Development of a method for state estimation and optimisation of multifactor semi-Markov systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.344494Keywords:
semi-Markov systems, system analysis and optimization, Erlang distribution, probabilistic modelingAbstract
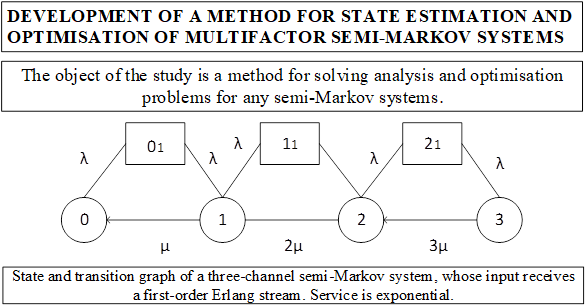
The object of this research is a method for solving problems of analysis and optimization of semi-Markov systems. The importance of this topic is determined by the following circumstances. First, traditional, standard theoretical and practical problems of stochastic system research are solved analytically only for Markov systems for which the laws of distribution of the duration of stay in each state before leaving are exponential. Clearly, this strict requirement is not met for real systems. Second, a general method of analytical study does not exist for many probabilistic systems. Third, only numerical methods for solving such problems are available and feasible. Moreover, in each case, a solution can only be obtained for the specific system under study, operating under specific conditions. Clearly, such a solution is uninformative and practically useless for optimization problems of multifactor systems. In this regard, the study aims to develop a universal method for solving analysis and optimization problems, suitable for any semi-Markov systems. The proposed method for solving the formulated problem solves it in two stages. In the first stage, a matrix of distribution densities is found by processing experimental data, representing the duration of the system's stay in each state before transitioning to another state. It is crucial that the densities be in the Erlang distribution class of some order. These densities are found using the least-squares method, using histograms obtained by processing the experimental data. In the second stage, the resulting distribution densities are used to construct a system of differential equations for the probabilities of the system's stay in each possible state. This constructively utilizes the unique property of Erlang distributions: any Erlang flow is a sifted simplest Poisson flow. Sequentially completing these two stages yields a solution to the problem of studying any probabilistic (semi-Markov) systems. Thus, the method proposed in this paper for solving problems of analysis and optimization of semi-Markov systems is universal.
References
- Grabski, F. (2016). Concept of Semi -Markov Process. Scientific Journal of Polish Naval Academy, 206 (3), 25–36. https://doi.org/10.5604/0860889x.1224743
- Liu, F. (2023). Semi-Markov processes in open quantum systems. II. Counting statistics with resetting. Physical Review E, 108 (6). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.108.064101
- Ranjith, K. R., Gopakumar, B., Nair, S. S. (2024). A Semi-Markovian Analysis of an Inventory Model with Inventory-Level Dependent Arrival and Service Processes. Information Technologies and Mathematical Modelling. Queueing Theory and Applications. Cham: Springer, 118–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-65385-8_9
- Kaalen, S., Nyberg, M., Bondesson, C. (2019). Tool-Supported Dependability Analysis of Semi-Markov Processes with Application to Autonomous Driving. 2019 4th International Conference on System Reliability and Safety (ICSRS). Springer Nature, 126–135. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsrs48664.2019.8987701
- Grabski, F. (2015). Semi-Markov processes: Applications in system reliability and maintenance. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2013-0-14260-2
- Janssen, J., Limnios, N. (Eds.) (1999). Semi-Markov models and applications. Springer, 404. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-3288-6
- Kalisz-Szwedzka, K. (2024). Optimization of Production Processes in the Furniture Industry Using Semi-Markov Models. European Research Studies Journal, XXVII (1), 772–787. https://doi.org/10.35808/ersj/3727
- Wang, J., Miao, Y. (2021). Optimal preventive maintenance policy of the balanced system under the semi-Markov model. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 213, 107690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2021.107690
- Verbeken, B., Guerry, M.-A. (2021). Discrete Time Hybrid Semi-Markov Models in Manpower Planning. Mathematics, 9 (14), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9141681
- Wu, D., Yuan, C., Kumfer, W., Liu, H. (2017). A life-cycle optimization model using semi-markov process for highway bridge maintenance. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 43, 45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.10.038
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lev Raskin, Larysa Sukhomlyn, Viacheslav Karpenko, Dmytro Sokolov, Vitalii Vlasenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







