AI-driven tools in modern software quality assurance: an assessment of benefits, challenges, and future directions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.330595Keywords:
quality assurance, testing, end-to-end test automation, test case, SDLC, AI, AI agents, LLMAbstract
Traditional quality assurance (QA) methods face significant challenges in addressing the complexity, scale, and rapid iteration cycles of modern software systems and are strained by limited resources available, leading to substantial costs associated with poor quality.
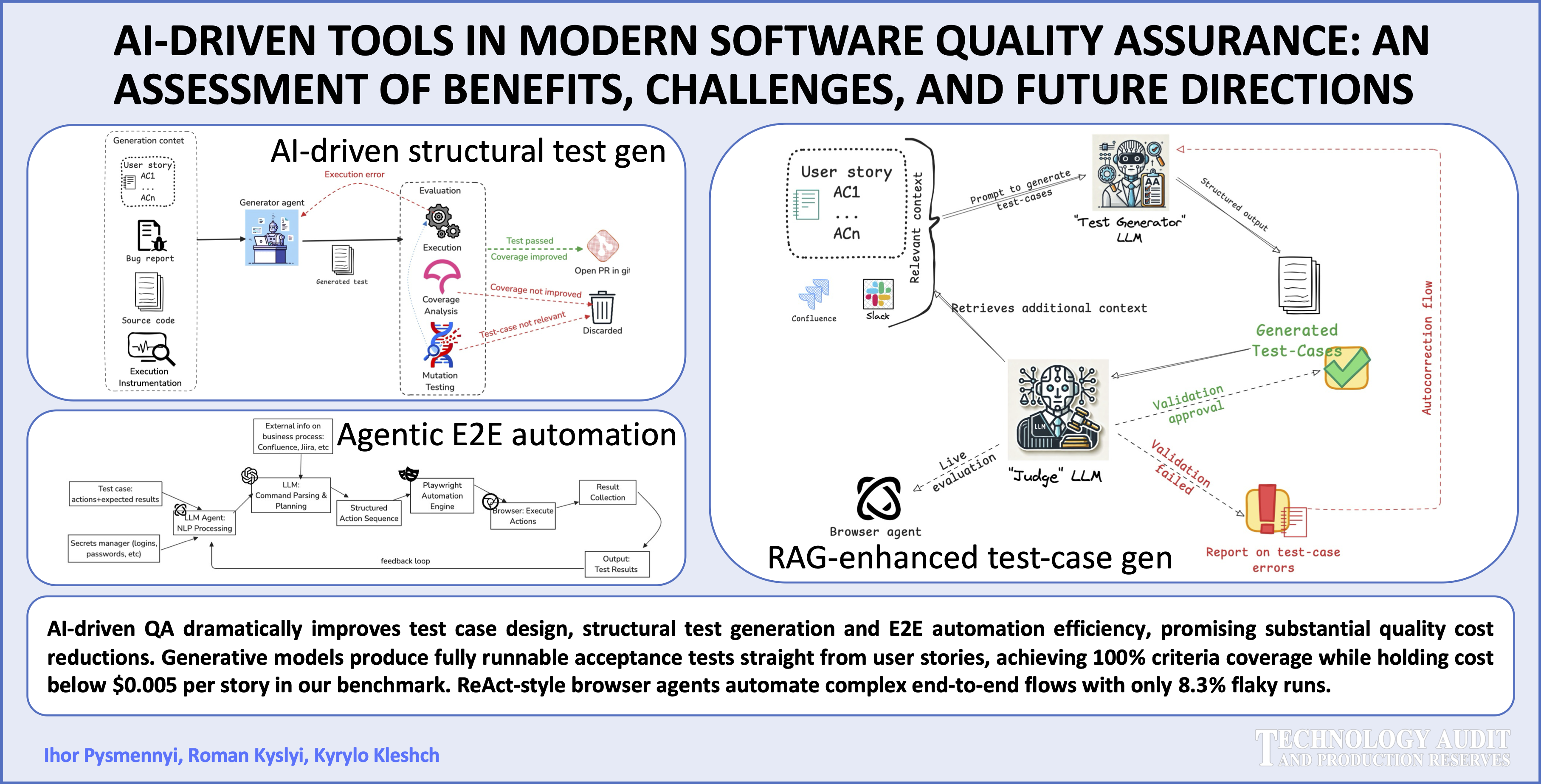
The object of this research is the quality assurance processes for modern distributed software applications. The subject of the research is the assessment of the benefits, challenges, and prospects of integrating modern AI-oriented tools into quality assurance processes. Comprehensive analysis of implications was performed on both verification and validation processes covering exploratory test analyses, equivalence partitioning and boundary analyses, metamorphic testing, finding inconsistencies in acceptance criteria (AC), static analyses, test case generation, unit test generation, test suit optimization and assessment, end to end scenario execution. End to end regression of sample enterprise application utilizing AI-agents over generated test scenarios was implemented as a proof of concept highlighting practical use of the study. The results, with only 8.3% flaky executions of generated test cases, indicate significant potential for the proposed approaches. However, the study also identified substantial challenges for practical adoption concerning generation of semantically identical coverage, “black box” nature and lack of explainability from state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs), the tendency to correct mutated test cases to match expected results, underscoring the necessity for thorough verification of both generated artifacts and test execution results.
The research demonstrates AI's transformative potential for QA but highlights the importance of a strategic approach to implementing these technologies, considering the identified limitations and the need for developing appropriate verification methodologies.
References
- Krasner, H. (2022). The Cost of Poor Software Quality In The Us: A 2022 Report. Austin. Available at: https://www.it-cisq.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2022/11/CPSQ-Report-Nov-22-2.pdf
- Cordy, M., Rwemalika, R., Franci, A., Papadakis, M., Harman, M. (2022). FlakiMe: Laboratory-Controlled Test Flakiness Impact Assessment. Proceedings of the 44th International Conference on Software Engineering. New York, 982–994. https://doi.org/10.1145/3510003.3510194
- Gumhold, F. (2022). How a lack of quality assurance can lead to a loss of $400 million in 37 seconds – ERNI. Available at: https://www.betterask.erni/how-a-lack-of-quality-assurance-can-lead-to-a-loss-of-400-million-in-37-seconds/
- Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge and The Standard for Project Management (2021). Newtown Square: Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Deshpande, S. A., Deshpande, A. N., Marathe, M. V., Garje, G. V. (2010). Improving Software Quality with Agile Testing. International Journal of Computer Applications, 1 (22), 68–73. https://doi.org/10.5120/440-673
- Introduction to Software testing (2025). University of Minnesota Software Engineering Center. Available at: https://www.coursera.org/learn/introduction-software-testing/lecture/ohzH2/introduction
- Swag Labs. Available at: https://www.saucedemo.com/
- Vokhranov, I., Bulakh, B. (2024). Transformer-based models application for bug detection in source code. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 5 (2 (79)), 6–15. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.310822
- 6X improvement over SonarQube – Raising the Maintainability bar. Available at: https://codescene.com/blog/6x-improvement-over-sonarqube
- Marjanov, T., Pashchenko, I., Massacci, F. (2022). Machine Learning for Source Code Vulnerability Detection: What Works and What Isn’t There Yet. IEEE Security & Privacy, 20 (5), 60–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/msec.2022.3176058
- Roman, A. (2018). A Study Guide to the ISTQB® Foundation Level 2018 Syllabus. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-98740-8
- Plein, L., Ouédraogo, W. C., Klein, J., Bissyandé, T. F. (2024). Automatic Generation of Test Cases based on Bug Reports: A Feasibility Study with Large Language Models. Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/ACM 46th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings, 360–361. https://doi.org/10.1145/3639478.3643119
- Ayon, Z. A. H., Husain, G., Bisoi, R., Rahman, W., Osborn, D. T. (2025). An efficient approach to represent enterprise web application structure using Large Language Model in the service of Intelligent Quality Engineering. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.06837
- Li, D., Jiang, B., Huang, L., Beigi, A., Zhao, C., Tan, Z. et al. (2024). From generation to judgment: Opportunities and challenges of LLM-as-a-judge. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2411.16594
- Müller, M., Žunič, G. (2024). Browser Use: Enable AI to control your browser. GitHub. Available at: https://github.com/browser-use/browser-use
- Martin, R. C. (2017). Clean Architecture: A Craftsman’s Guide to Software Structure and Design. Prentice Hall Press.
- Daka, E., Fraser, G. (2014). A Survey on Unit Testing Practices and Problems. 2014 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, 201–211. https://doi.org/10.1109/issre.2014.11
- Wang, J., Huang, Y., Chen, C., Liu, Z., Wang, S., Wang, Q. (2024). Software Testing With Large Language Models: Survey, Landscape, and Vision. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 50 (4), 911–936. https://doi.org/10.1109/tse.2024.3368208
- Alshahwan, N., Harman, M., Marginean, A., Tal, R., Wang, E. (2024). Observation-Based Unit Test Generation at Meta. Companion Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on the Foundations of Software Engineering, 173–184. https://doi.org/10.1145/3663529.3663838
- Alshahwan, N., Chheda, J., Finogenova, A., Gokkaya, B., Harman, M., Harper, I. et al. (2024). Automated Unit Test Improvement using Large Language Models at Meta. Companion Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on the Foundations of Software Engineering. New York, 185–196. https://doi.org/10.1145/3663529.3663839
- Foster, C., Gulati, A., Harman, M., Harper, I., Mao, K., Ritchey, J. et al. (2025). Mutation-guided LLM-based test generation at Meta. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.12862
- Shin, J., Aleithan, R., Hemmati, H., Wang, S. (2024, September). Retrieval-augmented test generation: How far are we? arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.12682
- Hu, R., Peng, C., Wang, X., Gao, C. (2025). An LLM-based agent for reliable Docker environment configuration. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2502.13681
- Gunawi, H. S., Hao, M., Leesatapornwongsa, T., Patana-anake, T., Do, T., Adityatama, J. et al. (2014). What Bugs Live in the Cloud? A Study of 3000+ Issues in Cloud Systems. Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Cloud Computing. New York. https://doi.org/10.1145/2670979.2670986
- Vocke, H. (2018). The Practical Test Pyramid. Available at: https://martinfowler.com/articles/practical-test-pyramid.html
- Yao, S., Zhao, J., Yu, D., Du, N., Shafran, I., Narasimhan, K., Cao, Y. (2022). ReAct: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models. arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2210.03629
- Ahlgren, J., Berezin, M., Bojarczuk, K., Dulskyte, E., Dvortsova, I., George, J. et al. (2021). Testing Web Enabled Simulation at Scale Using Metamorphic Testing. 2021 IEEE/ACM 43rd International Conference on Software Engineering: Software Engineering in Practice (ICSE-SEIP), 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1109/icse-seip52600.2021.00023
- Ribeiro, M. T., Wu, T., Guestrin, C., Singh, S. (2020). Beyond Accuracy: Behavioral Testing of NLP Models with CheckList. Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, 4902–4912. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.442
- John-Mathews, J.-M. (2022). How to test Machine Learning Models? Metamorphic testing. Available at: https://www.giskard.ai/knowledge/how-to-test-ml-models-4-metamorphic-testing
- Data for paper AI-Driven Testing Tools in Modern Quality Assurance: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Directions. Available at: https://github.com/igor-pysmennyi-kpi/qa-ai-overview-paper-2025
- Micco, J. (2016). Flaky Tests at Google and How We Mitigate Them. Google Testing Blog. Available at: https://testing.googleblog.com/2016/05/flaky-tests-at-google-and-how-we.html
- Valmeekam, K., Olmo, A., Sreedharan, S., Kambhampati, S. (2022). Large Language Models Still Can’t Plan (A Benchmark for LLMs on Planning and Reasoning about Change). iNeurIPS 2022 Foundation Models for Decision Making Workshop, New Orleans. Available at: https://openreview.net/forum?id=wUU-7XTL5XO
- Lee, H.-P. (Hank), Sarkar, A., Tankelevitch, L., Drosos, I., Rintel, S., Banks, R., Wilson, N. (2025). The Impact of Generative AI on Critical Thinking: Self-Reported Reductions in Cognitive Effort and Confidence Effects from a Survey of Knowledge Workers. Proceedings of the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713778
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ihor Pysmennyi, Roman Kyslyi, Kyrylo Kleshch

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







