Substantiation of safety and quality indicators of natural mineral and spring waters in Ukraine for the preparation of food for infants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.314338Keywords:
natural mineral water, spring water, infant food, safety indicators, Directive 2009/40/EC, Directive 2003/40/ECAbstract
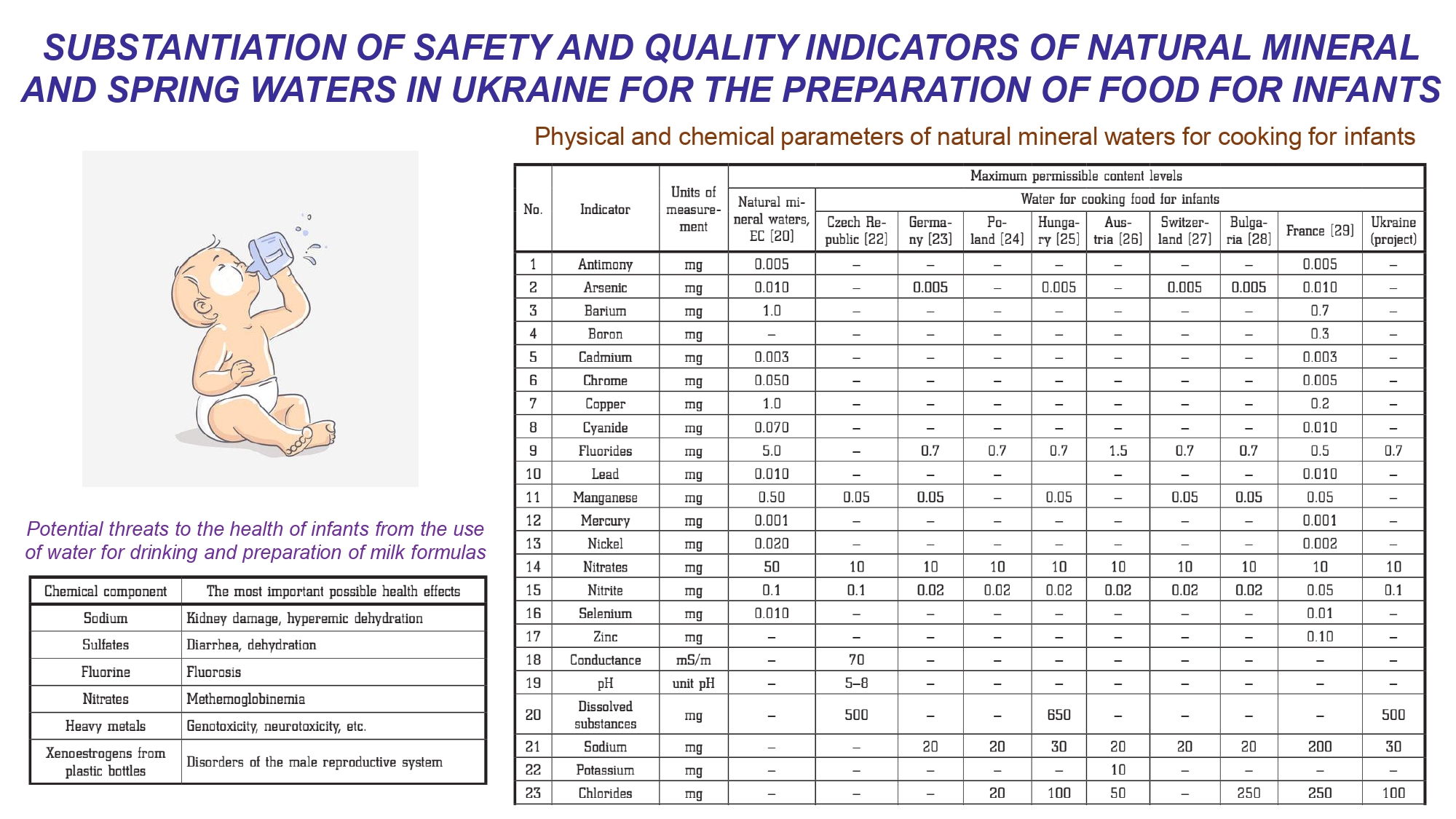
The object of the research is regulatory support for the use of natural mineral waters and spring waters for the preparation of food for infants. Along with drinking water, natural mineral water is used for the preparation of food for infants, which is more protected from contamination. Currently, there are no approved safety parameters for natural mineral waters and spring waters in Ukraine, as well as requirements for markings on packaging or labeling that relate to the suitability of these waters for feeding infants. In this work, based on the results of the analysis of the current legal documents of European countries (Poland, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, France, Germany) on the use of natural mineral waters in the preparation of food for infants, the indicators of the safety and quality of natural mineral and spring waters in Ukraine in the preparation of food are substantiated food for infants. Because of the specific physiological needs of children at an early age, water for cooking is an important factor in their normal psychophysical development. Water for preparing infant food must meet stricter criteria for total mineralization (suggested: ≤500 mg/l), the content of certain macro-components, nitrites (suggested: ≤0.1 mg/l), nitrates (suggested: ≤10 mg/l), ammonium (suggested: ≤0.1 mg/l), fluorides (suggested: ≤0.7 mg/l), sanitary and microbiological indicators (suggested normalization of the indicator of the total microbial number in the finished product). The peculiarities of the technology of industrial packaging of natural mineral waters and spring waters for the preparation of infant food are outlined. These waters are packaged only non-carbonated, without the addition of any preservatives or disinfectants. Packaging of these waters should take place near water points, which should be reliably protected from biological and chemical contamination. The obtained results can be used for the development and approval of a normative legal act in Ukraine on the regulation of the use of natural mineral waters and spring waters for the preparation of infant food.
References
- Pro zatverdzhennia Hihiienichnykh vymoh do vyrobnytstva ta obihu vod pryrodnykh mineralnykh i vod dzherelnykh (2021). Nakaz Ministerstva rozvytku ekonomiky, torhivli ta silskoho hospodarstva Ukrainy No. 741. 12.04.2021. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0657-21
- Directive 2009/54/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 June 2009 (2009). Off J Eur Union, L 164/45-58.
- Kysylevska, A. Yu., Kokhan, S. V., Tsurkan, O. I., Koieva, Kh. O., Slutsenko, D. O. (2022). Normatyvni ta zakonodavchi vymohy do markuvannia fasovanykh mineralnykh vod v Ukraini. Yakist, standartyzatsiia ta metrolohichne zabezpechennia. Kharkiv: UIPA, 69–70.
- Pro osnovni pryntsypy ta vymohy do bezpechnosti ta yakosti kharchovykh produktiv (1997). Zakon Ukrainy No. 771/97-VR. 23.12.1997. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/771/97-%D0%B2%D1%80#top
- Rudnicka, A., Hozyasz, K. K. (2018). Choice of water in healthy baby nutrition – practical aspects. Pediatria i Medycyna Rodzinna, 14 (1), 33–46. https://doi.org/10.15557/pimr.2018.0003
- Jéquier, E., Constant, F. (2009). Water as an essential nutrient: the physiological basis of hydration. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 64 (2), 115–123. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.111
- Feeding the non-breastfed child 6–24 months of age. Meeting report (2004). Department of Child and Adolescent Health and Development, Department of Nutrition for Health and Development. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Benelam, B., Wyness, L. (2010). Hydration and health: a review. Nutrition Bulletin, 35 (1), 3–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-3010.2009.01795.x
- Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for water (2010). EFSA Journal, 8 (3). https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1459
- Guidelines for drinking-water quality (2017). Geneva: World Health Organization, 631.
- Sevostianova, E. M., Butkova, O. L., Lozhkomoeva, M. M., Remneva, G. A., Khorosheva, E. V. (2011). Otcenka vozmozhnosti primeneniia mineralnoi vody v pitanii detei. Pishchevaia promyshlennost, 38–39.
- Quattrini, S., Pampaloni, B., Brandi, L. M. (2016). Natural mineral waters: chemical characteristics and health effects. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism, 13 (3), 173–180. https://doi.org/10.11138/ccmbm/2016.13.3.173
- Morr, S., Cuartas, E., Alwattar, B., Lane, J. M. (2006). How Much Calcium is in your Drinking Water? A Survey of Calcium Concentrations in Bottled and Tap Water and Their Significance for Medical Treatment and Drug Administration. HSS Journal®: The Musculoskeletal Journal of Hospital for Special Surgery, 2 (2), 130–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-006-9000-9
- Pro zatverdzhennia Derzhavnikh sanіtarnikh norm ta pravil «Gіgіenіchnі vimogi do vodi pitnoi, priznachenoi dlia spozhivannia liudinoiu» (DSanPіN 2.2.4-171-10) (2010). Nakaz MOZ Ukraini No. 400. 12.05.2010. Available at: https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0452-10#Text
- Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding (2003). World Health Organization, and UNICEF. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- Sievers, E. (2005). Nutrient minerals in drinking water: Implications for the nutrition of infants and young children. Nutrients in drinking water. Geneva: World Health Organization, 164–179.
- Report of the Scientific Committee on Food on the Revision of Essential Requirements of Infant Formulae and Follow-on Formulae (2003). SCF/CS/NUT/IF/65, SCF. Scientific Committee on Food.
- Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1996.
- Directive (EU) 2020/2184 (2020). European Parliament and of the Council on the quality of water intended for human consumption. 16.12.2020.
- Commission Directive 2003/40/EC of 16 May 2003 (2003). Off J Eur Union, L 126/34-39.
- Vody mineralni fasovani. Tekhnichni umovy: DSTU 878-93 (1994). Kyiv: Derzhspozhyvstandart Ukrainy, 88.
- Vyhláška č. 275/2004 Sb. (2004). Vyhláška o požadavcích na jakost a zdravotní nezávadnost balených vod a o způsobu jejich úpravy. Available at: https://www.zakonyprolidi.cz/cs/2004-275
- Mineral- und Tafelwasser-Verordnung vom 1. August 1984 (BGBl. I S. 1036) die zuletzt durch Artikel 2 der Verordnung vom 20. Juni 2023 (BGBl. 2023 I Nr. 159) geändert worden ist (2023). Available at: https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/min_tafelwv/BJNR010360984.html
- Rozporządzenie Ministra Zdrowia z dnia 31 marca 2011 r. w sprawie naturalnych wód mineralnych, wód źródlanych i wód stołowych (2011). Dziennik Ustaw, 85, 466. Available at: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20110850466/O/D20110466.pdf
- 65/2004. (IV. 27.) FVM–ESZCSM–GKM együttes rendelet a természetes ásványvíz, a forrásvíz, az ivóvíz, az ásványi anyaggal dúsított ivóvíz és az ízesített víz palackozásának és forgalomba hozatalának szabályairól (2003). Available at: https://net.jogtar.hu/jogszabaly?docid=a0400065.fvm
- Verordnung der Bundesministerin für Frauenangelegenheiten und Verbraucherschutz über natürliche Mineralwässer und Quellwässer (Mineralwasser- und Quellwasserverordnung) (CELEX-Nr.: 380L0777, 396L0070) StF: BGBl. II Nr. 309/199.
- Verordnung des EDI über Getränke vom 16. Dezember 2016 (Stand am 1. Juli 2020) 817.022.12 (2016). Available at: https://www.fedlex.admin.ch/eli/cc/2017/220/de
- Naredba za iziskvaniiata km butiliranite naturalni mineralni, izvorni i trapezni vodi, prednaznacheni za piteini tceli (2004). Prieta s PMS No. 178. 23.07.2004. Available at: https://lex.bg/laws/ldoc/2135488818
- Arrêté du 14 mars 2007 relatif aux critères de qualité des eaux conditionnées, aux traitements et mentions d'étiquetage particuliers des eaux minérales naturelles et de source conditionnées ainsi que de l'eau minérale naturelle distribuée en buvette publique (2007). NOR: SANP0721398A. Available at: https://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/loda/id/LEGIARTI000023453984/2011-01-09/
- Informe del Comité Científico de la Agencia Española de Consumo, Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AECOSAN) sobre los criterios necesarios para poder efectuar en las aguas minerales naturales la mención «indicada para la preparación de alimentos infantiles» (2014). Número de referencia: AECOSAN-2014-004. Revista del comité científico, 20, 11–43. Available at: https://www.aesan.gob.es/AECOSAN/docs/documentos/seguridad_alimentaria/evaluacion_riesgos/informes_comite/AGUAS_ALIMENTOS_INFANTILES.pdf
- Woś, H., Weker, H., Jackowska, T. et al. (2010). Stanowisko Grupy Ekspertów w sprawie zaleceń dotyczących spożycia wody i innych napojów przez niemowlęta, dzieci i młodzież. Stand Med Interna, 1, 7–15.
- Halushko, O., Bolyuk, M. (2018). Correction of sodium exchange disorders in intensive care patients: old methods and modern approaches. Emergency medicine, 2.89, 29–36. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0586.2.89.2018.126599
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Alona Kysylevska, Ihor Prokopovych, Svitlana Kokhan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







