Exhaustive characterization of marble to industrial applications: case of marble from the Filfila deposit (Skikda, northeast Algeria)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.337060Keywords:
marble, Filfila deposit, petrographic, scanning electron microscopy, Energy-Dispersive Spectrometry (EDS)Abstract
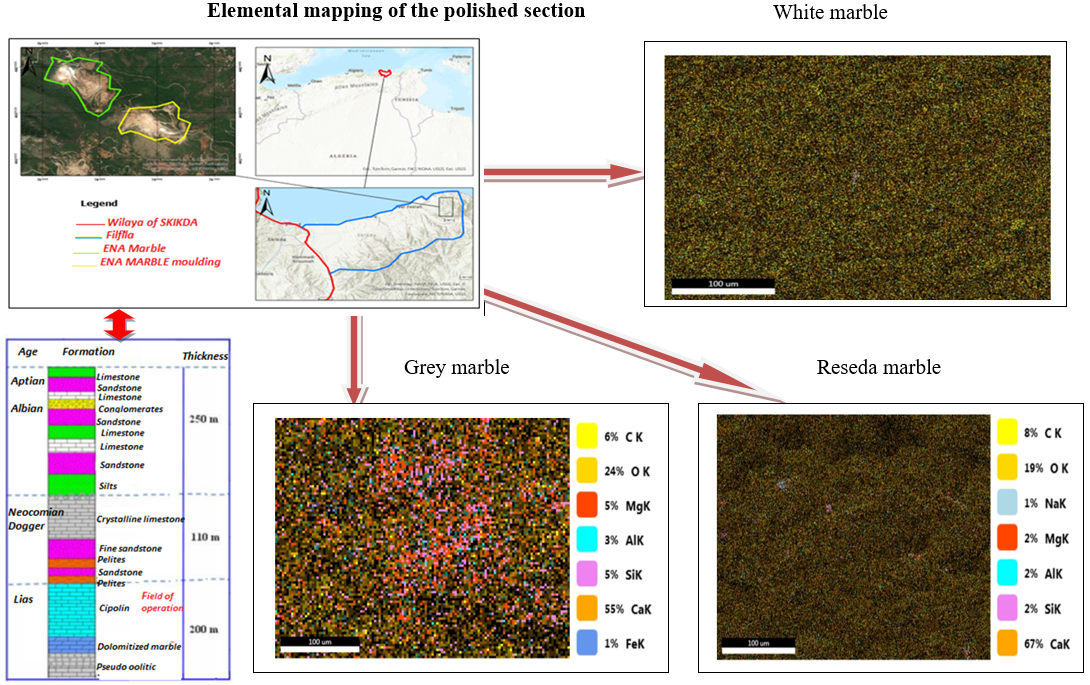
The object of this research is deals with the Filfila marble deposit of all types. The examined area is situated in the Filfila massif, a significant section of the Kabyle basement, in the inner region of the Alpine range in northeastern Algeria. Given that it has been mined for many years, this massif is especially notable for the importance of its marble reserves. There are three primary types of marble found in this deposit: mignonette marble, which is prized for its exquisite green tones; gray marble, which has delicate subtleties; and white marble, which is highly sought after due to its extreme purity.
Multi-scale petrographic techniques that integrate microscopic examinations with macroscopic observations (color, texture, and structure) form the basis of the methodology employed in this work. Under plane-polarized light, thin sections of 30 µm in thickness were created in the University of Annaba's geology lab. According to the results, the material had a uniformly large texture and was primarily composed of microcrystalline calcite. Carefully polished samples were subjected to scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis in order to advance the investigation. SEM was able to disclose fine microstructural characteristics, such as crystal shape, microcracks, porosity, and the distribution of mineral phases, because of its nanometric resolution, which shows a high purity of white marble in addition to the main impurities of gray marble. The mechanical characteristics and durability of the marbles were illuminated by these observations, which allowed for the identification of notable variations among them, especially with regard to the density of discontinuities and the size of the crystal grains. By combining optical and electron microscopy techniques, this integrated approach made it possible to thoroughly characterize Filfila marble by exposing its physical characteristics and mineralogical composition. The results offer a solid scientific basis for possible industrial uses and are useful reference information for upcoming comparative geological studies.
References
- Boumaraf, S. I., Attoui, R., Raaijmakers, M. de V. (2024). Les chapiteaux antiques remployés dans la mosquée de Bou Merouane (Algérie): essai de datation et de recontextualisation. Antiquités Africaines, 60, 101–122. https://doi.org/10.4000/12quc
- Bouabsa, L., Marignac, C., Chabbi, R., Cuney, M. (2010). The Filfila (NE Algeria) topaz-bearing granites and their rare metal minerals: Petrologic and metallogenic implications. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 56 (2–3), 107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.05.008
- Skovmøller, A. (2021). Thorvaldsen’s marble connections. Sculpture Journal, 30 (2), 163–175. https://doi.org/10.3828/sj.2021.30.2.5
- Perrin, C. (1969). Contribution à l'étude géologique du massif du Filfila (Algérie nord-orientale): stratigraphie et sédimentologie de la série mesozoïque de l'unité inférieure. [Doctoral dissertation].
- Tykot, R. H., Bouzidi, O., Herrmann, J. J., van den Hoek, A. (2018). Marble on Rome’s Southwestern Frontier: Thamugadi and Lambaesis. ASMOSIA XI, Interdisciplinary Studies on Ancient Stone. XI International Conference of ASMOSIA. University of Split, Arts Academy in Split, 467–479. https://doi.org/10.31534/xi.asmosia.2015/02.31
- Allaouchiche, S., Kacher, S., Sanz-Arauz, D. (2025). Documenting Ancient Materials for a Digital Materials Library Project. The Case of Three World Heritage Sites in Algeria. International Journal of Architectural Heritage, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2025.2495960
- Mebirouk, N., Amrane, M., Messast, S., Mazouzi, S. (2024). Enhanced analysis of landslide susceptibility mapping in the proximity of main roads in the province of Skikda, Algeria: using NAS for efficient performance and faster processing. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 10 (5), 6449–6474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-024-02129-6
- Menfoukh, I., Dernouni, D. (2024). Les techniques d’exploitation des gisements de marbre (cas de Filfila – Skikda). [Doctoral dissertation]. Available at: http://oldspace.univ-tebessa.dz:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/11606?show=full
- Babouri, L., Belmokre, K., Brioua, S., Bardeau, J. F. (2017). Study of the corrosion-erosion behavior of Cu70-Ni30 alloy in flowing water containing marble particles. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 9 (3), 141–152. Available at: https://www.jocpr.com/articles/study-of-the-corrosionerosion-behavior-of-cu70ni30-alloy-inflowing-water-containing-marble-particles.pdf
- Dehbi, N. M., Chaibet, C. (2019). Comportement rhéologique et physico-mécanique des mortiers autoplaçants avec ajouts minéraux. [Doctoral dissertation; Mouloud Mammeri Tizi Ouzou University]. Available at: https://dspace.ummto.dz/items/7afe89fc-4527-41b9-877b-d372f6a40b19
- Bourema, M., Goual, I., Ferhat, A. (2023). Experimental Contribution to Study the Physico-Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Lightweight Cellular Concrete Prepared with Different Types of Sand and Waste Marble Powder. Slovak Journal of Civil Engineering, 31 (4), 16–25. https://doi.org/10.2478/sjce-2023-0023
- Ghennai, A., Madani, S. (2022). La composition du paysage pétrolier des villes portuaires d’Afrique du Nord, le cas de Skikda (Algérie). Bulletin de La Société Géographique de Liège, 79–95. https://doi.org/10.25518/0770-7576.6995
- Bu Durays, A., Mezghache, H. (2019). Géostatistique et répartition spatiale des différents types de marbre dans le gisement de Filfila-Skikda-Algérie Nord Orientale. Synthèse, 25 (1), 16–32. Available at: https://search.emarefa.net/detail/BIM-890551
- Mamtani, M. A.; Suwas, S., Field, D. P. (Eds.) (2025). SEM-EBSD Studies of Tectonically Deformed Rocks and Kinematic Analysis. Advances in Texture, Microtexture, and Allied Techniques. Singapore: Springer, 337–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-5346-1_13
- Ghenai, G., Mrad, C. (2024). Etude Petrographique Du Marbre Du Gisement De Filfila (Skikda, Nord-Est Algerien). [Master thesis; Higher National School of Technology and Engineering ENSTI]. Available at: http://dspace.ensti-annaba.dz:4000/items/35e21d77-1fe4-4972-9a4a-6ff51886a469/full
- Houria, H., Leila, K., Assia, A., Mouloud, B.; Nemati, S., Tahmoorian, F. (Eds.) (2020). Introduction of Marble Waste Sand in the Composition of Mortar. Sandy Materials in Civil Engineering – Usage and Management. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.91254
- Karaouet, M., Djoudi, K., Lekoui, A. (2020). Etude De Synthése Bibliographique Sur Les Skarns Du Nord-est Algérien Et Leurs Potentiels Miniers. [Doctoral dissertation; Jijel University]. Available at: https://theses-algerie.com/2425024038909593/memoire-de-master/universite-mohammed-seddik-ben-yahia---jijel/etude-de-synth%C3%A9se-bibliographique-sur-les-skarns-du-nord-est-alg%C3%A9rien-et-leurs-potentiels-miniers
- Toubal Seghir, N., Mellas, M., Sadowski, Ł., Krolicka, A., Żak, A., Ostrowski, K. (2019). The Utilization of Waste Marble Dust as a Cement Replacement in Air-Cured Mortar. Sustainability, 11 (8), 2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11082215
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Imen Aichouri, Djamel Nettour, Rachid Chaib, Nesrine Derrardjia, Cherif Gherbi, Salim Bensehamdi, Yousra Boukhamla

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







