Development of innovation projects based on the synergy TRIZ principle and AI technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.322052Keywords:
innovation project development, TRIZ, artificial intelligence, project management, predictive analytics, decision makingAbstract
The object of the research is a novel development methodology for innovation projects that leverages the power of the synergy principle of the Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ). It integrates artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
The problem addressed in this research is the inefficiency and limitations of traditional methods for development innovation projects, which often fail to comprehensively evaluate their potential, risks, and alignment with future technological trends.
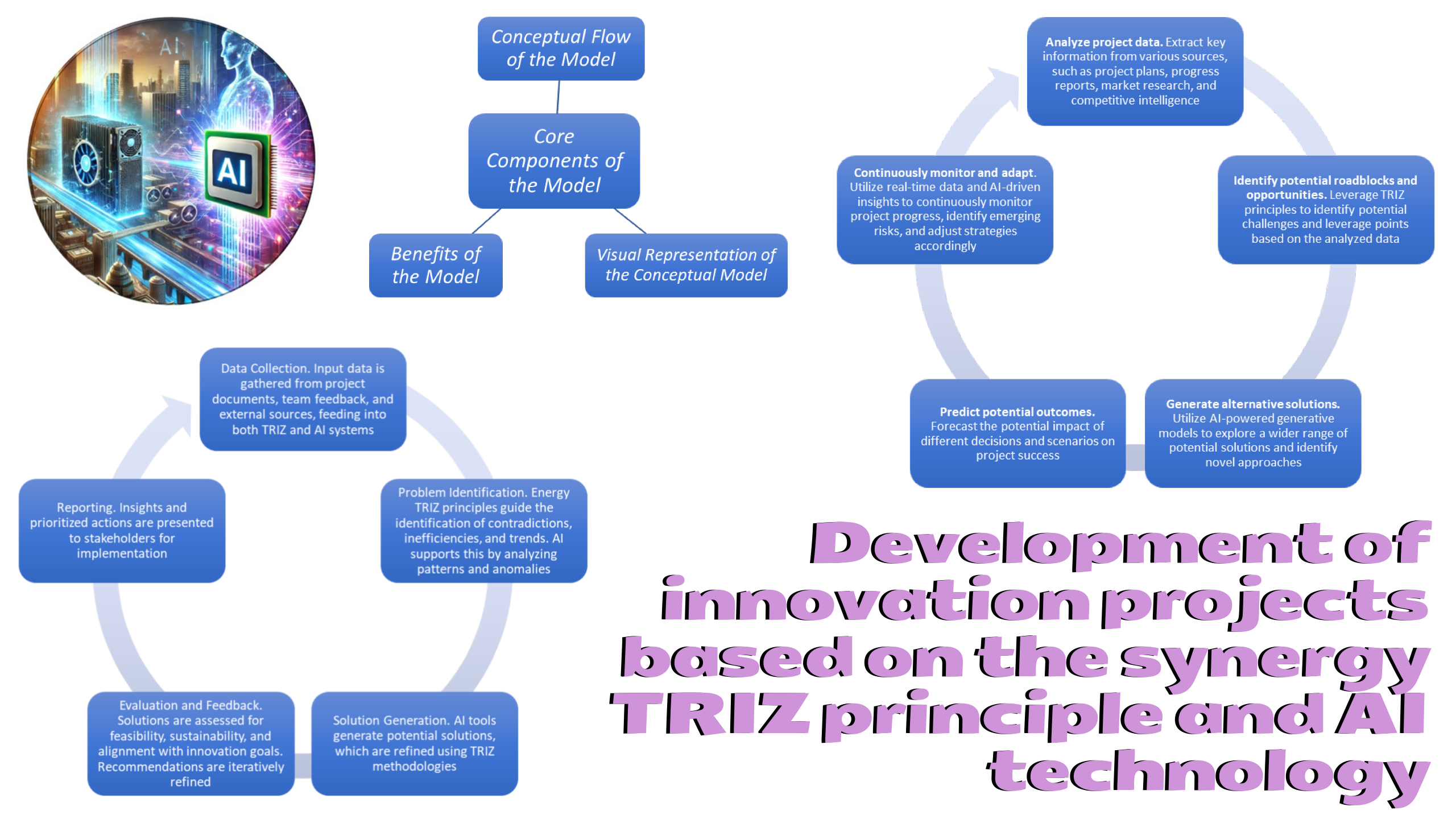
The research results in the synergistic application of TRIZ principles and AI technology for conducting comprehensive audits of innovation projects. By integrating the structured problem-solving framework of TRIZ with the analytical power of AI, a novel approach is proposed to enhance the evaluation and optimization of innovation initiatives. The paper explores how artificial intelligence algorithms can be used to analyze project data and identify potential obstacles and opportunities based on the principles of TEDx. As well as to create alternative solutions and predict possible outcomes, help identify synergies between different project elements and external factors. And to constantly monitor and adapt the innovation process based on real-time data and AI-driven insights.
The difference in the research is the integration of TRIZ principles into auditing innovative projects using AI systems. The presented case showed the effectiveness of the proposed conceptual, mathematical and process models of auditing innovative projects. The master's program in artificial intelligence implemented at the Kyiv National University of Construction and Architecture (Ukraine) was chosen as an example for the case study. The study demonstrates the potential of this audit-integrated approach to improve the success rate of innovation projects by providing more accurate assessments, identifying hidden opportunities, and facilitating proactive decision-making. This research contributes to more effective and successful innovation projects by providing a data-driven and intelligent approach to project development and improvement. Within the framework of the considered case, an assessment of the acceleration of analysis and decision-making processes was carried out using the example of the innovative development program for training masters in artificial intelligence. It was found that the analysis and decision-making processes are implemented 2.68 times faster without loss of decision quality.
References
- Ladewig, G. R. (2007). TRIZ: The Theory of Inventive Problem Solving. The PDMA ToolBook 3 for New Product Development, 3–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470209943.ch1
- Bushuyev, S., Piliuhina, K., Chetin, E. (2023). Transformation of values of the high technology projects from a VUCA to a BANI environment model. Innovative Technologies and Scientific Solutions for Industries, 2 (24), 191–199. https://doi.org/10.30837/itssi.2023.24.191
- Bushuyev, S., Ivko, A. (2024). Construction of models and application of syncretic innovation project management in the era of artificial intelligence. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3 (3 (129)), 44–54. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2024.306436
- Roper, S., Du, J., Love, J. H. (2008). Modelling the innovation value chain. Research Policy, 37 (6-7), 961–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2008.04.005
- Love, J. H., Roper, S. (2009). Organizing innovation: Complementarities between cross-functional teams. Technovation, 29 (3), 192–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2008.07.008
- Rammer, C., Czarnitzki, D., Spielkamp, A. (2008). Innovation Success of Non-R&D-Performers: Substituting Technology by Management in SMEs. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1314246
- Hidalgo, A., Albors, J. (2008). Innovation management techniques and tools: a review from theory and practice. R&D Management, 38 (2), 113–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9310.2008.00503.x
- Hansen, M., Birkinshaw, J. (2007). The innovation value chain. Harvard Business Review. Available at: https://hbr.org/2007/06/the-innovation-value-chain
- Shin, W.-S., Lee, S.-H., Sue, H.-J. (2024). Fostering Tech Innovation. Tehnički Glasnik, 18 (4), 588–597. https://doi.org/10.31803/tg-20231212081808
- Särner, E., Yström, A., Lakemond, N., Holmberg, G. (2024). Prospective Sensemaking in the Front End of Innovation of AI Projects. Research-Technology Management, 67 (4), 72–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2024.2350407
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sergey Bushuyev, Natalia Bushuyeva, Andrii Puziichuk, Denis Bushuiev

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







