Interconnections assessment of banking capitalization with macroeconomic stability, including corruption and shadow economy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2023.286657Keywords:
macroeconomic stability, capitalization, banking system, corruption, shadow economy, canonical analysisAbstract
The research focuses on bank capitalization and macroeconomic stability, including corruption and the shadow economy. A well-capitalized banking system and a low corruption level are important for maintaining macroeconomic stability and reducing the size of the shadow economy. The paper is aimed at assessing the relationship between bank capitalization and macroeconomic stability, which includes corruption and shadow economy through canonical analysis. The research is conducted on the basis of financial and economic reporting of 35 countries with different levels of socio-economic development during 2010–2021 based on data from the World Bank and the European Central Bank. The main input blocks macroeconomic stability – corruption – shadow economy are characterized.
During the research, the following tools were used:
– methods of grouping, analysis and comparison in determining the characteristics of the elements of the chain «level of capitalization of the banking system – macroeconomic stability – corruption – shadow economy»;
– factor analysis by applying the method of principal components in the selection of statistically significant indicators of the bank capitalization level and macroeconomic stability.
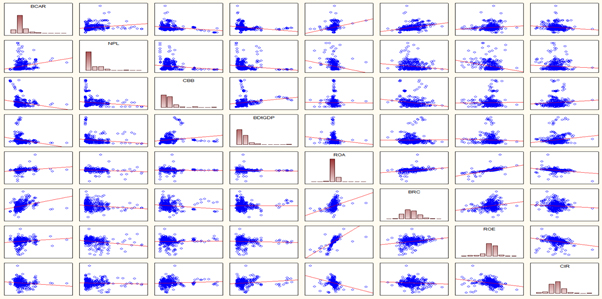
The quantitative assessment of the bank capitalization level revealed the following dependencies: there is a strong correlation between return on assets and the level of non-performing loans, return on assets and return on equity. Using the principal components method, the following statistically significant indicators of macroeconomic stability were identified: GDP, Gini index, corruption perception index, corruption control index, and political stability index.
Research, based on the canonical analysis, determined that 71.1% of changes in macroeconomic stability indicators are explained by fluctuations in the level of bank capitalization. The level of non-performing loans has a negative impact on macroeconomic stability, while the volatility of return on assets and return on equity has a greater positive impact on the development of the country's economy.
The obtained results can be used by banks in the development of their resource and management policies, in the analysis of the volatility of capitalization level, by state bodies in the development of national policies of the country's economic development.
Supporting Agency
- The work was carried out within the framework of the research topics «Data-Mining for countering cyber fraud and legalization of criminal income in the conditions of digitalization of the financial sector of the economy of Ukraine» (0121U100467) and «Modeling of the mechanisms of de-shadowing and de-corruption of the economy to ensure national security: the impact of the transformation of financial behavioral patterns» (state registration number 0122U000783).
References
- Leading banks in Europe as of December 31, 2022, by market capitalization. (2022). Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/382818/leading-banks-in-europe-by-market-capitalization/ Last accessed: 27.06.2023
- Yaki krainy maiut naibilshyi pokaznyk VVP: top-50 za 2021 rik (2021). Apostrof: Ekonomika. Available at: https://apostrophe.ua/ua/news/economy/2021-12-27/u-kakih-stran-samyiy-bolshoy-pokazatel-vvp-top-50-za-2021-god/254155 Last accessed: 27.06.2023
- Ohorodnyk, V. V. (2017). Development of modern ukrainian banking system. Problemy systemnoho pidkhodu v ekonomitsi, 6 (62), 112–117.
- Campbell, G., Coyle, C., Turner, J. D. (2016). This time is different: Causes and consequences of British banking instability over the long run. Journal of Financial Stability, 27, 74–94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfs.2016.09.007
- Clancy, D., Merola, R. (2017). Countercyclical capital rules for small open economies. Journal of Macroeconomics, 54, 332–351. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmacro.2017.04.009
- Stelmakh, V. S. (2001). Entsyklopediia bankivskoi sppavy Ukpainy. Kyiv: Molod: In Yupe, 680.
- Medina, L., Schneider, F. (2018). Shadow Economies Around the World: What Did We Learn Over the Last 20 Years? IMF Working Paper. Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WP/Issues/2018/01/25/Shadow-Economies-Around-the-World-What-Did-We-Learn-Over-the-Last-20-Years-45583
- Cavallaro, E., Maggi, B. (2016). State of confidence, overborrowing and macroeconomic stabilization in out-of-equilibrium dynamics. Economic Modelling, 59, 210–223. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2016.06.015
- Bain, J. S. (1941). The Profit Rate as a Measure of Monopoly Power. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 55 (2), 271. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/1882062
- Chen, S.-H. (2018). A note on nominal gdp targeting and macroeconomic (in)stability. Macroeconomic Dynamics, 23 (8), 3483–3508. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/s1365100518000111
- Switzerland: Macroeconomic Country Outlook (2022). GlobalData. Available at: https://www.globaldata.com/data-insights/macroeconomic/switzerland-macroeconomic-country-outlook/
- Luxembourg: Macroeconomic Country Outlook (2022). GlobalData. Available at: https://www.globaldata.com/data-insights/macroeconomic/luxembourg-macroeconomic-country-outlook/
- World Happiness Report 2023. Available at: https://worldhappiness.report/ed/2023/ Last accessed: 28.06.2023
- Goals of Sustainable Development (2023). United Nations. Available at: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal1 Last accessed: 10.06.2023
- DataBank (2021). World Bank. Available at: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators#
- Diwan, I., Haidar, J. I. (2020). Political Connections Reduce Job Creation: Firm-level Evidence from Lebanon. The Journal of Development Studies, 57 (8), 1373–1396. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00220388.2020.1849622
- Corruption perceptions index (2021). Transparency international. Available at: https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi/2021
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ірина Вікторівна Діденко, Аліна Юріївна Єфіменко

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







