Control of boiler equipments during starting and stopping periods and methods of optimizing these processes through the use of a decision support system with a machine vision subsystem
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.319820Keywords:
decision support system, machine vision, steam boiler, production equipment, control procedures, manual equipmentAbstract
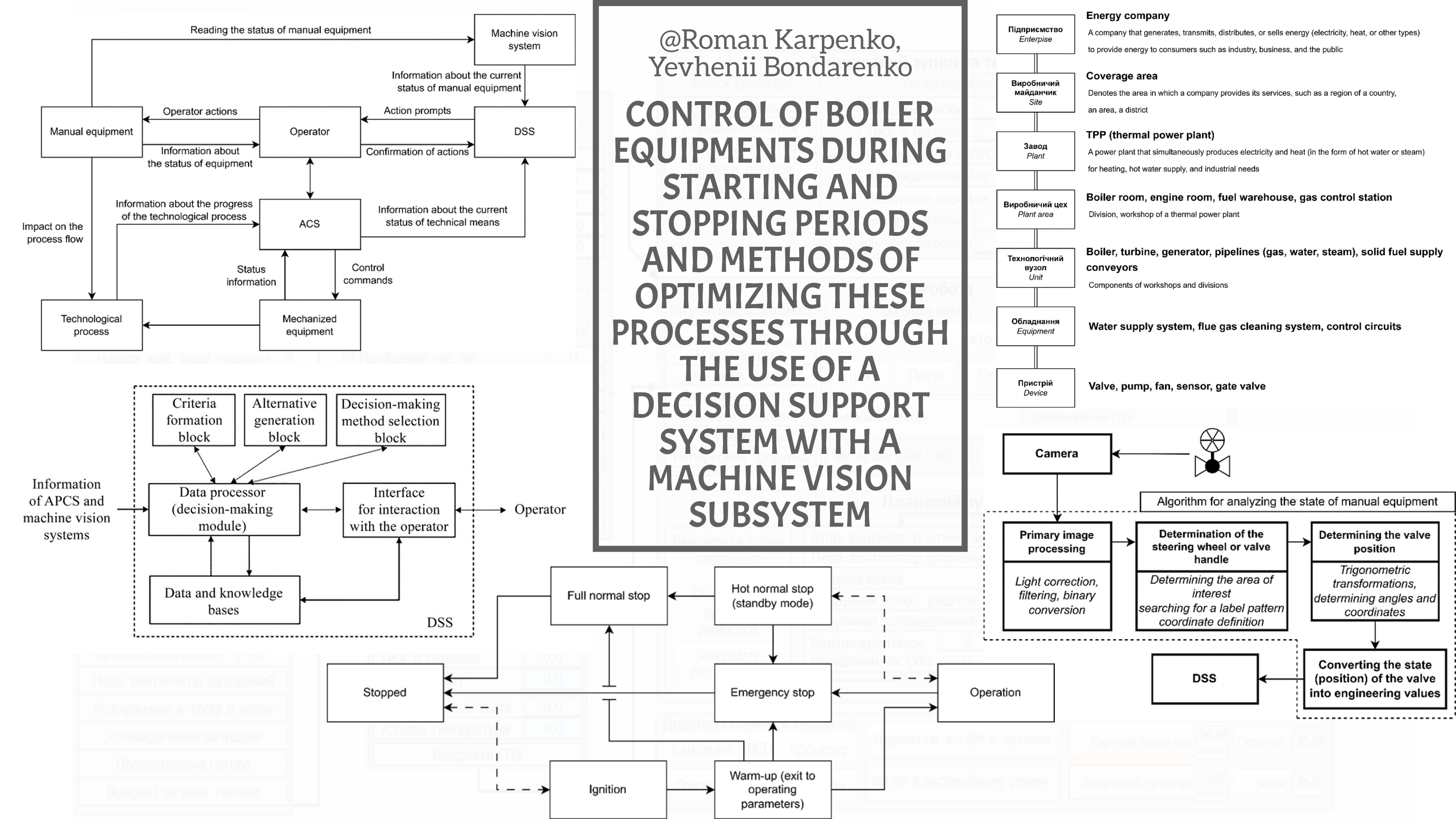
The object of research is the automation of starting and stopping steam power boilers. The problem of automating the starting and stopping of steam power boilers is important for thermal power plants (TPP) and industrial enterprises. These processes require significant efforts from service personnel due to their complexity, partial automation and the need to take into account the human factor. It is emphasized that full automation of starting and stopping steam boilers is economically impractical, since most of the time the boilers operate in continuous automatic operations and only a short time is allocated for periodic procedures, which are mostly performed manually. However, the significant impact of the human factor at critical stages of boiler operation requires the introduction of new technologies that can increase the efficiency and safety of such operations. The study outlines the main challenges associated with steam boiler control and proposes new approaches to solving these problems. It is noted that operators often perform actions during boiler starting and stopping based on instructions or their own experience. This knowledge can be formalized and integrated into the database of an expert decision support system (DSS), which automates some of the manual actions and helps operators avoid errors. For this purpose, it is proposed to use machine vision subsystems that can validate the operator's actions, analyze the interaction of personnel with the equipment and signal about possible incorrect actions. This approach can not only reduce the risk of errors due to fatigue or stress of personnel, but also make the starting and stopping processes safer and more efficient.
It is proposed to integrate machine vision subsystems to obtain information that is difficult to measure by traditional means, in particular, regarding the operator's interaction with manual mechanisms or its presence at the workplace. The structure of the proposed DSS also takes into account the possibility of transferring knowledge bases between different objects, which ensures the scalability and adaptability of the system. The implementation of such a system is based on modern international automation standards, in particular ISA-88, ISA-106 and VDI/VDE/VDMA 2632.
References
- Kochanek, S., Xing, J., Yilmaz, A., Edward Gibson, G., Tang, P. (2022). Using Computer Vision to Reduce Human Errors of Operating on the Wrong Control Valves in Nuclear Power Plants. Human Factors in Energy: Oil, Gas, Nuclear and Electric Power. https://doi.org/10.54941/ahfe1002217
- Mo, K., Lee, S. J., Seong, P. H. (2007). A neural network based operation guidance system for procedure presentation and operation validation in nuclear power plants. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 34 (10), 813–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2007.04.008
- Sethu, M., Titu, N., Hu, D., Madadi, M., Coble, J., Boring, R. et al. (2021). Using Artificial Intelligence to Mitigate Human Factor Errors in Nuclear Power Plants: A Review. 12th Nuclear Plant Instrumentation, Control and Human-Machine Interface Technologies (NPIC&HMIT 2021), 129–141. https://doi.org/10.13182/t124-34339
- Sun, Z., Xing, J., Tang, P., Cooke, N. J., Boring, R. L. (2020). Human reliability for safe and efficient civil infrastructure operation and maintenance – A review. Developments in the Built Environment, 4, 100028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dibe.2020.100028
- Shi, Y., Li, M., Wang, J., Wen, J., Cui, F., Qiao, G. (2022). Prediction of Ash Deposition on Heating Surfaces of Coal-fired Power Plant Boiler based on Dynamic Neural Network. 2022 34th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), 779–783. https://doi.org/10.1109/ccdc55256.2022.10034385
- Levchenko, O. I., Sidletskyi, V. M. (2014). Osnovy avtomatyzatsiyi teploenerhetychnykh protsesiv ta ustanovok. Kyiv: NUKhT, 227.
- Pupena, O., Klymenko, O., Shyshak, A., Mirkevych, R. (2019). Standarty intehruvannia system keruvannia pidpryiemstvom ta vyrobnytstvom: suchasnyi stan ta perspektyvy v Ukraini. Standart MEK 62264. Kyiv. Available at: https://tk185.appau.org.ua/whitepapers/62264.pdf
- Wilkins, M., Tennant, M. (2015). ISA-106 and concepts of procedural automation. InTech. Available at: https://web-material3.yokogawa.com/InTech_ISA106_ePrints.pdf
- Bondarenko, Ye. A. (2024). Avtomatyzatsiya kontroliu stanu ruchnykh mekhanichnykh ventyliv za dopomohoiu Python ta biblioteky kompiuternoho zoru OpenCV. Materialy XI Mizhnarodnoi naukovo-tekhnichnoi Internet-konferentsiyi “Suchasni metody, informatsiyne, prohramne ta tekhnichne zabezpechennia system keruvannia orhanizatsiyno-tekhnichnymy ta tekhnolohichnymy kompleksamy”. Kyiv: NUKhT, 191–192. Available at: http://kist.ntu.edu.ua/konferencii/53_konf_2024.pdf
- Ladaniuk, A. P., Smitiukh, Ya. V., Vlasenko, L. O. et al. (2013). Systemnyi analiz skladnykh system upravlinnia. Kyiv: NUKhT, 276.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Roman Karpenko, Yevhenii Bondarenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







