The impact of corporate culture of dignity on cognitive biases, strategic decision-making and technical debt management in IT engineering
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.329635Keywords:
dignity, cognitive biases, technical debt, decision-making, IT engineering, behavioral economicsAbstract
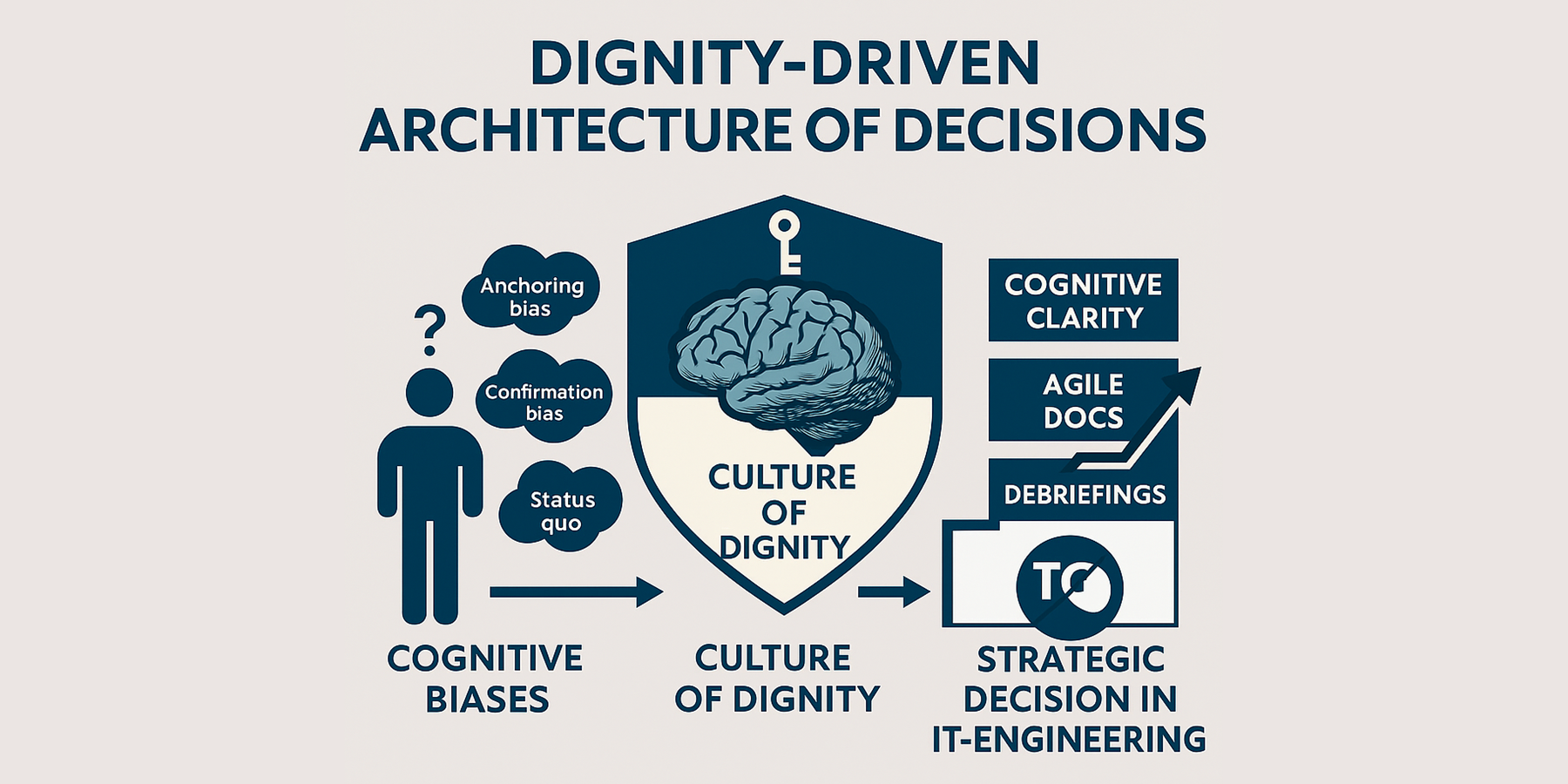
The object of research is the corporate culture of dignity as an interdisciplinary determinant of organizational behavior that operates at the intersection of IT engineering, cognitive science, behavioral economics and knowledge management. The analytical focus is on the impact of cultural variables on cognitive distortions in strategic decision-making, as well as on the dynamics of technical and social debt in IT companies.
The problem to be solved is the absence of a holistic cognitive-behavioral model that would describe the mechanisms of the transformative impact of a culture of dignity on organizational biases and structural inefficiencies in engineering systems. Existing approaches largely ignore the relationship between managerial ethics, team interaction architecture, and the cognitive ecology of decision-making.
The research methodology included a critical analysis of theoretical sources, the development of the author's analytical model, and a content analysis of cases of three global technology companies (Spotify, Google, Airbnb). A qualitative analysis of corporate practices and the content of open reports revealed a strong correlation between a high level of transparency, autonomy, psychological safety and feedback in organizations with a strong culture of dignity and a reduction in the frequency of cognitive distortions and the pace of technical debt elimination. The data are the result of analytical generalization rather than empirical quantitative research. Estimates show that such organizations demonstrate an acceleration in the pace of technical debt reduction by 15–20% compared to those without established feedback practices.
The practical significance of research lies in the possibility of using the results to develop organizational development policies, training programmes for IT team leaders, strategic management systems and technical debt audits.
The findings contribute to the expansion of theoretical understanding of the role of humanistic factors in high-tech management and have the potential to implement the UN Sustainable Development Goals, in particular in terms of decent work, inclusive governance and innovation sustainability.
References
- Mohanani, R., Salman, I., Turhan, B., Rodriguez, P., Ralph, P. (2020). Cognitive Biases in Software Engineering: A Systematic Mapping Study. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 46 (12), 1318–1339. https://doi.org/10.1109/tse.2018.2877759
- Chattopadhyay, S., Nelson, N., Au, A., Morales, N., Sanchez, C., Pandita, R., Sarma, A. (2022). Cognitive biases in software development. Communications of the ACM, 65 (4), 115–122. https://doi.org/10.1145/3517217
- Máté, D., Kiss, J. T., Csernoch, M. (2025). Cognitive biases in user experience and spreadsheet programming. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-025-13392-0
- Borowa, K., Kamoda, S., Ogrodnik, P., Zalewski, A. (2023). Fixations in Agile Software Development Teams. Foundations of Computing and Decision Sciences, 48 (1), 3–18. https://doi.org/10.2478/fcds-2023-0001
- Paulus, D., de Vries, G., Janssen, M., Van de Walle, B. (2022). The influence of cognitive bias on crisis decision-making: Experimental evidence on the comparison of bias effects between crisis decision-maker groups. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 82, 103379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.103379
- Drury-Grogan, M. L., O’Dwyer, O. (2013). An investigation of the decision-making process in agile teams. International Journal of Information Technology & Decision Making, 12 (6), 1097–1120. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219622013400105
- Berthet, V. (2022). The Impact of Cognitive Biases on Professionals’ Decision-Making: A Review of Four Occupational Areas. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.802439
- Paulus, D., Fathi, R., Fiedrich, F., de Walle, B. V., Comes, T. (2022). On the Interplay of Data and Cognitive Bias in Crisis Information Management. Information Systems Frontiers, 26 (2), 391–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-022-10241-0
- Edmondson, A. C., Lei, Z. (2014). Psychological Safety: The History, Renaissance, and Future of an Interpersonal Construct. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1 (1), 23–43. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091305
- Alkalha, Z., Jum’a, L., Zighan, S., Abualqumboz, M. (2025). A multi-faceted approach for leveraging AI and intellectual capital for enhanced supply chain decision-making. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 26 (2), 491–525. https://doi.org/10.1108/jic-07-2024-0201
- Tamburri, D. A., Kruchten, P., Lago, P., Vliet, H. van. (2015). Social debt in software engineering: insights from industry. Journal of Internet Services and Applications, 6 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13174-015-0024-6
- Martini, A., Stray, V., Moe, N. B.; Hoda, R. (Ed.) (2019). Technical-, Social- and Process Debt in Large-Scale Agile: An Exploratory Case-Study. Agile Processes in Software Engineering and Extreme Programming – Workshops. XP 2019. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol 364. Cham: Springer, 112–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30126-2_14
- Saeeda, H., Ovais Ahmad, M., Gustavsson, T. (2024). Navigating social debt and its link with technical debt in large-scale agile software development projects. Software Quality Journal, 32 (4), 1581–1613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11219-024-09688-y
- Besker, T., Ghanbari, H., Martini, A., Bosch, J. (2020). The influence of Technical Debt on software developer morale. Journal of Systems and Software, 167, 110586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2020.110586
- Kniberg, H. (2014). Spotify engineering culture (Part 1). Try Spotify portal. Available at: https://engineering.atspotify.com/2014/03/spotify-engineering-culture-part-1/
- Pretty, N. (2024). Project Aristotle: Google’s Data-Driven Insights on High-Performing Teams. Avaialble at: https://www.aristotleperformance.com/post/project-aristotle-google-s-data-driven-insights-on-high-performing-teams
- Martines, K. S., O’Donnell, S., Yuan, L.-H., Zhu, Y. (2025). How Airbnb Measures Listing Lifetime Value. The Airbnb Tech Blog. Avaialble at: https://medium.com/airbnb-engineering/how-airbnb-measures-listing-lifetime-value-a603bf05142c
- Tamburri, D. A., Kruchten, P., Lago, P., van Vliet, H. (2013). What is social debt in software engineering? 2013 6th International Workshop on Cooperative and Human Aspects of Software Engineering (CHASE), 93–96. https://doi.org/10.1109/chase.2013.6614739
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tetiana Korobkinа, Natalia Dashenkova, Iryna Danchenko, Halyna Omelchenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







