X-ray diagnostics of gunshot wounds of main vessels of the limbs: theoretical analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4798.2023.291217Keywords:
gunshot wounds, wound channel, main vessels, MSCT-angiographyAbstract
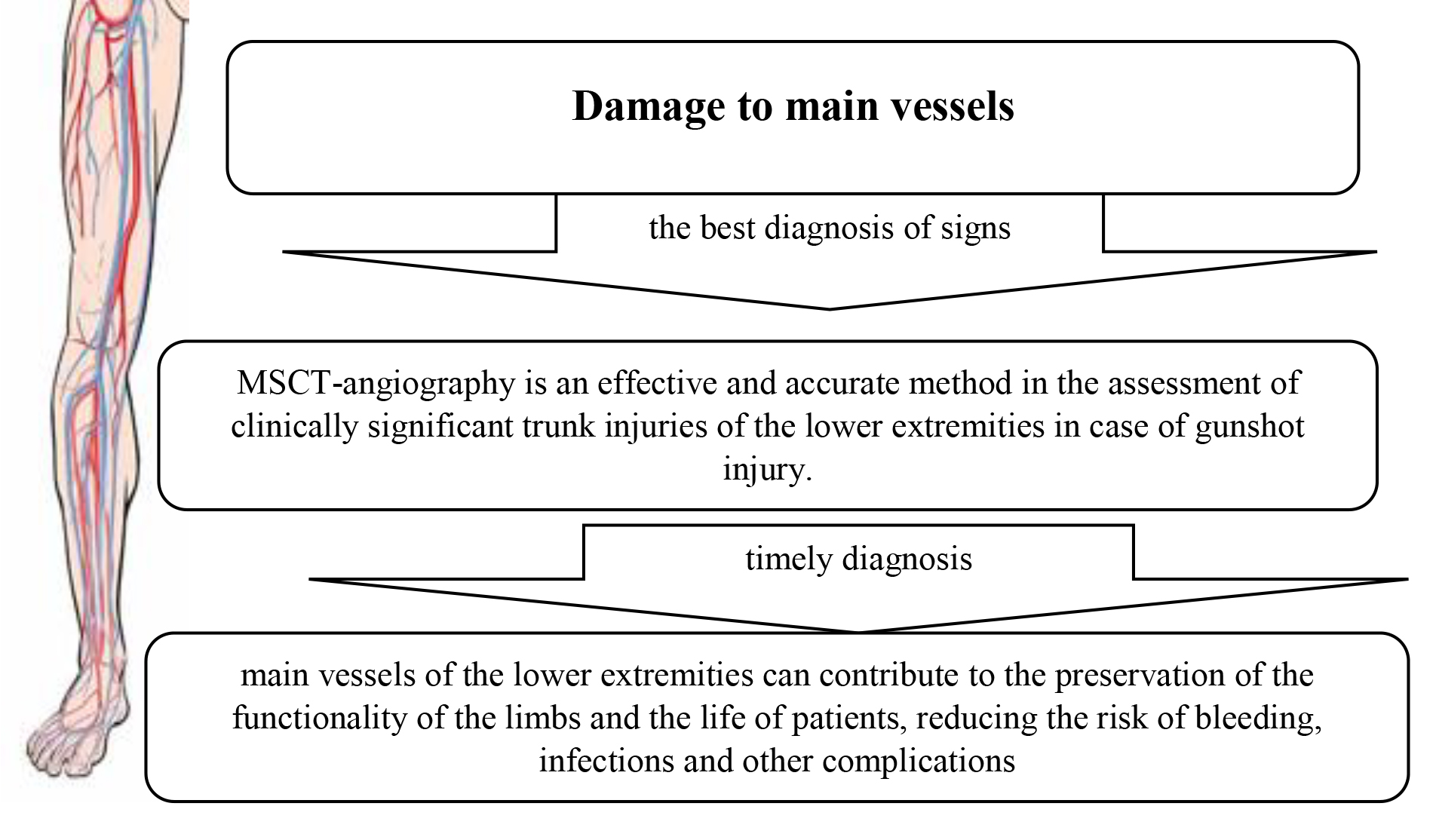
The analysis of damage to the main vessels of the limbs was considered for the formation of further organizational and tactical instructions for the provision of emergency medical care at the stages of evacuation of the injured to specialized wartime departments. It was determined that with the help of MSCT-angiography, signs of damage to main vessels can be accurately diagnosed, and additional information about damage to bone structures, neighbouring organs and tissues can be obtained. It is emphasized that MSCT is an effective and accurate method in the assessment of clinically significant arterial injuries of the lower extremities in case of gunshot injury. It was noted that timely diagnosis of vessels gunshot wounds can contribute to the preservation of the functionality of the limbs and the life of patients, reducing the risk of bleeding, infections and other complications. It was noted that the correct medical decisions, in particular, the correct diagnosis of gunshot injuries to blood vessels will help doctors make informed decisions regarding emergency surgical care, the choice of treatment methods and preoperative preparation.
The aim. The aim of the work is the theoretical substantiation of gunshot injuries of the main vessels of the limbs and the definition of practical diagnostic methods.
Materials and methods: analysis of theoretical sources, comparison, induction of isolated analytical data. The study was conducted based on the database of the State institution "National Institute of Cardiovascular Surgery named after M. M. Amosov of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine".
Results. It was determined that with the help of MSCT-angiography, signs of damage to main vessels can be accurately diagnosed, and additional information about damage to bone structures, neighboring organs and tissues can be obtained.
Conclusions. Radiological diagnosis of gunshot injuries of the main vessels of the limbs demonstrates the importance of using radiological diagnostics in the detection and analysis of vascular injuries in gunshot injuries of the extremities. The study confirms the high efficiency of this method, its accuracy and reliability in determining the nature of damage. In addition, radiological diagnostics allows timely and accurate determination of the extent and nature of injuries, which is important for making informed clinical decisions and providing adequate medical care to the injured
References
- Zarutskyi, Ya. L., Zaporozhan, V. M., Bilyi, V. Ya., Denysenko, V. M., Aslanian, S. A.; Zarutskyi, Ya. L., Zaporozhan, V. M. (Eds.) (2016). Voienno-polova khirurhiia. Odesa: ONMedU, 415.
- Kashtalian, M. A., Herasymenko, O. S., Tertyshnyi, S. V., Yenin, R. V., Dkhauadi, F. (2017). Novi napriamky v likuvanni vohnepalnykh ran. Problemy viiskovoi okhorony zdorovia, 48, 360–366.
- Rushai, A. K., Skiba, V. V., Borzykh, N. A., Kozlov, V. V., Hryb, A. M. (2017). Features of the treatment of the comminuted gunshot fractures of the extremities at an early hospital stage. Odeskyi medychnyi zhurnal, 3, 56–59.
- Fox, C. J., Patel, B., Clouse, W. D. (2011). Update on Wartime Vascular Injury. Perspectives in Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy, 23 (1), 13–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1531003511400625
- Wani, M. L., Sheikh, M. T., Nayeem-ul-Hassan, Irshad, I., Ahangar, A. G., Ganie, F. A. et al. (2014). Evaluating peripheral vascular injuries: is color Doppler enough for diagnosis? International Cardiovascular Research Journal, 8 (1), 15–17.
- Bozlar, U., Ogur, T., Norton, P. T., Khaja, M. S., All, J., Hagspiel, K. D. (2013). CT Angiography of the Upper Extremity Arterial System: Part 1 – Anatomy, Technique, and Use in Trauma Patients. American Journal of Roentgenology, 201 (4), 745–752. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.13.11207
- Gakhal, M. S., Sartip, K. A. (2009). CT Angiography Signs of Lower Extremity Vascular Trauma. American Journal of Roentgenology, 193 (1), W49–W57. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.08.2011
- Ramdass, M., Harnarayan, P. (2017). A decade of major vascular trauma: Lessons learned from gang and civilian warfare. The Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England, 99 (1), 70–75. doi: https://doi.org/10.1308/rcsann.2016.0296
- Adibi, A., Krishnam, M. S., Dissanayake, S., Plotnik, A. N., Mohajer, K., Arellano, C., Ruehm, S. G. (2014). Computed tomography angiography of lower extremities in the emergency room for evaluation of patients with gunshot wounds. European Radiology, 24 (7), 1586–1593. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3174-1
- Halvorson, J. J., Anz, A., Langfitt, M., Deonanan, J. K., Scott, A., Teasdall, R. D., Carroll, E. A. (2011). Vascular Injury Associated With Extremity Trauma: Initial Diagnosis and Management. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeon, 19 (8), 495–504. doi: https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-201108000-00005
- Gurien, L. A., Kerwin, A. J., Yorkgitis, B. K., Renkosik, J., Allmon, J. C., Habib, J. H., Dennis, J. W. (2018). Reassessing the utility of CT angiograms in penetrating injuries to the extremities. Surgery, 163 (2), 419–422. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2017.09.019
- Polishchuk, M. Ye., Starcha, V. I., Slynko, Ye. I., Zavalniuk, A. Kh. (2005). Vohnepalni ushkodzhennia tsentralnoi nervovoi systemy. Ternopil: TDMU: Ukrmedknyha, 184.
- Alam, H. B., DiMusto, P. D. (2015). Management of Lower Extremity Vascular Trauma. Current Trauma Reports, 1 (1), 61–68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40719-014-0007-2
- Michaud, K., Grabherr, S., Lesta, M. del M., Augsburger, M., Doenz, F., Mangin, P. (2012). Ruptured pseudo-aneurysm of a femoral artery in a drug abuser revealed by post-mortem CT angiography. International Journal of Legal Medicine, 127 (4), 819–823. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-012-0803-6
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mykola Rudenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.
Authors, who are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. The authors reserve the right to authorship of the work and pass the first publication right of this work to the journal under the terms of a Creative Commons CC BY, which allows others to freely distribute the published research with the obligatory reference to the authors of the original work and the first publication of the work in this journal.
2. The authors have the right to conclude separate supplement agreements that relate to non-exclusive work distribution in the form in which it has been published by the journal (for example, to upload the work to the online storage of the journal or publish it as part of a monograph), provided that the reference to the first publication of the work in this journal is included.








