Determination of the dependence of the filtration properties of a biopolymer system on pressure, temperature and concentration of components
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.325362Keywords:
biopolymer system, rheological properties, biopolymer stability, formulation optimization, high-temperature stabilityAbstract
The object of study is the biopolymer system “X”, which is used as a clay-free drilling fluid for development of productive horizons. Biopolymer system “X” is a clay-free drilling fluid for drilling directional and horizontal wells, development of productive horizons under high pressures and temperatures.
A distinctive feature of the biopolymer system is a high level of mineralization, increased heat resistance and high density, which significantly expands the scope of clay-free muds.
At the same time, this system has a number of significant advantages:
– high level of mineralization;
– increased heat resistance (operable up to 150 °C);
– high density, which expands the scope of application;
– provides a higher coefficient of recovery of reservoir permeability compared to traditional weighted solutions;
– low content of colloidal particles, which reduces the risk of deterioration of reservoir performance;
– ability to control filtration properties at high temperatures and pressures.
The following disadvantages can be identified based on the research:
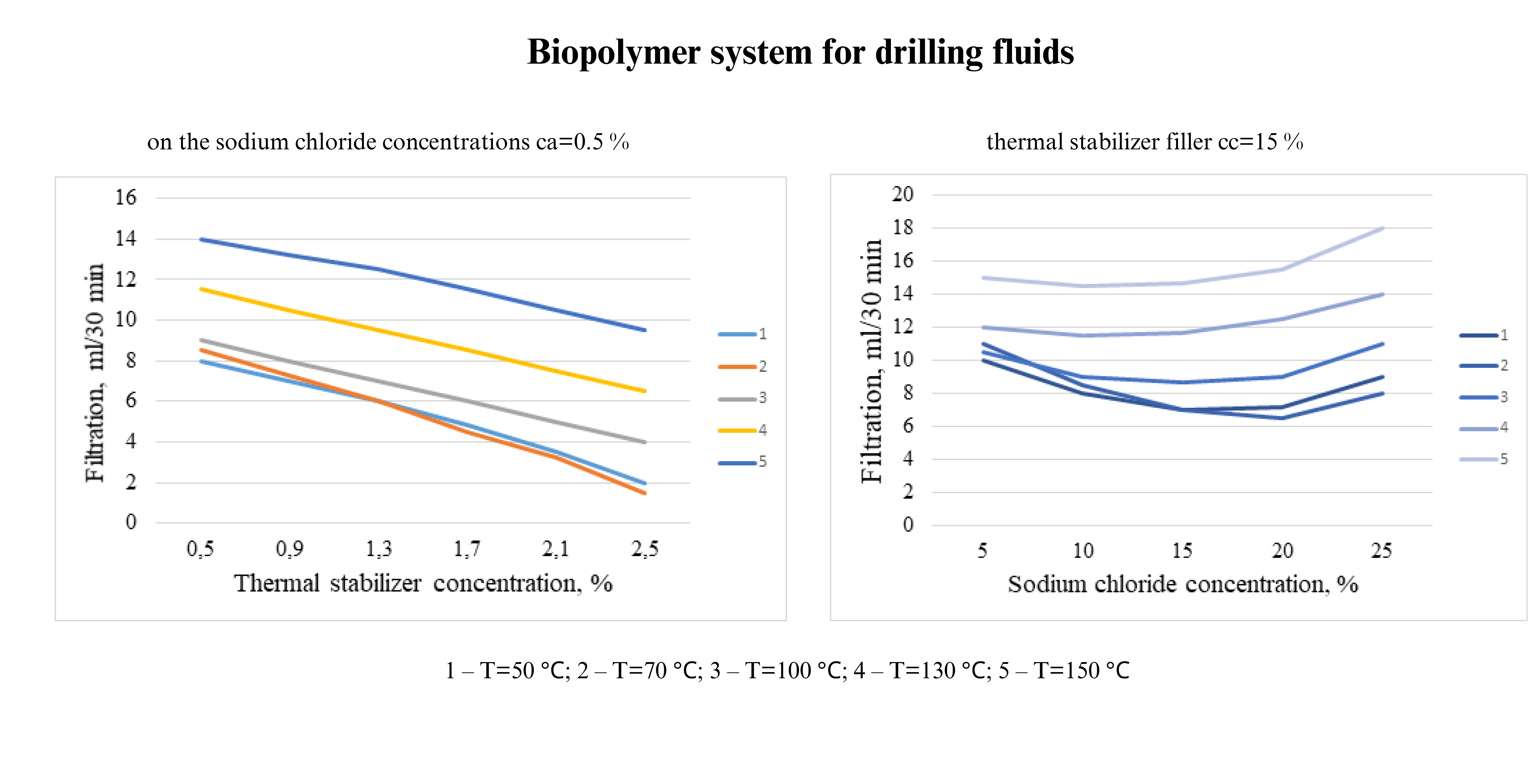
- Significant increase in the filtration rate with increasing temperature (nonlinear dependence with a correlation coefficient of 0.773).
- 2. The need to maintain a constant concentration of potassium chloride (~3 %) to ensure the development quality of productive formations.
- Difficulty in controlling the properties due to the need to accurately select the concentrations of various components (sodium chloride and organomineral colmatant).
The optimal ratio of components to ensure the stability of the system at temperatures up to 150 °C was obtained: sodium chloride concentration 15–20 %, stabilizer 0.75–1 %. This is due to the fact that the proposed composition has a number of features of synergistic interaction of the components, in particular the formation of stable complexes between biopolymers and sodium ions, which prevents the thermal destruction of polymer chains at high temperatures. At the same time, the stabilizer forms an additional protective layer around the polymer molecules, ensuring their resistance to oxidation and hydrolysis under high pressure of up to 7 MPa.
The obtained research results indicate the possibility of effective use of the biopolymer system at high temperatures and pressures due to the thermostabilizing effect of sodium chloride and organo-mineral colmatant.
References
- Luban, Yu. V., Kuntsiak, Ya. V., Luban, S. V., Bileka, O. A. et al. (2008). “BIOKAR” – bezghlynysta promyvalna ridyna dlia burinnia pokhylo-skerovanykh i horyzontalnykh sverdlovyn ta rozkryttia produktyvnykh horyzontiv. Naftova i hazova promyslovist, 4, 18–21.
- Mysliuk, M. A., Salyzhyn, Yu. M. (2007). Systema vyboru optymalnykh retseptur obrobky burovykh rozchyniv. Naftova i hazova promyslovist, 5, 25–28.
- Rubel, V., Slichenko, R. (2024). Selection of the optimal formulation of the biopolymer system for the stimulation of productive formations. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 5 (1 (79)), 57–61. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.314230
- Luban, Yu. V., Luban, S. V., Dudzych, V. V., Boiko, A. H., Semeniuk, V. H. (2013). Zastosuvannia bezghlynystykh promyvalnykh ridyn v umovakh vysokykh plastovykh tyskiv i temperatur. Naftohazova haluz Ukrainy, 2, 18–22.
- Koroviaka, Ye. A., Stavychnyi, Ye. M., Martsynkiv, O. B., Ihnatov, A. O., Yavorskyi, A. V. (2024). Research on occurrence features and ways to improve the quality of productive hydrocarbon horizons demarcation. Naukovyi Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu, 3, 5–11. https://doi.org/10.33271/nvngu/2024-3/005
- Liu, T., Leusheva, E., Morenov, V., Li, L., Jiang, G., Fang, C. et al. (2020). Influence of Polymer Reagents in the Drilling Fluids on the Efficiency of Deviated and Horizontal Wells Drilling. Energies, 13 (18), 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184704
- Polutrenko, М. S., Bogoslavets, V. V., Voloshyn, Yu. D. (2021). Study of surface and rheological properties of clayless biopolymer drilling mud treated with M-1 surfactants. Oil and Gas Power Engineering, 1 (35), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.31471/1993-9868-2021-1(35)-91-97
- Boyer, C., Figueiredo, L., Pace, R., Lesoeur, J., Rouillon, T., Visage, C. L. et al. (2018). Laponite nanoparticle-associated silated hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose as an injectable reinforced interpenetrating network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia, 65, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.027
- Gu, M., Fan, S., Zhou, G., Ma, K., Yao, X., Zhang, Y. (2022). Effects of dynamic mechanical stimulations on the regeneration of in vitro and in vivo cartilage tissue based on silk fibroin scaffold. Composites Part B: Engineering, 235, 109764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109764
- Salati, M. A., Khazai, J., Tahmuri, A. M., Samadi, A., Taghizadeh, A., Taghizadeh, M. et al. (2020). Agarose-Based Biomaterials: Opportunities and Challenges in Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Polymers, 12 (5), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051150
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Viktoria Rubel, Roman Slichenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







