Investigating the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical device strategy and firm performance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2022.267191Keywords:
COVID-19 pandemic, economic effects, health care, medical device strategy, firm performanceAbstract
The object of study is the importance of medical technology and healthcare delivery in the COVID-19 pandemic.
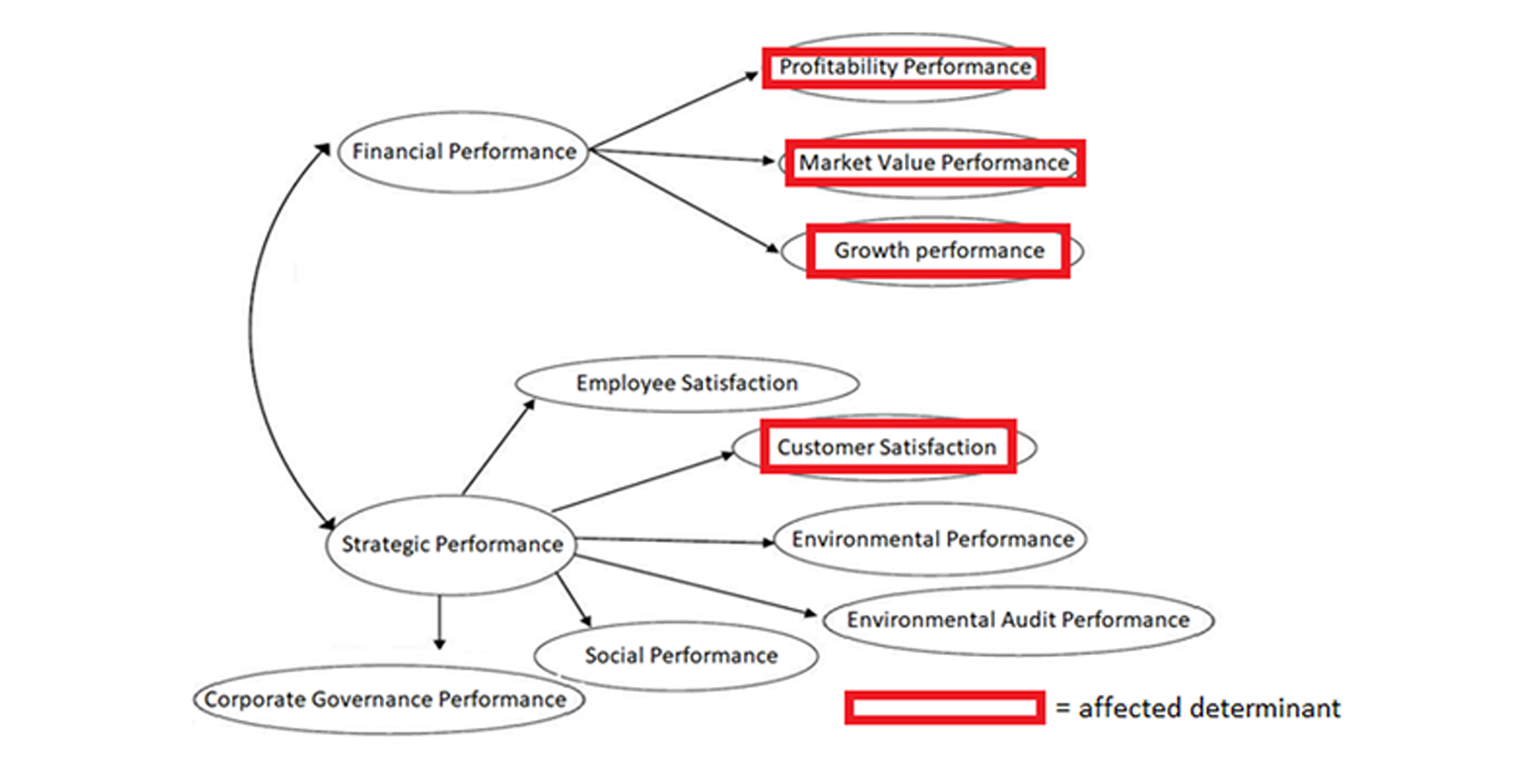
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to the business, healthcare, and societal landscape. The changes have had varying effects on key industries, demanding them to realign to fit new pandemic-imposed environmental conditions. This study seeks to investigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical device strategy and firm performance of company X, and to provide recommendations and insights on strategies to ensure continuity post-pandemic. A qualitative analysis of the results from nine interviews with associates regarding the effects of COVID-19 on firm performance and strategy at company X was explored. The findings from a thematic analysis of the interview data are reported and related to the study's research objectives. Findings showed that the COVID-19 pandemic forced company X to adjust its strategy to align it with the changing environment. However, the data showed that the unknown nature and uncertainty of the COVID-19 pandemic environment meant that the realignment of strategy to the prevailing dynamics was unique. This study's key findings indicate that COVID-19 strongly influenced financial performance, which influenced firm performance significantly. In addition, financial performance measures were found to have more impact than non-financial performance measures such as strategic performance. The main recommendation emanating from the study was to improve the organization’s agility, versatility, and speed. This would be achieved through simplifying processes, streamlining decision-making, and enhancing speed in the market. Agility and versatility are necessary to overcome or take advantage of new developments from the pandemic and post-pandemic environment.
This research study can assist medical enterprises in other countries to stream their services and align strategy to meet the dynamic environment caused by the COVID-19.
Supporting Agency
- Presentation of research in the form of publication through financial support in the form of a grant from SUES (Support to Ukrainian Editorial Staff).
References
- Hatefi, S., Smith, F., Abou-El-Hossein, K., Alizargar, J. (2020). COVID-19 in South Africa: lockdown strategy and its effects on public health and other contagious diseases. Public Health, 185, 159–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2020.06.033
- Johnson, T., Van Biesen, T. (2020). Medtech: The Post–COVID-19 Growth Strategy. Bain. Available at: https://www.bain.com/insights/medtech-the-post-COVID-19-growth-strategy/ Last accessed: 05.03.2022
- South Africa – Healthcare: Medical Devices and Pharmaceuticals (2021). International Trade Administration. Available at: https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/south-africa-healthcare-medical-devices-and-pharmaceuticals Last accessed: 12.02.2022
- Abutabenjeh, S., Jaradat, R. (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36 (3), 237–258. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0144739418775787
- Cirera, X., Cruz, M., Grover, A., Iacovone, L., Medvedev, D., Pereira-Lopez, M., Reyes, S. (2021). Firm Recovery during COVID-19: Six Stylized Facts. Washington: World Bank. doi: https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-9810
- Alharahsheh, H. H., Pius, A. (2020). A review of key paradigms: Positivism VS interpretivism. Global Academic Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 2 (3), 39–43.
- Anakpo, G., Mishi, S. (2021). Business response to COVID-19 impact: Effectiveness analysis in South Africa. The Southern African Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management, 13 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.4102/sajesbm.v13i1.397
- Banerjee, I., Robinson, J., Sathian, B., Van Teijlingen, E. R. (2020). South Africa and its COVID-19 prohibition predilection. Nepal Journal of Epidemiology, 10 (3), 874–877. doi: https://doi.org/10.3126/nje.v10i3.31543
- Antonini, M.-J., Plana, D., Srinivasan, S., Atta, L., Achanta, A., Yang, H. et al. (2021). A Crisis-Responsive Framework for Medical Device Development Applied to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in Digital Health, 3. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2021.617106
- Aspers, P., Corte, U. (2019). What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research. Qualitative Sociology, 42 (2), 139–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11133-019-9413-7
- Atmowardoyo, H. (2018). Research Methods in TEFL Studies: Descriptive Research, Case Study, Error Analysis, and R & D. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 9 (1), 197–204. doi: https://doi.org/10.17507/jltr.0901.25
- Gerald, E., Obianuju, A., Chukwunonso, N. (2020). Strategic agility and performance of small and medium enterprises in the phase of Covid-19 pandemic. International Journal of Financial, Accounting, and Management, 2 (1), 41–50. doi: https://doi.org/10.35912/ijfam.v2i1.163
- About BD – BD (2022). BD. Available at: https://www.bd.com/en-mena/about-bd Last accessed: 15.10.2022
- Castleberry, A., Nolen, A. (2018). Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: Is it as easy as it sounds? Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 10 (6), 807–815. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cptl.2018.03.019
- Akhigbe, E. A., Onuoha, B. (2019). Strategic Agility and Organizational Resilience of Food and Beverage Firms in Rivers State. Nigeria. Available at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Strategic-Agility-and-Organizational-Resilience-of-Akhigbe-Onuoha/84b9ed7bf0a3a2f56740a2fea41a4c84752c551d
- Craven, M., Liu, L., Mysore, M., Wilson, M. (2020). COVID-19: Implications for business. Vol. 8. McKinsey & Company.
- Dolgorukov, D. (2021). Council Post: Thriving Post-Pandemic: A Strategic Cost Reduction. Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesfinancecouncil/2021/01/20/thriving-post-pandemic-a-strategic-cost-reduction/ Last accessed: 20.06.2022
- Medical Devices Market Size, Share, Trends | Analysis, 2028 (2021). Fortune Business Insights. Available at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/medical-devices-market-100085 Last accessed: 05.05.2022
- Bell, E., Bryman, A., Harley, B. (2019). Business Research Methods. Oxford: Oxford university press.
- Bhorat, H., Köhler, T., Oosthuizen, M., Stanwix, B., Steenkamp, F., Thornton, A. (2020). The Economics of COVID-19 in South Africa: Early Impressions, No. Working Paper 202004. Development Policy Research unit. Cape Town: University of Cape Town.
- South Africa’s office and work-from-home plans have changed for 2022 (2021). Businesstech. Available at: https://businesstech.co.za/news/business/545052/south-africas-office-and-work-from-home-plans-have-changed-for-2022/ Last accessed: 07.05.2022
- Jackson, J. K., Weiss, M. A., Schwarzenberg, A. B., Nelson, R. M., Sutter, K. M., Sutherland, M. D. (2021). Global Economic Effects of COVID-19, No. R46270. Congressional Research Service.
- Ghemawat, P. (2016). Evolving Ideas about Business Strategy. Business History Review, 90 (4), 727–749. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007680516000702
- Ellul, A., Erel, I., Rajan, U. (2020). The COVID-19 Pandemic Crisis and Corporate Finance. The Review of Corporate Finance Studies, 9 (3), 421–429. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/rcfs/cfaa016
- Overview of the Health Technology Sector in South Africa: Opportunities for Collaboration. No. RVO-053-2021/RP-INT (2021). Netherlands Enterprise Agency. Prinses Beatrixlaan.
- Arndt, C., Davies, R., Gabriel, S., Harris, L., Makrelov, K., Modise, B., Robinson, S. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on the South African economy. Southern Africa-Towards Inclusive Economic Development Working Paper, Vol. 111.
- Gartner, E. (2020). Employees Likely to Work Remotely Post COVID-19. Gartner. Available at: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2020-04-14-gartner-hr-survey-reveals-41--of-employees-likely-to- Last accessed: 14.02.2022
- Basias, N., Pollalis, Y. (2018). Quantitative and qualitative research in business & technology: Justifying a suitable research methodology. Review of Integrative Business and Economics Research, Society of Interdisciplinary Business Research, 7, 91–105.
- Donthu, N., Gustafsson, A. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 on business and research. Journal of Business Research, 117, 284–289. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.008
- Golubeva, O. (2021). Firms’ performance during the COVID-19 outbreak: international evidence from 13 countries. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 21 (6), 1011–1027. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/cg-09-2020-0405
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Buhlebenkosi Lunga Msweli, Muntuwenkosi Chili, Jeremiah Madzimure

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







