Integration of contact network and autonomous trolleybuses for improving the city's transport system
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.340517Keywords:
autonomous trolleybuses, station, pantograph, charging, battery, contact network, powerAbstract
The object of the study is the technical characteristics of autonomous trolleybuses and the systems that ensure their uninterrupted power supply.
A key challenge is the dependence of conventional trolleybuses on contact networks, which limits their route versatility, complicates operations in historic city centers, bridge crossings, and regions with underdeveloped infrastructure.
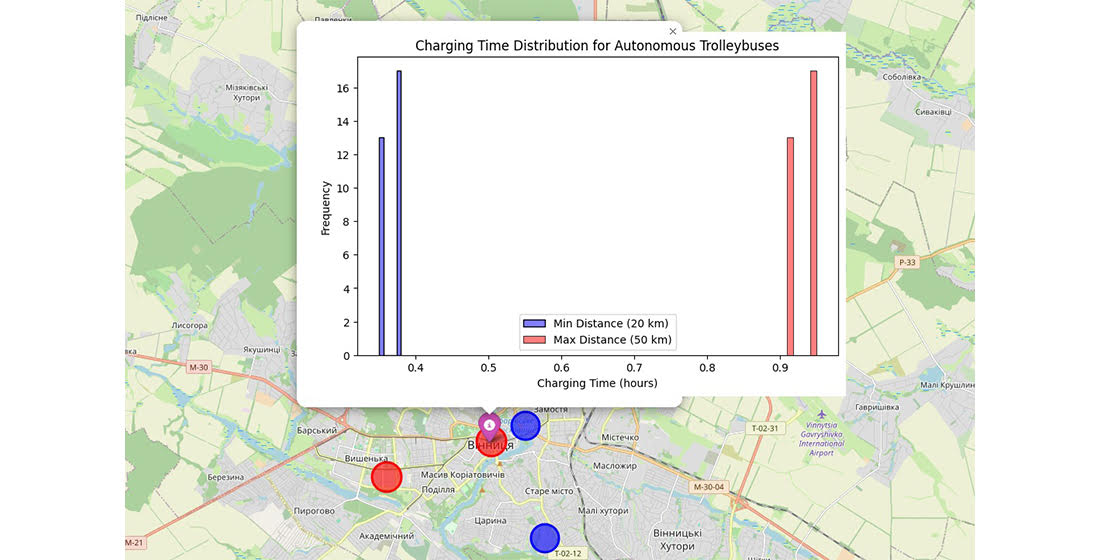
The article examines key technological aspects of autonomous trolleybuses, including types of charging stations (contact, inductive, with pantographs), charging efficiency, energy consumption, and autonomous range. Examples of the implementation of this technology in Ukraine are presented, along with an analysis of charging costs and energy characteristics for runs of 20–50 km. The prospects of using autonomous trolleybuses for optimizing the city transport network, reducing CO₂ emissions, and improving the quality of passenger service are emphasized. Calculations have been made of the energy required for a trolleybus to travel a distance of 20–50 km, taking into account the average energy consumption (1.2–2.0 kWh/km), charging station capacity (up to 100 kW,) and charging efficiency (0.9). Calculations have shown that for an autonomous trolleybus run of 30 km, 45 kWh of energy is required. Modern lithium-ion batteries and charging stations with a capacity of up to 100 kW provide a full charge in 30 minutes. Intermediate charging at stops minimizes contact infrastructure while maintaining transport system flexibility. Autonomous trolleybuses reduce dependence on contact networks, which is especially relevant for bridge crossings with complicated construction or maintenance and historic centers requiring architecture preservation without excess infrastructure. They also significantly reduce CO₂ emissions to promote ecological sustainability and improve urban air quality by lowering pollution and benefiting public health.
References
- Wołek, M., Wolański, M., Bartłomiejczyk, M., Wyszomirski, O., Grzelec, K., Hebel, K. (2021). Ensuring sustainable development of urban public transport: A case study of the trolleybus system in Gdynia and Sopot (Poland). Journal of Cleaner Production, 279, 123807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123807
- Kivekas, K., Lajunen, A., Baldi, F., Vepsalainen, J., Tammi, K. (2019). Reducing the Energy Consumption of Electric Buses With Design Choices and Predictive Driving. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68 (12), 11409–11419. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2019.2936772
- Abdelaty, H., Mohamed, M. (2021). A Prediction Model for Battery Electric Bus Energy Consumption in Transit. Energies, 14 (10), 2824. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14102824
- Xu, H., Tu, R., Li, T., Chen, H. (2023). Interpretable bus energy consumption model with minimal input variables considering powertrain types. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 119, 103742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2023.103742
- Andrusenko, S., Dembitskyi, V., Budnychenko, I., Dykyi, V. (2024). Research on the feasibility of using electric buses on bus and trolleybus routes in cities. Advances in mechanical engineering and transport, 1 (22), 76–88. https://doi.org/10.36910/automash.v1i22.1348
- Yankivskyi, D., Bryzhalov, V., Liahushkin, A. (2019). Power supply sources for autonomous electric vehicles and the effectiveness of their application. Bulletin of Lviv National Agrarian University. Agroengineering Research, 23, 106–116. https://doi.org/10.31734/agroengineering2019.23.106
- Polievoda, Y., Kupchuk, I., Hontaruk, Y., Furman, I., Mytko, M. (2022). Method for determining homogeneity of fine dispersed mixtures based on the software analysis of photo cross-cut of the sample. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny, 1 (11), 111–115. https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2022.11.20
- Borysiuk, D., Spirin, A., Kupchuk, I., Tverdohlib, I., Zelinskyi, V., Smyrnov, Y. et al. (2021). The methodology of determining the place of installation of accelerometers during vibrodiagnostic of controlled axes of wheeled tractors. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny, 1 (10), 46–50. https://doi.org/10.15199/48.2021.10.09
- Kupchuk, I., Burlaka, S., Galushchak, A., Yemchyk, T., Galushchak, D., Prysiazhniuk, Y. (2022). Research of autonomous generator indicators with the dynamically changing component of a two-fuel mixture. Polityka Energetyczna – Energy Policy Journal, 25 (2), 147–162. https://doi.org/10.33223/epj/150746
- Tokarchuk, O., Tokarchuk, D., Mytko, M., Bahrii, V. (2024). Modern innovative technologies and materials for enhancing the efficiency of solar panels. Engineering, Energy, Transport AIC, 1 (124), 140–148. https://doi.org/10.37128/2520-6168-2024-1-16
- New trolleybus line (and thirteen 24-metre double-articulated by Hess) in Bern (2024). Sustainable-bus.com. Available at: https://www.sustainable-bus.com/trolleybus-tramway/new-trolleybus-line-and-thirteen-24-metre-double-articulated-by-hess-in-bern
- Novye investitcii v obshchestvennyi transport: Poznan zakazyvaet 37 elektroavtobusov Solaris (2020). Hevcars.com.ua. Available at: https://hevcars.com.ua/polsha-solaris-poluchaet-zakaz-na-eshhe-37-elektricheskih-avtobusov
- Yutong: the Chinese leader on worldwide expansion (as electric buses gain ground) (2025). Sustainable-bus.com. Available at: https://www.sustainable-bus.com/news/yutong-bus-zhengzhou-electric-bus
- U Vinnytsi planuiut zibraty shche 10 enerhooshchadnykh nyzkopidlohovykh troleibusiv “VinLine” (2023). Vezha.ua. Available at: https://vezha.ua/u-vinnytsi-planuyut-zibraty-shhe-10-energooshhadnyh-nyzkopidlogovyh-trolejbusiv-vinline
- Ponad 70 milioniv hryven vytratiat na novi troleibusy VinLine (2023). Vn.20minut.ua. Available at: https://vn.20minut.ua/Podii/ponad-70-milyoniv-griven-vitratyat-na-novi-troleybusi-vinline-11859875.html
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykola Mytko, Serhii Burlaka, Oleksandr Halushchak, Dmytro Halushchak, Viacheslav Zelinskyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







