Research of algorithm for calculating the vector-parametric bispline based on polynomial of the fourth degree
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2016.80457Keywords:
segment of three points and two first derivatives, vector-parametric spline of fourth degreeAbstract
In the course of the audit process of the vector-parametric spline of fourth degree on the basis of a segment of three points and two first derivatives at the end points is easy to see that it cannot be set to the same number of boundary conditions at both ends, as for polynomials of third and fifth degree, because a polynomial of the fourth degree is «unbalanced».
New method is proposed to eliminate these disadvantages in the design of fourth degree splines and bisplines (vector parametric surfaces) based on them.
It is proposed to consider the next variant of polynomial of the fourth degree for bispline design: the endpoints, derivatives in them and another middle point are given.
Based on the proposed functions of the polynomial:
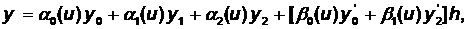
Vector parametric spline of fourth degree on the basis of a segment of three points and two first derivatives is noted:
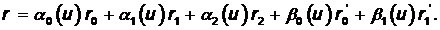
Based on the segment of the fourth degree for the portions of the surface recorded this equation is noted:
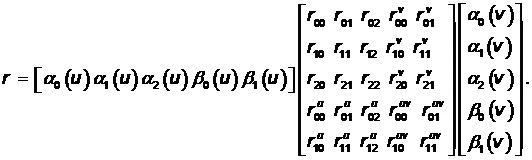
To specify a portion it must have not only first derivatives but also the mixed derivatives at the nodal points.
Based on these formulas, it became possible to write a test program for visualization of bispline (vector parametric surface) fourth degree in the language Auto Lisp in AutoCAD, spline of fourth degree showed good «custom» properties, the surface is adequate to the input data, subjectively nice-looking.
The paper shows the ability of the splines of the fourth degree to give biplane. Due to the peculiarities of their structure (the ability to give an additional medial condition) the proposed curve has an additional possibility of a more correct and adequate to the task of specifying the conditions. The achieved effect (a new polynomial) gives a method the right to life for designing smooth curves and surfaces.
References
- Faux, I. D., Pratt, M. J. (1982). Computational Geometry for Design and Manufacture. Translated from English. Moscow: Mir, 304.
- Zav'ialov, Yu. S., Kvasov, B. I., Miroshnichenko, V. L. (1982). Metody splain-funktsii. Moscow: Nauka, 352.
- Kovtun, A. M. (2004). Polinomialni splainy chetvertoho stepenia. Mizhvidomchyi naukovo-tekhnichnyi zbirnyk «Prykladna heometriia ta inzhenerna hrafika», Vol. 74, 239–243.
- Golovanov, N. N. (2002). Geometricheskoe modelirovanie. Moscow: Izdatel'stvo fiziko-matematicheskoi literatury, 472.
- Badaev, Yu. I., Kovtun, A. M. (2011). Spetsial'nye splainy iz polinomov tret'ei, chetviortoi i piatoi stepenei v geometricheskom modelirovanii. Odessa: Feniks, 316.
- Badaev, Yu. I., Kovtun, A. M. (2003). Vektorno-parametrychni sehmenty, poverkhni ta tila za intsydentnymy z nymy tochkamy. Pratsi Tavriiskoi derzhavnoi ahrotekhnichnoi akademii. Prykladna heometriia ta inzhenerna hrafika, Vol. 4, № 18, 37–40.
- Csurcsia, P. Z., Schoukens, J., Kollar, I. (2012, May). Identification of time-varying systems using a two-dimensional B-spline algorithm. 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Available: https://doi.org/10.1109/i2mtc.2012.6229494
- Rogers, D., Adams, J. (2001). Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics. Translated from English. Moscow: Mir, 604.
- Yakunin, V. I. (1980). Geometricheskie osnovy avtomatizirovannogo proektirovaniia tehnicheskih poverhnostei. Moscow: Mai, 86.
- Zav'ialov, Yu. S., Leus, V. A., Skorospelov, V. A. (1985). Splainy v inzhenernoi geometrii. Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 224.
- Watt, A. (2000). 3D Computer Graphics. Ed. 3. Addison-Wesley, 570.
- Zamani, M. (2010). A simple 2D interpolation model for analysis of nonlinear data. Natural Science, Vol. 2, № 6, 641–645. doi:10.4236/ns.2010.26080
- Chen, L., Hu, S. (2011, May). A Comparison of Improvements for Shear Warp Algorithm Using Lagrange or Cubic Spline Interpolation. 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Available: https://doi.org/10.1109/icbbe.2011.5780354
- Herman, G. T., Bucholtz, C. A., Jingsheng Zheng. (1991). Shape-based Interpolation Using Modified Cubic Splines. Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vol. 13, № 1. Available: https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.1991.683941
- Badaev, Yu. I., Kovtun, A. M. (2003). Aproksymatsiia splainamy na osnovi kryvykh z intsydentnymy tochkamy. Pratsi Natsionalnoho universytetu «Lvivska politekhnika» (spetsvypusk). Materialy mizhnarodnoi naukovo-praktychnoi konferentsii «Suchasni problemy heometrychnoho modeliuvannia». Lviv: Natsionalnyi universytet «Lvivska politekhnika», 75–77.
- Moreno, J., Gonzalez, I., Algar, M. J., Catedra, F. (2014, April). Analysis of NURBS dielectric volumes by using the Method of Moments. The 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2014). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). Available: https://doi.org/10.1109/eucap.2014.6902306
- Kovtun, A. M. (2006). Spetsialni polinomialni splainy tretoho, chetvertoho i piatoho stepeniv u heometrychnomu modeliuvanni. Kyiv, 21.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 Александр Михайлович Ковтун

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







