Development of a multi-criteria destruction management model for a better urban transport system quality
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2023.293203Keywords:
disturbance management, service quality, customer satisfaction, urban transit, urban bus operationsAbstract
The object of the research is the urban transport quality. The problem to be solved in the course of the study to optimize current planning systems while reducing human impact on managing daily disruptions that affect urban transport quality and citizen well-being. This will allow all buses to run on time and all users to travel in good conditions. This study aims to address the most critical problems of the growing demand for public transportation, the inability to meet these demands, and the approved ineffectiveness of existing planning.
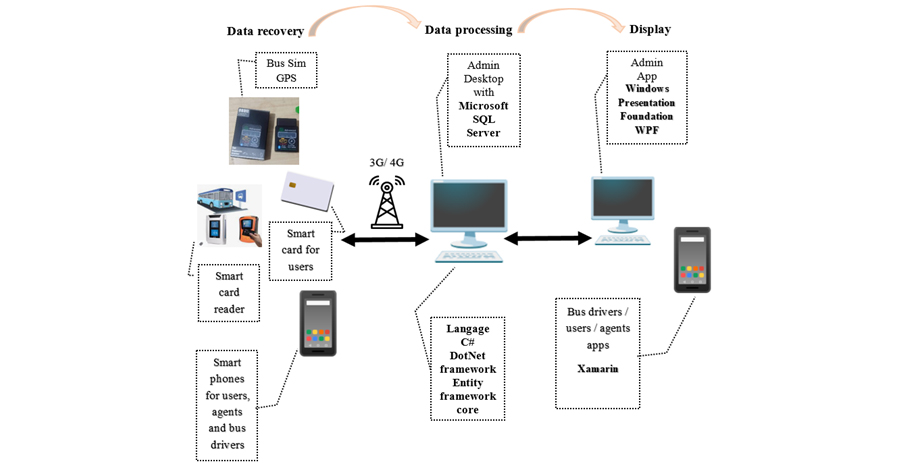
In the course of the research, it is proposed to apply a model for managing daily disturbances that used a developed algorithm based on four major aspects. These aspects include admitting all actors into the system, collecting real-time data, processing data to manage their exploitation and destruction as quickly as possible, and even achieving an ideal operational strategy to handle potential disruptions to the system.
Authors’ proposal for achieving this goal involves two types of hardware and software architectures, taking into consideration the use of modern technological innovations and their potential application. While ensuring a good flow of information, which contributes greatly to the proper functioning of the network and even to the proper management of disturbances in real-time. To validate this work, it is possible to simulate an application of this model on an existing situation of a transport line in the city of Constantine (Algeria), already studied in a previous study to see the evolution of the situation in terms of quality reflected by the journey time.
As a result of the research, it is shown that positive feedback and improvement were observed after the first simulation of the application. This result only encourages the application of this proposed approach, which could ensure a better quality of service offered to the users. In the future, the application of this proposed approach could be the revolution of the field of urban transport in Algeria, which is the pillar of the viability, productivity, and efficiency of a city and the well-being of the citizens.
Supporting Agency
- Presentation of research in the form of publication through financial support in the form of a grant «Scientific Developments Applicable to the Reconstruction of Ukraine» from the publisher TECHNOLOGY CENTER PC (Kharkiv, Ukraine).
References
- Fouzia, A., Baghdad, A., Karim, B. (2009). Vers un système de régulation cellulaire: cas d’un réseau de transport urbain.
- Harishankar, C. V., Desai, Y., Dosani, P., Halbe, A. (2020). Optimal Allocation and Scheduling of Buses. 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), 290–296. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/iciccs48265.2020.9120910
- Wagale, M., Singh, A. P., Sarkar, A. K., Arkatkar, S. (2013). Real-time Optimal Bus Scheduling for a City Using A DTR Model. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 104, 845–854. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.11.179
- Daftary, K., Kapadia, R., Prajapati, D., Shirole, M. (2018). Routed: A Dynamic Bus Scheduling System. 2018 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI). doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ssci.2018.8628885
- Hans, E. (2015). Modélisation des lignes de bus pour la prévision temps réel et la régulation dynamique. École Nationale des Travaux Publics de l'État.
- Stéphan, M. (2015). Fiabilité du temps de transport: Mesures, valorisation monétaire et intégration dans le calcul économique public. Université Montpellier.
- Fan, W., Gurmu, Z. (2015). Dynamic Travel Time Prediction Models for Buses Using Only GPS Data. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 4 (4), 353–366. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s2046-0430(16)30168-x
- Saadi, A., Sahnoune, T. (2019). Le problème de la circulation et du stationnement dans le centre-ville de Constantine. Synthèse: Revue des Sciences et de la Technologie, 25 (1), 45–6.
- Beldjoudi, I. R. B., Labii, B. (2012). Constantine: ville congestionnee par les transports urbains. Sciences & Technologie. D, Sciences de la terre, 41–49.
- Asgari, F., Gauthier, V., Becker, M. (2013). A survey on human mobility and its applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1307.0814. doi: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1307.0814
- .NET documentation. Microsoft Ignite (2022). Available at: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/
- XAMARIN documentation. Microsoft Ignite (2022). Available at: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-gb/xamarin/
- Desktop Guide (WPF. NET). NET documentation. Microsoft Ignite (2022). Available at: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/desktop/wpf/?view=netdesktop-6.0
- Descoimps, É. (2011). Analyse des données issues d’un système de perception par carte à puce d’une société de transport en commun: normalité des déplacements et influence des conditions météorologiques. École Polytechnique de Montréal.
- Kelilba, M., Chaib, R. (2022). Towards better efficient management of urban public transportation by bus in the city of constantine. Transport Problems’2022. Katowice: Silesian University of Technology, 999.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mounira Kelilba, Rachid Chaib, Ion Verzea

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







