Development of a preprocessing methodology for imbalanced datasets in machine learning training
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.330639Keywords:
imbalanced classification, fraud detection pipeline, stratified sampling, outlier removal, support vector classifierAbstract
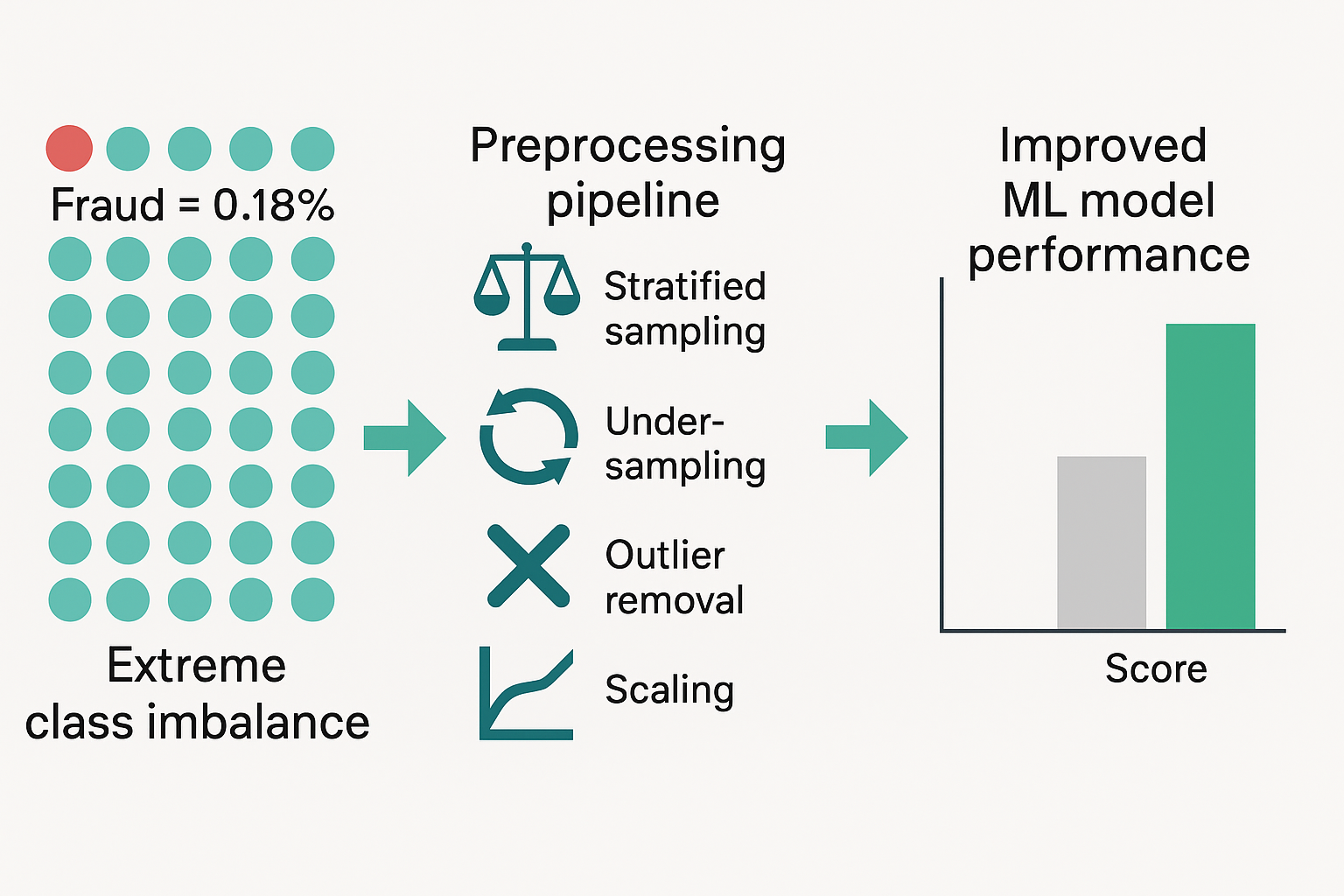
The object of the study is an imbalanced dataset of credit card transactions, where fraudulent cases represent only 0.18% of the total. One of the most problematic places is the inability of standard machine learning models to correctly detect rare fraud events, often resulting in high false-negative rates. This occurs because the models focus on the majority class, which leads to biased outcomes and undetected fraud. The presented analyses used a structured preprocessing pipeline to address this issue. It includes scaling of numeric values to eliminate bias, stratified sampling to preserve class proportions, random undersampling to balance the dataset, and outlier removal to reduce noise. These steps were applied before training three classification models: logistic regression (LR), K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and support vector classifier (SVC). The obtained results show that all models performed well in both cross-validation accuracy and ROC-AUC metrics, with SVC achieving the best ROC-AUC score of 0.9787. This is because the proposed preprocessing pipeline has many features customized to the characteristics of imbalanced data, in particular the combination of data balancing with careful filtering of noise and redundancy. This provides the possibility of achieving robust performance when detecting minority class events. Compared with similar known preprocessing workflows, it provides the following advantages: better class separation, reduced model bias, and improved generalization on unseen data. The results are especially relevant for financial institutions, where fraud detection must be both timely and accurate. The approach offers a practical method for improving security systems without requiring complex or high-cost infrastructure. It can also be adapted for use in other domains where rare events must be detected from large datasets. In future research, the pipeline can be extended by integrating synthetic sampling techniques such as SMOTE or GANs. Additional experiments with real-time streaming data will further validate the robustness of the proposed methodology.
References
- Tadvi, F., Shinde, S., Patil, D., Dmello, S. (2021). Real time credit card fraud detection. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 8 (5), 2177–2180.
- Ounacer, S., Jihal, H., Bayoude, K., Daif, A., Azzouazi, M. (2022). Handling Imbalanced Datasets in the Case of Credit Card Fraud. Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development (AI2SD’2020). Cham: Springer International Publishing, 666–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90633-7_56
- Pozzolo, A. D., Caelen, O., Johnson, R. A., Bontempi, G. (2015). Calibrating Probability with Undersampling for Unbalanced Classification. 2015 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1109/ssci.2015.33
- Dal Pozzolo, A., Caelen, O., Le Borgne, Y.-A., Waterschoot, S., Bontempi, G. (2014). Learned lessons in credit card fraud detection from a practitioner perspective. Expert Systems with Applications, 41 (10), 4915–4928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.02.026
- Yang, Y., Khorshidi, H. A., Aickelin, U. (2024). A review on over-sampling techniques in classification of multi-class imbalanced datasets: insights for medical problems. Frontiers in Digital Health, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2024.1430245
- Ileberi, E., Sun, Y., Wang, Z. (2022). A machine learning based credit card fraud detection using the GA algorithm for feature selection. Journal of Big Data, 9 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-022-00573-8
- Joloudari, J. H., Marefat, A., Nematollahi, M. A., Oyelere, S. S., Hussain, S. (2023). Effective Class-Imbalance Learning Based on SMOTE and Convolutional Neural Networks. Applied Sciences, 13 (6), 4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13064006
- Tian, L., Lu, Y. (2021). An Intrusion Detection Model Based on SMOTE and Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1828 (1), 012024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1828/1/012024
- Park, J., Kwon, S., Jeong, S.-P. (2023). A study on improving turnover intention forecasting by solving imbalanced data problems: focusing on SMOTE and generative adversarial networks. Journal of Big Data, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-023-00715-6
- Liu, Y., Liu, Q. (2025). SMOTE oversampling algorithm based on generative adversarial network. Cluster Computing, 28 (4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-024-04980-9
- Mahmoodi, N., Shirazi, H., Fakhredanesh, M., DadashtabarAhmadi, K. (2024). Automatically weighted focal loss for imbalance learning. Neural Computing and Applications, 37 (5), 4035–4052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-024-10323-x
- Machine Learning Group. Machine Learning Group – ULB. Université Libre de Bruxelles. Available at: http://mlg.ulb.ac.be/
- Bolton, R. J., Hand, D. J. (2001). Unsupervised profiling methods for fraud detection. Credit scoring and credit control, VII, 235–255.
- Carcillo, F., Dal Pozzolo, A., Le Borgne, Y.-A., Caelen, O., Mazzer, Y., Bontempi, G. (2018). SCARFF : A scalable framework for streaming credit card fraud detection with spark. Information Fusion, 41, 182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.09.005
- Lebichot, B., Le Borgne, Y.-A., He-Guelton, L., Oblé, F., Bontempi, G. (2019). Deep-Learning Domain Adaptation Techniques for Credit Cards Fraud Detection. Recent Advances in Big Data and Deep Learning. Springer International Publishing, 78–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16841-4_8
- Abdulhafedh, A. (2022). Comparison between Common Statistical Modeling Techniques Used in Research, Including: Discriminant Analysis vs Logistic Regression, Ridge Regression vs LASSO, and Decision Tree vs Random Forest. OALib, 9 (2), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1108414
- Itoo, F., Meenakshi, Singh, S. (2020). Comparison and analysis of logistic regression, Naive Bayes and KNN machine learning algorithms for credit card fraud detection. International Journal of Information Technology, 13 (4), 1503–1511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-020-00430-y
- Wang, H., Bell, D. (2004). Extended k-Nearest Neighbours based on Evidence Theory. The Computer Journal, 47 (6), 662–672. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/47.6.662
- Halder, R. K., Uddin, M. N., Uddin, Md. A., Aryal, S., Khraisat, A. (2024). Enhancing K-nearest neighbor algorithm: a comprehensive review and performance analysis of modifications. Journal of Big Data, 11 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-024-00973-y
- Srisuradetchai, P., Suksrikran, K. (2024). Random kernel k-nearest neighbors regression. Frontiers in Big Data, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdata.2024.1402384
- Hejazi, M., Singh, Y. P. (2013). One-class support vector machines approach to anomaly detection. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 27 (5), 351–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/08839514.2013.785791
- Sahin, Y., Duman, E. (2011). Detecting credit card fraud by decision trees and support vector machines. Proceedings of the International Multiconference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, 1.
- Kumar, S., Gunjan, V. K., Ansari, M. D., Pathak, R. (2022). Credit card fraud detection using support vector machine. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Recent Trends in Machine Learning, IoT, Smart Cities and Applications: ICMISC 2021. Singapore: Springer, 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-6407-6_3
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykola Zlobin, Volodymyr Bazylevych

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







