Finite element modeling of composite biomechanical structures: analysis of the lumbo-pelvis and cranial-maxillofacial complexes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.323751Keywords:
biomechanical system modelling, finite element analysis, digital simulation, stress-strain state, osseointegration, kinematic analysis, computational biomechanics of biological tissuesAbstract
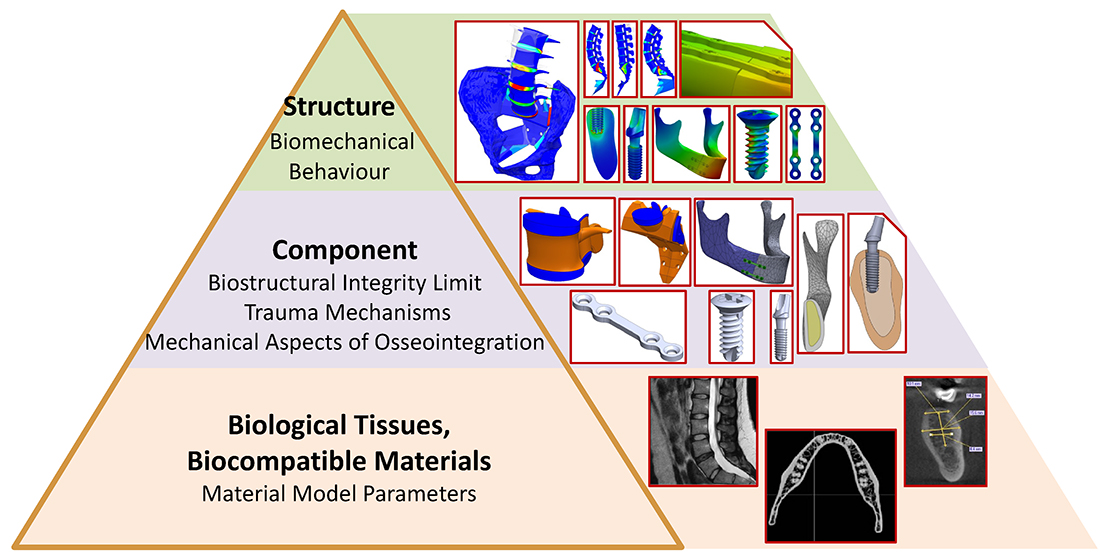
The object of this study is human biomechanical systems in both normal and pathological conditions, focusing on the lumbo-pelvic and craniofacial complexes, including restorative structures such as miniplates, screws, and dental implants. The military actions caused by Russian aggression against Ukraine have prompted the development of more effective methods for injury treatment and rehabilitation.
This research proposes novel digital modelling methods for biomechanical systems that incorporate individual mechanical properties of biological tissues and enable a comprehensive stress-strain analysis under normal conditions, pathological changes, and post-reconstructive states. The study utilizes finite element analysis (FEA) and computer simulation, integrated with CT and MRI data, ensuring high accuracy in predicting the functional behaviour of biological tissues. The dominant biomechanical factors that help prevent mechanical overload of tissues and reduce the risk of complications have been identified. The study investigates the kinematic chain “lumbar spine – sacroiliac joint – pelvis”, assessing the impact of pathological variations in lumbar lordosis and sacral inclination angle. For the craniofacial complex, the research examines the biomechanical conditions for successful osseointegration of miniplates, screws, and implants in jaw reconstruction.
The practical applications of the obtained results include orthopedics, traumatology, dentistry, and rehabilitation medicine. The proposed methods contribute to improving surgical planning accuracy, optimizing rehabilitation procedures, and developing durable implants adapted to the patient’s anatomical features. This will help minimize the risk of complications and accelerate patient recovery.
Supporting Agency
- This publication was prepared as part of the scholarship work of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine for young scientists – Doctors of Sciences “Methodology of the simulation modeling of stress-strain behavior and destruction of composite structures of the human biomechanical systems” (No. 0124U003911).
References
- El-Tallawy, S. N., Nalamasu, R., Salem, G. I., LeQuang, J. A. K., Pergolizzi, J. V., Christo, P. J. (2021). Management of Musculoskeletal Pain: An Update with Emphasis on Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain. Pain and Therapy, 10 (1), 181–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-021-00235-2
- Urits, I., Burshtein, A., Sharma, M., Testa, L., Gold, P. A., Orhurhu, V. et al. (2019). Low Back Pain, a Comprehensive Review: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Current Pain and Headache Reports, 23 (3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-019-0757-1
- Zhang, Q., Chon, T., Zhang, Y., Baker, J. S., Gu, Y. (2021). Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 136, 104745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104745
- Azadi, A., Arjmand, N. (2021). A comprehensive approach for the validation of lumbar spine finite element models investigating post-fusion adjacent segment effects. Journal of Biomechanics, 121, 110430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110430
- Umale, S., Yoganandan, N., Kurpad, S. N. (2020). Development and validation of osteoligamentous lumbar spine under complex loading conditions: A step towards patient-specific modeling. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 110, 103898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.103898
- Xu, M., Yang, J., Lieberman, I. H., Haddas, R. (2016). Lumbar spine finite element model for healthy subjects: development and validation. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 20 (1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2016.1193596
- Eremina, G., Smolin, A., Xie, J., Syrkashev, V. (2022). Development of a Computational Model of the Mechanical Behavior of the L4–L5 Lumbar Spine: Application to Disc Degeneration. Materials, 15 (19), 6684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196684
- Areias, B., Caetano, S. C., Sousa, L. C., Parente, M., Jorge, R. N., Sousa, H., Gonçalves, J. M. (2020). Numerical simulation of lateral and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion, two minimally invasive surgical approaches. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 23 (8), 408–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2020.1734579
- Más, Y., Gracia, L., Ibarz, E., Gabarre, S., Peña, D., Herrera, A. (2017). Finite element simulation and clinical follow-up of lumbar spine biomechanics with dynamic fixations. PLOS ONE, 12 (11), e0188328. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188328
- Skrypa, O. L., Bandrivsky, Y. L. (2020). Determining the frequency of functional disorders of the TMJ in patients with mandible fractures depending on the location. Wiadomości Lekarskie, 73 (2), 245–249. https://doi.org/10.36740/wlek202002107
- Yamamoto, K., Matsusue, Y., Horita, S., Murakami, K., Sugiura, T., Kirita, T. (2019). Maxillofacial Fractures Associated With Interpersonal Violence. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 30 (4), e312–e315. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000005306
- Stanford-Moore, G., Murr, A. H. (2022). Mandibular Angle Fractures. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 30 (1), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2021.08.009
- Mathew, N., Singh, I., Gandhi, S., Solanki, M., Bedi, N. S. (2020). The Efficacy of Fixation of Unilateral Mandibular Angle Fracture with Single 3D Plate vs Single Miniplate Using Transbuccal Approach. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, 21 (2), 405–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-020-01465-1
- Meslier, Q. A., Shefelbine, S. J. (2023). Using Finite Element Modeling in Bone Mechanoadaptation. Current Osteoporosis Reports, 21 (2), 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-023-00776-9
- Prasadh, S., Krishnan, A. V., Lim, C. Y. H., Gupta, M., Wong, R. (2022). Titanium versus magnesium plates for unilateral mandibular angle fracture fixation: biomechanical evaluation using 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 18, 2064–2076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.03.111
- Orassi, V., Duda, G. N., Heiland, M., Fischer, H., Rendenbach, C., Checa, S. (2021). Biomechanical Assessment of the Validity of Sheep as a Preclinical Model for Testing Mandibular Fracture Fixation Devices. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.672176
- Kurakar, M., Joshi, U. (2021). Comparative Study of Miniplate vs Reconstruction Plate in the Management of Bilateral Parasymphysis Mandible Fracture: FEM Analysis. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, 22 (1), 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01649-3
- Snyder, E., Trabia, M., Trabelsi, N. (2022). An approach for simultaneous reduction and fixation of mandibular fractures. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 26 (9), 1064–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2022.2105143
- Overmann, A. L., Aparicio, C., Richards, J. T., Mutreja, I., Fischer, N. G., Wade, S. M. et al. (2020). Orthopaedic osseointegration: Implantology and future directions. Journal of Orthopaedic Research, 38 (7), 1445–1454. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24576
- Mao, B., Tian, Y., Wang, C., Liu, D., Zhou, Y., Li, J. (2023). The application of optimization design in stomatology: A literature review. Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices, 19, 100252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medntd.2023.100252
- Guha, I., Zhang, X., Rajapakse, C. S., Chang, G., Saha, P. K. (2022). Finite element analysis of trabecular bone microstructure using CT imaging and continuum mechanical modeling. Medical Physics, 49 (6), 3886–3899. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.15629
- Golovanevskiy, V., Kondratiev, A. (2021). Elastic Properties of Steel-Cord Rubber Conveyor Belt. Experimental Techniques, 45 (2), 217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-021-00439-3
- Li, J., Jansen, J. A., Walboomers, X. F., van den Beucken, J. JJP. (2020). Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 103, 103574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.103574
- Barua, S. L., Poduval, T. S., Rani, S., Jain, N., Thakur, S. (2023). Stress distribution in bone around an implant-supported three-unit fixed dental prosthesis using two different computer-aided designing/computer-aided milling provisional crown materials: Milled polymethylmethacrylate and milled polyetheretherketone – A finite element analysis. Dental Research Journal, 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-3327.372650
- Qiu, P., Cao, R., Li, Z., Fan, Z. (2024). A comprehensive biomechanical evaluation of length and diameter of dental implants using finite element analyses: A systematic review. Heliyon, 10 (5), e26876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26876
- Kondratiev, A., Demenko, V., Linetskiy, I., Weisskircher, H.-W., Linetska, L. (2024). Evaluation of Bone Turnover around Short Finned Implants in Atrophic Posterior Maxilla: A Finite Element Study. Prosthesis, 6 (5), 1170–1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis6050084
- Pjetursson, B., Fehmer, V., Sailer, I. (2022). EAO Position Paper: Material Selection for Implant-Supported Restorations. The International Journal of Prosthodontics, 35 (1), 7–16. https://doi.org/10.11607/ijp.8013
- Linetskiy, I., Sutcliffe, M., Kondratiev, A., Demenko, V., Linetska, L., Yefremov, O. (2023). A Novel Method of Load Bearing Ability Analysis of Short Plateau Implants Placed in Compromised Bone. 2023 IEEE 4th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/khpiweek61412.2023.10312831
- Gontarovskyi, P., Smetankina, N., Garmash, N., Melezhyk, I. (2021). Numerical Analysis of Stress-Strain State of Fuel Tanks of Launch Vehicles in 3D Formulation. Integrated Computer Technologies in Mechanical Engineering – 2020, 609–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66717-7_52
- Gerlici, J., Lovska, A., Pavliuchenkov, M. (2024). Study of the Dynamics and Strength of the Detachable Module for Long Cargoes under Asymmetric Loading Diagrams. Applied Sciences, 14 (8), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083211
- Sagin, S., Kuropyatnyk, O., Sagin, A., Tkachenko, I., Fomin, O., Píštěk, V., Kučera, P. (2022). Ensuring the Environmental Friendliness of Drillships during Their Operation in Special Ecological Regions of Northern Europe. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10 (9), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091331
- Lisiak-Myszke, M., Marciniak, D., Bieliński, M., Sobczak, H., Garbacewicz, Ł., Drogoszewska, B. (2020). Application of Finite Element Analysis in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery – A Literature Review. Materials, 13 (14), 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143063
- Matos, J. D. M. de, Queiroz, D. A., Nakano, L. J. N., Andrade, V. C., Ribeiro, N. de C. R., Borges, A. L. S. et al. (2022). Bioengineering Tools Applied to Dentistry: Validation Methods for In Vitro and In Silico Analysis. Dentistry Journal, 10 (8), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj10080145
- Xie, B., Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Chu, Y., Lu, Y. (2024). Finite element analysis in the Dental Sciences: A Bibliometric and a Visual Study. International Dental Journal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2024.08.005
- Kondratiev, A., Smetankina, N., Staude, V. (2024). Biomechanical Analysis of Stress–Strain Distribution in the Lumbar Spine-Sacrum-Pelvis System with Emphasis on Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction. Prosthesis, 7 (1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/prosthesis7010004
- Ogurkowska, M. B., Błaszczyk, A. (2020). Distribution of Young’s modulus at various sampling points in a human lumbar spine vertebral body. The Spine Journal, 20 (11), 1861–1875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2020.06.013
- Müller, A., Rockenfeller, R., Damm, N., Kosterhon, M., Kantelhardt, S. R., Aiyangar, A. K., Gruber, K. (2021). Load Distribution in the Lumbar Spine During Modeled Compression Depends on Lordosis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.661258
- Kondratiev, A., Sutcliffe, M., Demenko, V., Linetskiy, I., Yefremov, O., Linetska, L. (2024). Efficiency of Miniplates Fixation in Mandibular Oblique Fractures. 2024 IEEE 5th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/khpiweek61434.2024.10878063
- Alaneme, K. K., Kareem, S. A., Ozah, B. N., Alshahrani, H. A., Ajibuwa, O. A. (2022). Application of finite element analysis for optimizing selection and design of Ti-based biometallic alloys for fractures and tissues rehabilitation: a review. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 19, 121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.001
- Kuritsyn, A., Taranenko, I., Miroshnikov, V., Demenko, V., Kondratiev, A. (2024). Regression Analysis of Geometric Parameters of “Screw Implant – Maxillary Segment” Biomechanical System. Integrated Computer Technologies in Mechanical Engineering – 2023, 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-61415-6_20
- Perren, S. M. (1979). Physical and biological aspects of fracture healing with special reference to internal fixation. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 138, 175–196.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andrii Kondratiev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







