ang, H. M. (2014). Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 209, 172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002
- Heidarinejad, Z., Dehghani, M. H., Heidari, M., Javedan, G., Ali, I., Sillanpää, M. (2020). Methods for preparation and activation of activated carbon: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 18 (2), 393–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00955-0
- Paul Nayagam, J. O., Prasanna, K. (2022). Utilization of shell-based agricultural waste adsorbents for removing dyes: A review. Chemosphere, 291, 132737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132737
- Hambisa, A. A., Regasa, M. B., Ejigu, H. G., Senbeto, C. B. (2022). Adsorption studies of methyl orange dye removal from aqueous solution using Anchote peel-based agricultural waste adsorbent. Applied Water Science, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01832-y
- Jiang, Z., Hu, D. (2019). Molecular mechanism of anionic dyes adsorption on cationized rice husk cellulose from agricultural wastes. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 276, 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.11.153
- Moharm, A. E., El Naeem, G. A., Soliman, H. M. A., Abd-Elhamid, A. I., El-Bardan, A. A., Kassem, T. S. et al. (2022). Fabrication and Characterization of Effective Biochar Biosorbent Derived from Agricultural Waste to Remove Cationic Dyes from Wastewater. Polymers, 14 (13), 2587. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132587
- Samantray, J., Anand, A., Dash, B., Ghosh, M. K., Behera, A. K. (2022). Silicate minerals – Potential source of potash – A review. Minerals Engineering, 179, 107463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107463
- Li, H., Chen, X., Shen, D., Wu, F., Pleixats, R., Pan, J. (2021). Functionalized silica nanoparticles: classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications. Nanoscale, 13 (38), 15998–16016. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nr04048k
- Goswami, B., Mahanta, D. (2019). Polyaniline coated nickel oxide nanoparticles for the removal of phenolic compounds: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 582, 123843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123843
- El-Qanni, A., Nassar, N. N., Vitale, G. (2017). Experimental and computational modeling studies on silica-embedded NiO/MgO nanoparticles for adsorptive removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. RSC Advances, 7 (23), 14021–14038. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00615b
- Mustafa, S., Mahmood, F., Shafqat, U., Hussain, S., Shahid, M., Batool, F. et al. (2023). The Biosynthesis of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles: An Eco-Friendly Approach for Azo Dye Decolorization and Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability, 15 (20), 14965. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152014965
- Rubab, R., Ali, S., Rehman, A. U., Khan, S. A., Khan, A. M. (2021). Templated synthesis of NiO/SiO2 nanocomposite for dye removal applications: Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic properties. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 615, 126253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126253
- El Ghmari, B., Farah, H., Ech-Chahad, A. (2023). Biosynthesis, Characterization of Nickel (II) Oxide Nanoparticles NiO and their High-Efficient Photocatalytic Application. International Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 19 (3), 135–147. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijnn.2023.560608.2262
- Rebelo, Q. H. F., Ferreira, C. S., Santos, P. L., Bonacin, J. A., Passos, R. R., Pocrifka, L. A., Paula, M. M. S. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of a nanocomposite NiO/SiO2 from a sustainable source of SiO2. Particulate Science and Technology, 37 (8), 911–915. https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2018.1455781
- Ferreira, C. S., Santos, P. L., Bonacin, J. A., Passos, R. R., Pocrifka, L. A. (2015). Rice Husk Reuse in the Preparation of SnO2/SiO2Nanocomposite. Materials Research, 18 (3), 639–643. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.009015
- Murashkevich, A. N., Lavitskaya, A. S., Barannikova, T. I., Zharskii, I. M. (2008). Infrared absorption spectra and structure of TiO2-SiO2 composites. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 75 (5), 730–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-008-9097-3
- Yu, J., Bondarieva, A., Tobilko, V., Pavlenko, V. (2024). Adsorption removal of cu (II) using ni-modified silica gel. water and water purification technologies. Scientific and technical news, 37 (3), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.20535/2218-930032023302423
- Andersson, K. I., Eriksson, M., Norgren, M. (2011). Removal of Lignin from Wastewater Generated by Mechanical Pulping Using Activated Charcoal and Fly Ash: Adsorption Isotherms and Thermodynamics. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 50 (13), 7722–7732. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie200378s
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Junjie Yu, Viktoriia Tobilko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







