Development of a decision support system using advanced multi-criteria decision-making techniques
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.323377Keywords:
TOPSIS, fuzzy TOPSIS, Z-number TOPSIS, decision-making methods, DSSAbstract
The object of research is decision-making processes in conditions of uncertainty, with an emphasis on improving the accuracy and reliability of multi-criteria decision-making methods. The problem to be solved is the difficulty of making reliable and optimal decisions in dynamic environments where data variability, incomplete information, and subjective judgments pose significant challenges. Traditional methods often fail to adequately address these complexities, leading to suboptimal or unreliable outcomes.
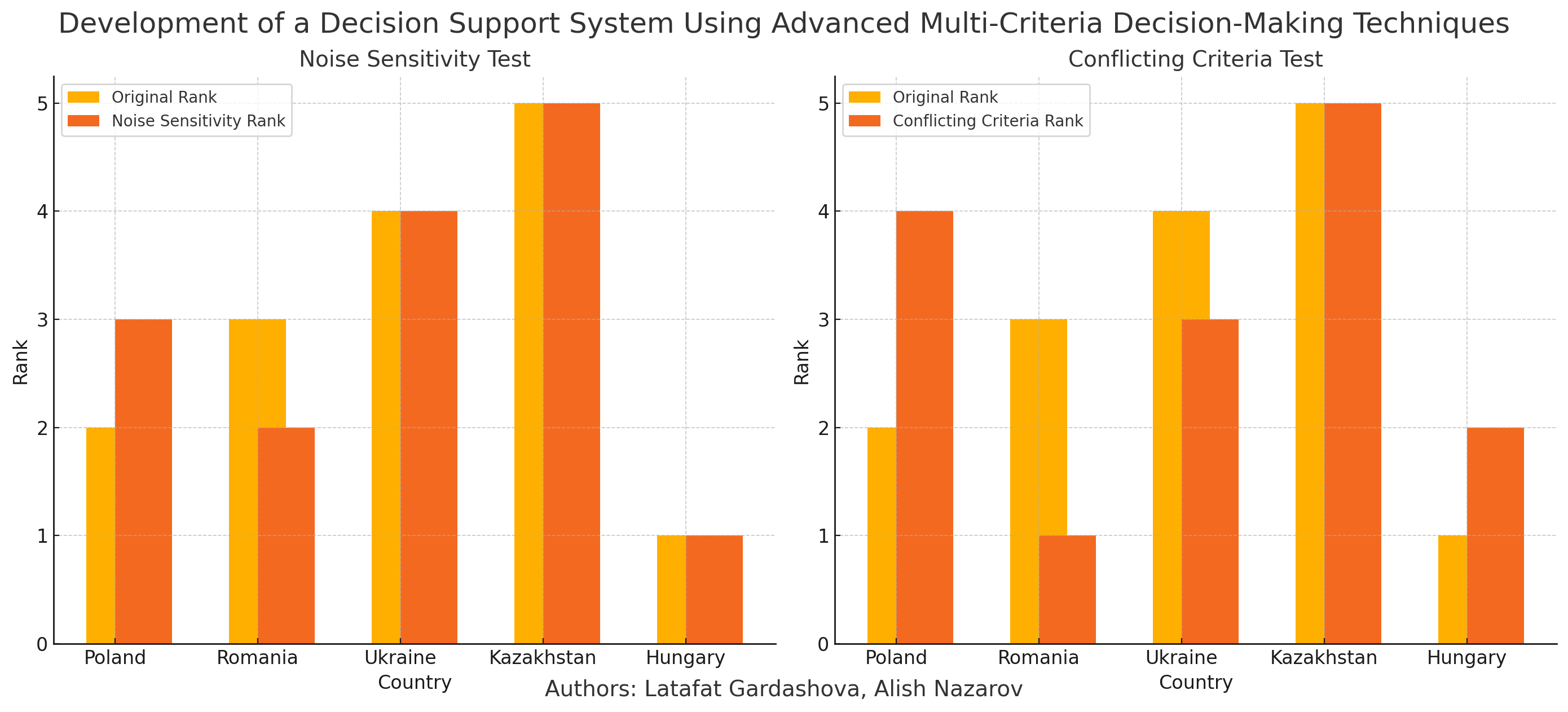
The essence of the results lies in the creation of a DSS (Decision Support System) that leverages Z-number TOPSIS (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution) to combine performance metrics with confidence levels, providing a more comprehensive framework for decision-making. The system is uniquely suited to prioritize alternatives effectively, even when faced with high levels of uncertainty and variability in input data. Due to its features and characteristics, the DSS allows for greater adaptability and precision in decision-making, ensuring results that are not only accurate but also reliable. The explanation for these results lies in Z-number TOPSIS’s ability to integrate quantitative analysis with the evaluation of data reliability, making it far more effective than traditional MCDM (Multi Criteria Decision Making) techniques. A systematic comparison with other methods, such as traditional TOPSIS and Fuzzy TOPSIS, demonstrates that Z-number TOPSIS consistently outperforms these approaches, particularly in scenarios involving dynamic and uncertain conditions. The study contributes to the advancement of decision-making methodologies by providing insights into how uncertainty can be systematically incorporated into ranking models. A comparative analysis with traditional TOPSIS and Fuzzy TOPSIS shows that Z-number TOPSIS outperforms these methods, providing a 10 % improvement in consistency under noisy data conditions and a 15 % better adaptability under conflicting criteria scenarios.
The results are applicable in fields such as supply chain management, where decision-makers must optimize inventory distribution and supplier selection under fluctuating demand, healthcare, where prioritization of patient treatment is required under resource constraints, and financial risk assessment, where investment decisions depend on uncertain economic conditions. The findings highlight the potential of Z-number TOPSIS in supporting more reliable and adaptable decision-making processes in complex and uncertain environments.
References
- Alam, N. M. F. H. N. B., Ku Khalif, K. M. N., Jaini, N. I., Gegov, A. (2023). The Application of Z-Numbers in Fuzzy Decision Making: The State of the Art. Information, 14 (7), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14070400
- Cheng, R., Zhang, J., Kang, B. (2022). A Novel Z-TOPSIS Method Based on Improved Distance Measure of Z-Numbers. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 24 (6), 2813–2830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01297-w
- Jahanshahloo, G. R., Lotfi, F. H., Izadikhah, M. (2006). Extension of the TOPSIS method for decision-making problems with fuzzy data. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 181 (2), 1544–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2006.02.057
- Mahdavi, I., Mahdavi-Amiri, N., Heidarzade, A., Nourifar, R. (2008). Designing a model of fuzzy TOPSIS in multiple criteria decision making. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 206 (2), 607–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2008.05.047
- Mahdavi, I., Heidarzade, A., Sadeghpour-Gildeh, B., Mahdavi-Amiri, N. (2009). A general fuzzy TOPSIS model in multiple criteria decision making. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 45 (3-4), 406–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-1971-5
- Chen, C.-T. (2000). Extensions of the TOPSIS for group decision-making under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 114 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0114(97)00377-1
- Zadeh, L. A. (1996). Knowledge Representation in Fuzzy Logic. Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Logic, and Fuzzy Systems, 764–774. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814261302_0039
- Kacprzyk, J., Fedrizzi, M. (Eds.) (2012). Multiperson decision making models using fuzzy sets and possibility theory. Vol. 18. Springer Science & Business Media, 346. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-2109-2
- Mamdani, E. H., Assilian, S. (1975). An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 7 (1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7373(75)80002-2
- Zulqarnain, R. M., Saeed, M., Ahmad, N., Dayan, F., Ahmad, B. (2020). Application of TOPSIS method for decision making. International Journal of Scientific Research in Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, 7 (2), 76–81.
- Zou, Z., Yun, Y., Sun, J. (2006). Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 18 (5), 1020–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(06)60032-6
- Afshar, A., Mariño, M. A., Saadatpour, M., Afshar, A. (2010). Fuzzy TOPSIS Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Applied to Karun Reservoirs System. Water Resources Management, 25 (2), 545–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9713-x
- Gardashova, L. A. (2018). Z-Number Based TOPSIS Method in Multi-Criteria Decision Making. 13th International Conference on Theory and Application of Fuzzy Systems and Soft Computing – ICAFS-2018. Springer International Publishing, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04164-9_10
- Lee, S. (2015). Determination of Priority Weights under Multiattribute Decision-Making Situations: AHP versus Fuzzy AHP. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 141 (2). https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)co.1943-7862.0000897
- Balioti, V., Tzimopoulos, C., Evangelides, C. (2018). Multi-Criteria Decision Making Using TOPSIS Method Under Fuzzy Environment. Application in Spillway Selection. EWaS3 2018, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110637
- Gardashova, L. A. (2022). University Selection by Using Z-TOPSIS Methodology. 12th World Conference “Intelligent System for Industrial Automation” (WCIS-2022). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51521-7_4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Alish Nazarov, Latafat Gardashova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







