Development of a model of power-linear conversion of digital images for dark tones
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.323535Keywords:
power-linear transformation, simulator, gradation characteristics, optical density, contrast sensitivity, posterizationAbstract
The object of research is the technological process of digital image processing using power transformation in pre-printing processes.
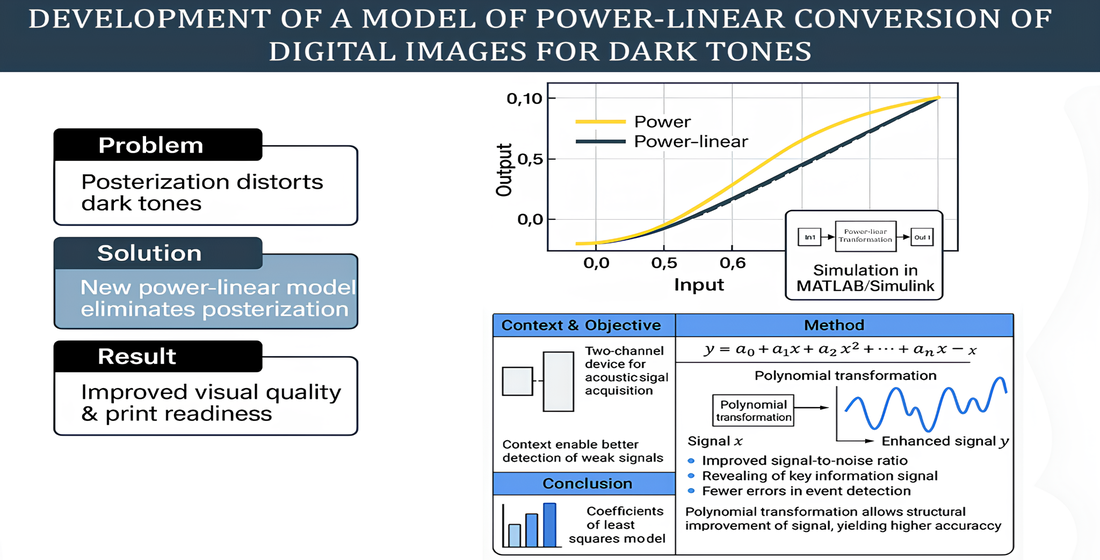
A significant problem in preparing an image for printing is the phenomenon of posterization, which distorts the image and limits the possibilities of power transformation for correcting dark areas of the image. This is a disadvantage of power transformation, which is that at power indicators (r<0.45) and (r>1.5) power transformation is too sensitive to changes in black levels.
The mathematical model of power-linear transformation of images for dark tones has been improved, which, unlike the known ones, involves the summation of power and linear transformation and includes a simulator of power-linear transformation of images. Taking into account the improved model, gradation characteristics, optical density dependences and contrast sensitivity were obtained, which quantitatively assess the perception of images by the human visual system.
The validity of the improved model was verified by mathematical modeling using object-oriented programming and the MATLAB:Simulink software package.
The results of mathematical modeling indicate that the development of the mathematical model allowed to further expand the possibilities of image correction. This is due to the fact that the length of the discrete gradation characteristics is 3–4 levels, which are not noticed by the human visual system (posterization is eliminated).
The proposed model has significant advantages over image conversion methods used in printing. In particular, it expands the range of visual perception of images, eliminates the phenomenon of posterization, provides the ability to change (stretch and compress) contrast within wide limits. At the same time, it expands the functionality of power-law image conversion, and accordingly provides an increase in image quality when preparing it for printing.
The results of the conducted research are recommended to be used at the stage of preparing images for printing and in workflows by operators and technologists.
References
- Lutskiv, M. M., Muzyka, O. O. (2022). Modeling of raster transformation of digital images for square elements. Computer Technologies of Printing, 2 (48), 257–267. https://doi.org/10.32403/2411-9210-2022-2-48-257-267
- Serdiuk, Yu. O. (2023). Vyznachennia kontrastnoi chutlyvosti hama peretvorennia zobrazhen temnykh toniv. Polihrafiia i vydavnycha sprava, 1 (85), 22–31.
- Durnyak, B., Lutskiv, M., Shepita, P., Hunko, D., Savina, N. (2021). Formation of linear characteristics of normalized raster transformation for rhombic elements. Intelligent Information Technologies & System of Information Security. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2853, 127–133.
- Blanchet, G., Charbit, M. (2015). Digital signal and image processing using MATLAB®. Vol. 2, Advances and applications: The Deterministic Case. ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons Inc, 287. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118999592
- Image Processing Toolbox™ User's Guide MATLAB The MathWorks, Inc.1 (2020). Apple Hill Drive Natick, 1286.
- Lutskiv, M. M., Nakonechnyi, M. D. (2022). Modeling and analysis of digital images inkingv. Computer Technologies of Printing, 2 (48), 245–256. https://doi.org/10.32403/2411-9210-2022-2-48-245-256
- Buczynski, L. (2005). Skanery i skanowanie. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo MIKOMA, 885.
- Durniak, B. V., Senkivskyi, V. M., Lutskiv, M. M., Musiiovska, M. M. (2021). Informatsiina tekhnolohiia tonovidtvorennia v korotkykh farbodrukarskykh systemakh poslidovnoi struktury. Lviv: UAD, 176.
- Kovalskyi, B. M., Semeniv, M. V., Shovheniuk, M. V. (2016). Kompiuterna prohrama syntezu zobrazhennia na vidbytku dlia novoi informatsiinoi ta tradytsiinykh tekhnolohii kolorovoho druku. Science and Education a New Dimention: Natural and Technical Science, IV (10 (91)), 72–78.
- Kaminski, B. (2001). Nowoczesny prepres. Warszawa: Wydawca: Translator, 352.
- Bredies, K., Lorenz, D. (2018). Mathematical Image Processing. Birkhäuser. Cham: Springer Nature, 481. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01458-2
- Distante, A., Distante, C. (2020). Handbook of Image Processing and Computer Vision. Vol. 2: From Image to Pattern. Cham: Springer Nature, 448. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-42374-2
- Gonzales, R. C., Woods, R. E. (2008). Digital image processing: international Version. lnc publishind as Prentice Hall. Copyright, 1104.
- Scott, E. (2023). Digital Image Processing and Analysis. Computer Vision and Image Analysis. CRC Press, 441. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003221135
- Lukiv, M. M. (2012). Tsyfrovi tekhnolohii drukarstva. Lviv: UAD, 488.
- Pashulia, P. L. (2011). Standartyzatsiia, metrolohiia, vidpovidnist, yakist u polihraf. Lviv: UAD, 408.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sviatoslav Kavyn

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







