Recognition of eye movement based on bioelectrical signals using neural networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.339890Keywords:
movements, eyes, QVar, windows, classification, signals, VitalCore, recognition, directions, gaze, sensors, learningAbstract
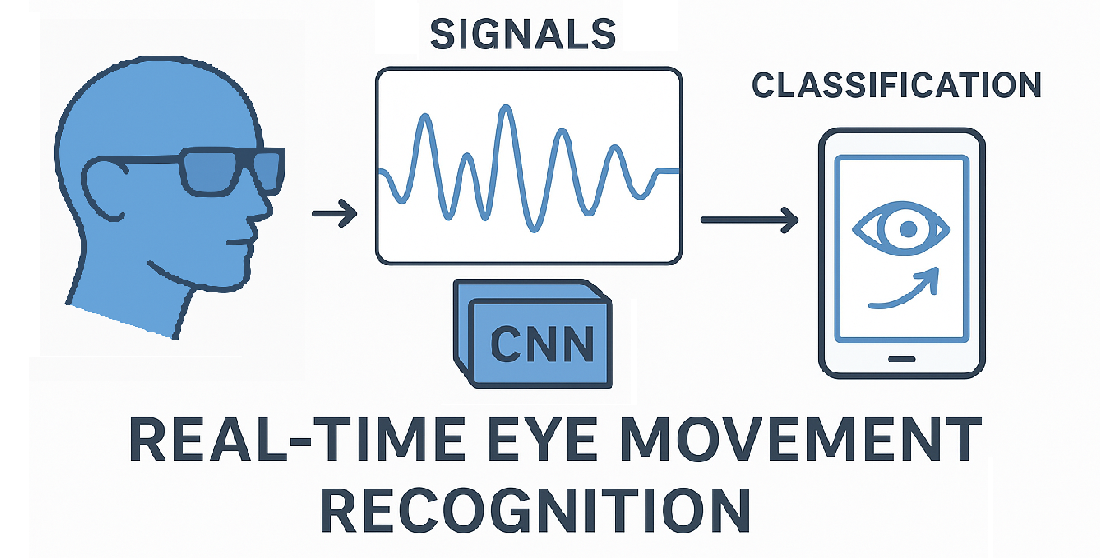
The object of research is the process of generating and recording electrical signals caused by eye movements; the subject of research is the method of real-time recognition of eye movements based on these signals. It is implemented on the open VitalCore platform and uses a convolutional neural network (CNN) for real-time movement classification. One of the most problematic aspects is ensuring high accuracy with low power consumption and limited computing resources, as well as reducing the impact of noise and delay during signal processing. This is of particular importance when using the system in wearable devices and in real-world environments where signal quality may be unstable.
The study uses digital signal processing methods, in particular, filtering by the Savitsky-Goley algorithm, as well as architectural solutions in the field of neural networks: the use of a five-channel CNN with ordinary and transposed convolutional layers, Flatten and softmax. The use of frequent sliding windows (every 8 ms) is proposed, which increases accuracy and reduces latency.
The result is obtained: the recognition accuracy reaches 85% with a time window of 625–833 ms and a latency of about 40 ms, which provides the ability to detect up to five movements per second. This is due to the combination of an energy-efficient sensor with an optimized CNN architecture, which provides noise immunity and fast classification in real time.
Thus, the method allows to achieve stable and reliable results while maintaining low power consumption. Compared with known analogues, it is distinguished by openness, scalability, reproducibility and the ability to work on peripheral devices without high-performance computing resources. The development can be integrated into wearable devices and used in brain – computer interfaces, VR/AR, assistive technologies and medical research, which emphasizes its practical value.
References
- Kovalyk, S. V. (2019). Electromyographic signal selection system for the problem of bioprosthetics of the hand. Ternopilskyi natsionalnyi tekhnichnyi universytet imeni Ivana Puliuia. Ternopil, 96. Available at: https://elartu.tntu.edu.ua/handle/lib/29791
- Nykolaichuk, V. I. (2019). Development of signal selection tools for electroencephalographic diagnostic systems. TNTU im. I. Puliuia. Ternopil, 85. Available at: https://elartu.tntu.edu.ua/handle/lib/29792
- Levenets, S. V., Havryliuk, S. V., Boiarchuk, O. D. (2010). Osnovy neirofiziolohii ta vyshchoi nervovoi diialnosti. Luhansk: LNU im. T. Shevchenka, 166. Available at: https://anatomy.luguniv.edu.ua/ukr_studies/neurophysiology_tutorial.pdf
- Kovalova, A. A., Kovalova, O. V., Kovalova, O. V., Burka, O. M., Prysiazhniuk, O. A. (2022). Neirobiolohiia rozvytku ta navchannia. Zaporizhzhia: NU “Zaporizka politekhnika”, 325. Available at: https://eir.zp.edu.ua/handle/123456789/9232
- Alieva, A. D. (2022). Analiz EEH liudyny. Kyiv, 39. Available at: https://ela.kpi.ua/handle/123456789/58280
- Tang, J., Luk, P., Zhou, Y. (2023). Wearable and Invisible Sensor Design for Eye-Motion Monitoring Based on Ferrofluid and Electromagnetic Sensing Technologies. Bioengineering, 10 (5), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050514
- Kazanskiy, N. L., Khonina, S. N., Butt, M. A. (2023). Smart Contact Lenses – A Step towards Non-Invasive Continuous Eye Health Monitoring. Biosensors, 13 (10), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13100933
- Choi, C., Choi, M. K., Liu, S., Kim, M., Park, O. K., Im, C. et al. (2017). Human eye-inspired soft optoelectronic device using high-density MoS2-graphene curved image sensor array. Nature Communications, 8 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01824-6
- Wang, V., Kuriyan, A. E. (2020). Optoelectronic Devices for Vision Restoration. Current Ophthalmology Reports, 8 (2), 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40135-020-00232-2
- Xie, M., Yao, G., Zhang, T., Wang, Q., Mo, X., Dong, Q. et al. (2022). Multifunctional flexible contact lens for eye health monitoring using inorganic magnetic oxide nanosheets. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01415-8
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oleksiy Mormitko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







