Exploration of describing the vector-parametric bi-spline, defined by the forth degree spline with control points incident with surface of appropriate smoothness
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2015.51287Keywords:
vector & parametric spline, bispline, spline with control points incidental to curved surface, third degree smoothnessAbstract
The article proposes description technique for spline vector & parametrical surfaces of the fourth degree with control points incidental to the surface and gives testing examples of application of this technique. Main purpose of researches is to develop an algorithm for solving some application problems which often impose specific demands to tools available with developers’ or designers’ workplace. For instance, it sometime becomes troublesome to produce smooth configuration, since the obtained curve does not belong to pre-set dotted carcass.
The technique of producing a vector & parametrical bispline with control points incidental (belonging) to relevant surface is proposed to overcome such inconvenience. Hence, a polynomial function of the fourth degree determined with five points x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, x4, y4 may be represented, as below:
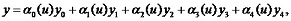
with function αi(u) being the Lagrange polynomial coefficients.
Polynomial equation in matrix format may be expressed, as follows:
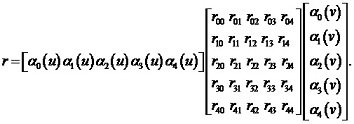
With provided derivatives equity up to the third degree (inclusive) the equity of compound derivatives along the gluing line criterion is also met (i. e. continuity of the second quadric form is achieved throughout the entire surface). Equity of the compound derivatives should be achieved to obtain fine smoothness of the third degree surface, i. e.:

Calculation formulae for spline with third degree of smoothness should be applied to achieve this effect. Thus linear equations system with quadrodiagonal leading matrix may be obtained by means of preset three boundary conditions (thus increasing the flexibility of the method) providing a stable and unambiguous solution. Algorithm for development of the fourth degree bispline with control points belonging to relevant surface is developed. Results of the research may be helpful for developers, designers, APS users providing them with additional opportunities in developing smooth curved contours for elements and parts of machinery operating in mobile environments.
Test examples are provided for the fourth degree bisplines with third degree smoothness with control points incidental to the surface.
The proposed algorithm is suggested for implementation to improve efficient work of constructors, designers, developers.
References
- Fox, A., Pratt, M. (1982). Vychislitel'naia geometriia. Translated from English. Moscow: Mir, 304.
- Zav'ialov, Yu. S., Kvasov, B. I., Miroshnichenko, V. L. (1982). Metody splain-funktsii. Moscow: Nauka, 352.
- Kovtun, O. M. (2004). Polinomialni splainy chetvertoho stepenia. Prykladna heometriia ta inzhenerna hrafika, 74, 239–243.
- Golovanov, N. N. (2002). Geometricheskoe modelirovanie. Moscow: Izdatel'stvo Fiziko-matematicheskoi literatury, 472.
- Rogers, D., Adams, J. (2001). Matematicheskie osnovy mashinnoi grafiki. Moscow: Mir, 604.
- Yakunin, V. I. (1980). Geometricheskie osnovy avtomatizirovannogo proektirovaniia tehnicheskih poverhnostei. Moscow: Mai, 86.
- Zav'ialov, Yu. S., Leus, V. A., Skorospelov, V. A. (1985). Splainy v inzhenernoi geometrii. Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 224.
- Watt, A. (2000). 3D Computer Graphics. Ed. 3. Addison-Wesley, 570.
- Zamani, M. (2010). A simple 2D interpolation model for analysis of nonlinear data. Natural Science, Vol. 02, № 06, 641–645. doi:10.4236/ns.2010.26080
- Chen, L., Hu, S. (2011, May). A Comparison of Improvements for Shear Warp Algorithm Using Lagrange or Cubic Spline Interpolation. 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE), 1–4. doi:10.1109/icbbe.2011.5780354
- Herman, G. T., Bucholtz, C. A., Jingsheng Zheng. (1991). Shape-based Interpolation Using Modified Cubic Splines. Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vol. 13, № 1, 291–292. doi:10.1109/iembs.1991.683941
- Badaev, Yu. I., Kovtun, A. M. (2011). Spetsial'nye splainy iz polinomov tret'ei, chetviortoi i piatoi stepenei v geometricheskom modelirovanii. Odessa: Feniks, 315.
- Badaiev, Yu. I., Kovtun, O. M. (2003). Aproksymatsiia splainamy na osnovi kryvykh z intsydentnymy tochkamy. Suchasni problemy heometrychnoho modeliuvannia. Pratsi Natsionalnoho universytetu «Lvivska politekhnika» (spetsvypusk). Materialy mizhnarodnoi naukovo-praktychnoi konferentsii. Lviv: Natsionalnyi universytet «Lvivska politekhnika», 75–77.
- Badaiev, Yu. I., Kovtun, O. M. (2003). Vektorno-parametrychni sehmenty, poverkhni ta tila za intsydentnymy z nymy tochkamy. Prykladna heometriia ta inzhenerna hrafika. Pratsi Tavriiskoi derzhavnoi ahrotekhnichnoi akademii, Vol. 4, № 18. Melitopol: TDATA, 37–40.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 Александр Михайлович Ковтун

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.








