Enhancing writer identification and writer retrieval with CenSurE and Vision Transformers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.343943Keywords:
machine learning, writer identification, transformer, image, neural networks, handwriting, preprocessingAbstract
The object of research is the process of writer identification based on handwritten text. Despite significant progress, existing methods for author identification from handwritten text have limitations that prevent them from achieving maximum accuracy and reliability.
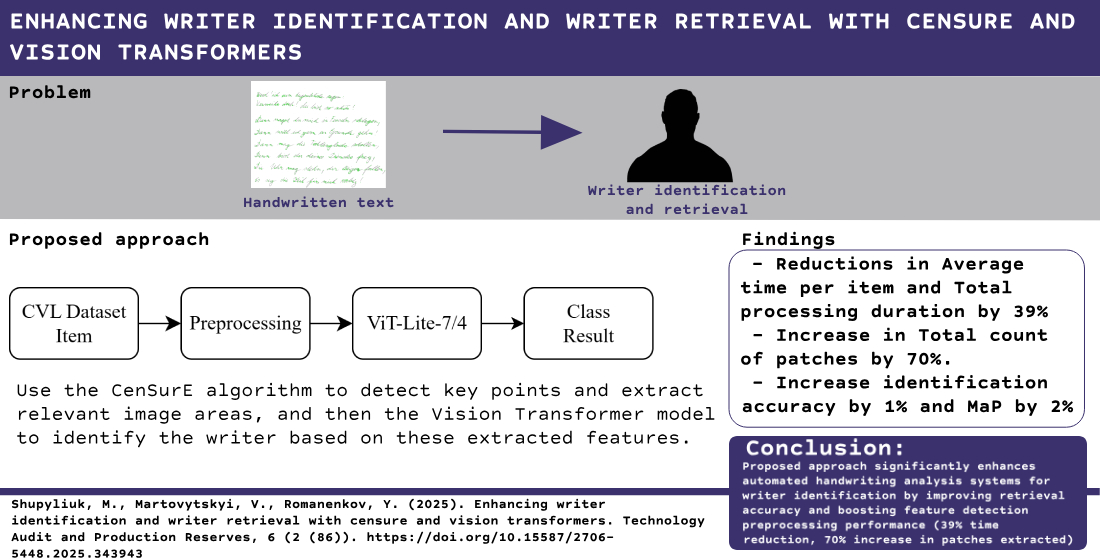
This paper focuses on optimizing and improving the efficiency of writer identification from handwritten text by integrating image preprocessing methods, feature detection, and modern machine learning architectures. To this end, a functional model was developed that uses the CenSurE algorithm to detect key points and extract relevant image areas, and then the Vision Transformer model to identify the writer based on these extracted features. To reduce the variability of the results, experimental validation was conducted using a dual search and classification methodology. The use of the public CVL dataset increases reproducibility and helps in comparative analysis. The findings indicate that the implementation of the proposed approach leads to an improvement in the identification accuracy during retrieval, surpassing the results of other studies. This is evidenced by increased accuracy values of hard top k and soft top k by 1% and mean average precision by 2%. In addition, findings indicate significant performance improvement in the feature detection preprocessing stage. This improvement is quantitatively supported by reductions in both the average time per item and total processing duration by 39%, alongside the increase in total count of patches extracted by 70%.
The results obtained contribute to increasing the reliability of automated handwriting analysis systems, especially for the task of writer identification. This achievement is a valuable tool for graphologists and forensic document experts, supporting such critical tasks as the forensic authorship process.
References
- Hengl, M. (2014). Comparison of the Branches of Handwriting Analysis. Chasopys Natsionalnoho universytetu “Ostrozka akademiia”. Seriia: Pravo, 2 (10).
- Shupyliuk, M., Martovytskyi, V., Bolohova, N., Romanenkov, Y., Osiievskyi, S., Liashenko, S. et al. (2025). Devising an approach to personality identification based on handwritten text using a vision transformer. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 1 (2 (133)), 53–65. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2025.322726
- Aliyev, E. (2024). Forensic Handwriting Analysis to Determine the Psychophysiological Traits. International Journal of Religion, 5 (6), 511–530. https://doi.org/10.61707/2r6bmr11
- Pandey, N., Singh, B., Singh, S. (2024). Review on handwriting examination on unusual surface. IP International Journal of Forensic Medicine and Toxicological Sciences, 8 (4), 125–131. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijfmts.2023.028
- Romanenkov, Y., Pronchakov, Y., Zieiniiev, T. (2020). Algorithmic Support for Auto-modes of adaptive short-term Forecasting in predictive Analytics Systems. 2020 IEEE 15th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies (CSIT), 230–233. https://doi.org/10.1109/csit49958.2020.9321875
- Christlein, V., Bernecker, D., Hönig, F., Maier, A., Angelopoulou, E. (2017). Writer Identification Using GMM Supervectors and Exemplar-SVMs. Pattern Recognition, 63, 258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.10.005
- Christlein, V., Gropp, M., Fiel, S., Maier, A. (2017). Unsupervised Feature Learning for Writer Identification and Writer Retrieval. 2017 14th IAPR International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), 991–997. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdar.2017.165
- Chen, S., Wang, Y., Lin, C.-T., Ding, W., Cao, Z. (2019). Semi-supervised feature learning for improving writer identification. Information Sciences, 482, 156–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.024
- He, S., Schomaker, L. (2019). Deep adaptive learning for writer identification based on single handwritten word images. Pattern Recognition, 88, 64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.11.003
- Helal, L. G., Bertolini, D., Costa, Y. M. G., Cavalcanti, G. D. C., Britto, A. S., Oliveira, L. E. S. (2019). Representation Learning and Dissimilarity for Writer Identification. 2019 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), 63–68. https://doi.org/10.1109/iwssip.2019.8787293
- Sulaiman, A., Omar, K., Nasrudin, M. F., Arram, A. (2019). Length Independent Writer Identification Based on the Fusion of Deep and Hand-Crafted Descriptors. IEEE Access, 7, 91772–91784. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2927286
- Kumar, P., Sharma, A. (2020). Segmentation-free writer identification based on convolutional neural network. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106707
- He, S., Schomaker, L. (2020). FragNet: Writer Identification Using Deep Fragment Networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 15, 3013–3022. https://doi.org/10.1109/tifs.2020.2981236
- Koepf, M., Kleber, F., Sablatnig, R. (2022). Writer identification and writer retrieval using Vision Transformer for forensic documents. Document Analysis Systems. Cham: Springer, 352–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06555-2_24
- Semma, A., Hannad, Y., Siddiqi, I., Djeddi, C., El Youssfi El Kettani, M. (2021). Writer Identification using Deep Learning with FAST Keypoints and Harris corner detector. Expert Systems with Applications, 184, 115473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115473
- He, S., Schomaker, L. (2021). GR-RNN: Global-context residual recurrent neural networks for writer identification. Pattern Recognition, 117. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.05036
- Suteddy, W., Agustini, D. A. R., Atmanto, D. A. (2024). Offline Handwriting Writer Identification using Depth-wise Separable Convolution with Siamese Network. JOIV : International Journal on Informatics Visualization, 8 (1), 535–541. https://doi.org/10.62527/joiv.8.1.2148
- Kleber, F., Fiel, S., Diem, M., Sablatnig, R. (2013). CVL-DataBase: An Off-Line Database for Writer Retrieval, Writer Identification and Word Spotting. 2013 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, 560–564. https://doi.org/10.1109/icdar.2013.117
- Smelyakov, K., Sandrkin, D., Ruban, I., Vitalii, M., Romanenkov, Y. (2018). Search by Image. New Search Engine Service Model. 2018 International Scientific-Practical Conference Problems of Infocommunications. Science and Technology (PIC S&T), 181–186. https://doi.org/10.1109/infocommst.2018.8632117
- Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T. et al. (2021). An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.11929
- Shupyliuk, M., Martovytskyi, V. (2025). Analysis of personality detection and writer identification methods. Control, Navigation and Communication Systems, 79 (1), 138–142. https://doi.org/10.26906/SUNZ.2025.1.138-142
- Agrawal, M., Konolige, L., Blas, M. (2008). CenSurE: Center Surround Extremas for Realtime Feature Detection and Matching. 10th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 102–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88693-8_8
- Otsu, N. (1979). A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 9 (1), 62–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.1979.4310076
- Hassani, A., Walton, S., Shah, N., Abuduweili, A., Li, J., Shi, H. (2021). Escaping the Big Data Paradigm with Compact Transformers. arXiv:2104.05704. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.05704
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykyta Shupyliuk, Vitalii Martovytskyi, Yuri Romanenkov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







