Підвищення енергоефективності при лікуванні гіпертермії: розробка та аналіз частотно-перестроюваної L-подібної антени
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.298795Ключові слова:
частота, що переналаштовується, антена, смуга пропусканн, лікування гіпертермії, коефіцієнт підсилення, варатор, коефіцієнт спрямованостіАнотація
Об'єктом дослідження є частотно-перестроювана L-подібна антена. У цій роботі представлено інноваційне дослідження, присвячене розробці та аналізу частотно-перестроюваної L-подібної антени з конкретним застосуванням у лікуванні гіпертермії. Антена, що працює в діапазоні частот від 2,5 до 8 ГГц, використовує варактор для досягнення гнучкості та спрощення конструкції, тим самим зменшуючи кількість компонентів. Конфігурація L-подібної форми, побудована на підкладці Roggers RT5880 (з втратами), забезпечує оптимальну продуктивність. Включення одного варактора, що діє як перехідна ємність, не тільки забезпечує просте налаштування, але й сприяє підвищенню енергоефективності за рахунок зменшення загального енергоспоживання в антенній системі, що переналаштовується. У дослідженні було використано програмне забезпечення CST Microwave Studio для моделювання електромагнітного поля в 3D на основі розв'язувача в часовій області, а валідація проводилася за допомогою розв'язувача в частотній області. Результати моделювання демонструють роботу антени в різних частотних режимах.
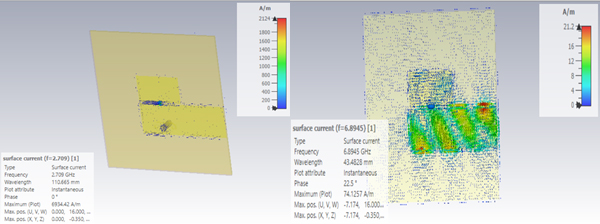
На частоті стану налаштування 2,7 ГГц антена демонструє вражаючий коефіцієнт підсилення 1,905 дБ і спрямованість 7,530 дБ. Аналогічно, на частоті стану налаштування 6,89 ГГц коефіцієнт підсилення становить 6,806 дБ, а коефіцієнт спрямованості – 7,490 дБ. Запропонована L-подібна конструкція антени не тільки демонструє значний потенціал для лікування гіпертермії, дозволяючи цілеспрямоване нагрівання в діапазоні частот від 2,5 до 8 ГГц, але й узгоджується з мультидисциплінарним фокусом медичної науки. Цей внесок відображає прагнення розвивати медичну науку за допомогою оригінальних досліджень, сприянню інноваціям та просуванню енергоефективних рішень, що мають практичне застосування в клінічних умовах.
Посилання
- Naveen Kumar, M., Venkata Narayana, M., Immadi, G., Satyanarayana, P., Navya, A. (2023). Analysis of a low-profile, dual band patch antenna for wireless applications. AIMS Electronics and Electrical Engineering, 7 (2), 171–186. doi: https://doi.org/10.3934/electreng.2023010
- Hum, S. V., Perruisseau-Carrier, J. (2014). Reconfigurable Reflectarrays and Array Lenses for Dynamic Antenna Beam Control: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 62 (1), 183–198. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2013.2287296
- Songnan Yang, Chunna Zhang, Pan, H. K., Fathy, A. E., Nair, V. K. (2009). Frequency-Reconfigurable Antennas for Multiradio Wireless Platforms. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 10 (1), 66–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/mmm.2008.930677
- Aboufoul, T., Parini, C., Chen, X., Alomainy, A. (2013). Pattern-Reconfigurable Planar Circular Ultra-Wideband Monopole Antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 61 (10), 4973–4980. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2013.2274262
- Bayraktar, O., Civi, O. A., Akin, T. (2012). Beam Switching Reflectarray Monolithically Integrated With RF MEMS Switches. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60 (2), 854–862. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2011.2173099
- Christodoulou, C. G., Tawk, Y., Lane, S. A., Erwin, S. R. (2012). Reconfigurable Antennas for Wireless and Space Applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 100 (7), 2250–2261. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2012.2188249
- Haupt, R. L., Lanagan, M. (2013). Reconfigurable Antennas. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 55 (1), 49–61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/map.2013.6474484
- Alhamad, R., Almajali, E., Mahmoud, S. (2023). Electrical Reconfigurability in Modern 4G, 4G/5G and 5G Antennas: A Critical Review of Polarization and Frequency Reconfigurable Designs. IEEE Access, 11, 29215–29233. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3260073
- Ying, K., Gao, Z., Chen, S., Gao, X., Matthaiou, M., Zhang, R., Schober, R. (2024). Reconfigurable Massive MIMO: Harnessing the Power of the Electromagnetic Domain for Enhanced Information Transfer. IEEE Wireless Communications, 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/mwc.014.2200418
- Sexton, C., Kaminski, N. J., Marquez-Barja, J. M., Marchetti, N., DaSilva, L. A. (2017). 5G: Adaptable Networks Enabled by Versatile Radio Access Technologies. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 19 (2), 688–720. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/comst.2017.2652495
- van der Zee, J. (2002). Heating the patient: a promising approach? Annals of Oncology, 13 (8), 1173–1184. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdf280
- Datta, N. R., Rogers, S., Ordóñez, S. G., Puric, E., Bodis, S. (2015). Hyperthermia and radiotherapy in the management of head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 32 (1), 31–40. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/02656736.2015.1099746
- Franckena, M., Lutgens, L. C., Koper, P. C., Kleynen, C. E., van der Steen-Banasik, E. M., Jobsen, J. J., Leer, J. W., Creutzberg, C. L., Dielwart, M. F., van Norden, Y., Canters, R. A. M., van Rhoon, G. C., van der Zee, J. (2009). Radiotherapy and Hyperthermia for Treatment of Primary Locally Advanced Cervix Cancer: Results in 378 Patients. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, 73 (1), 242–250. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.03.072
- Seynhaeve, A. L. B., Amin, M., Haemmerich, D., van Rhoon, G. C., ten Hagen, T. L. M. (2020). Hyperthermia and smart drug delivery systems for solid tumor therapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 163-164, 125–144. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.02.004
- Chang, M., Hou, Z., Wang, M., Li, C., Lin, J. (2020). Recent Advances in Hyperthermia Therapy‐Based Synergistic Immunotherapy. Advanced Materials, 33 (4). doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202004788
- Rajebi, S., Ghobadi, C., Nourinia, J., Mostafapour, E. (2019). SAR Enhancement of Slot Microstrip Antenna by Using Silicon Layer in Hyperthermia Applications. Wireless Personal Communications, 111 (3), 1761–1774. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-019-06955-1
- Chishti, A. R., Aziz, A., Aljaloud, K., Tahir, F. A., Abbasi, Q. H., Khan, Z. U., Hussain, R. (2023). A sub 1 GHz ultra miniaturized folded dipole patch antenna for biomedical applications. Scientific Reports, 13 (1). doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36747-4
- Rodrigo, D., Cetiner, B. A., Jofre, L. (2014). Frequency, Radiation Pattern and Polarization Reconfigurable Antenna Using a Parasitic Pixel Layer. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 62 (6), 3422–3427. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2014.2314464
- Venneri, F., Costanzo, S., Di Massa, G. (2012). Reconfigurable aperture-coupled reflectarray element tuned by single varactor diode. Electronics Letters, 48 (2), 68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2011.3691
- Nguyen-Trong, N., Hall, L., Fumeaux, C. (2016). A Frequency- and Pattern-Reconfigurable Center-Shorted Microstrip Antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 15, 1955–1958. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2016.2544943
- Chen, W., Lv, G., Liu, X., Wang, D., Ghannouchi, F. M. (2020). Doherty PAs for 5G Massive MIMO: Energy-Efficient Integrated DPA MMICs for Sub-6-GHz and mm-Wave 5G Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 21 (5), 78–93. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/mmm.2020.2971183
- Nguyen-Trong, N., Piotrowski, A., Fumeaux, C. (2017). A Frequency-Reconfigurable Dual-Band Low-Profile Monopolar Antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 65 (7), 3336–3343. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2017.2702664
- Chen, G., Yang, X.-L., Wang, Y. (2012). Dual-Band Frequency-Reconfigurable Folded Slot Antenna for Wireless Communications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 11, 1386–1389. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2012.2227293
- Cetiner, B. A., Crusats, G. R., Jofre, L., Biyikli, N. (2010). RF MEMS Integrated Frequency Reconfigurable Annular Slot Antenna. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 58 (3), 626–632. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2009.2039300
- Tu, Z.-H., Li, W.-A., Chu, Q.-X. (2014). Single-Layer Differential CPW-Fed Notch-Band Tapered-Slot UWB Antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 13, 1296–1299. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/lawp.2014.2332355
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Reddy Leelakrishna, Segun Akinola

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








