Development of vector models and methods for their solution for optimization of logistics problems in e-commerce
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.337246Keywords:
e-commerce, logistics processes, optimization, vector transport problems, potential method, unloading cyclesAbstract
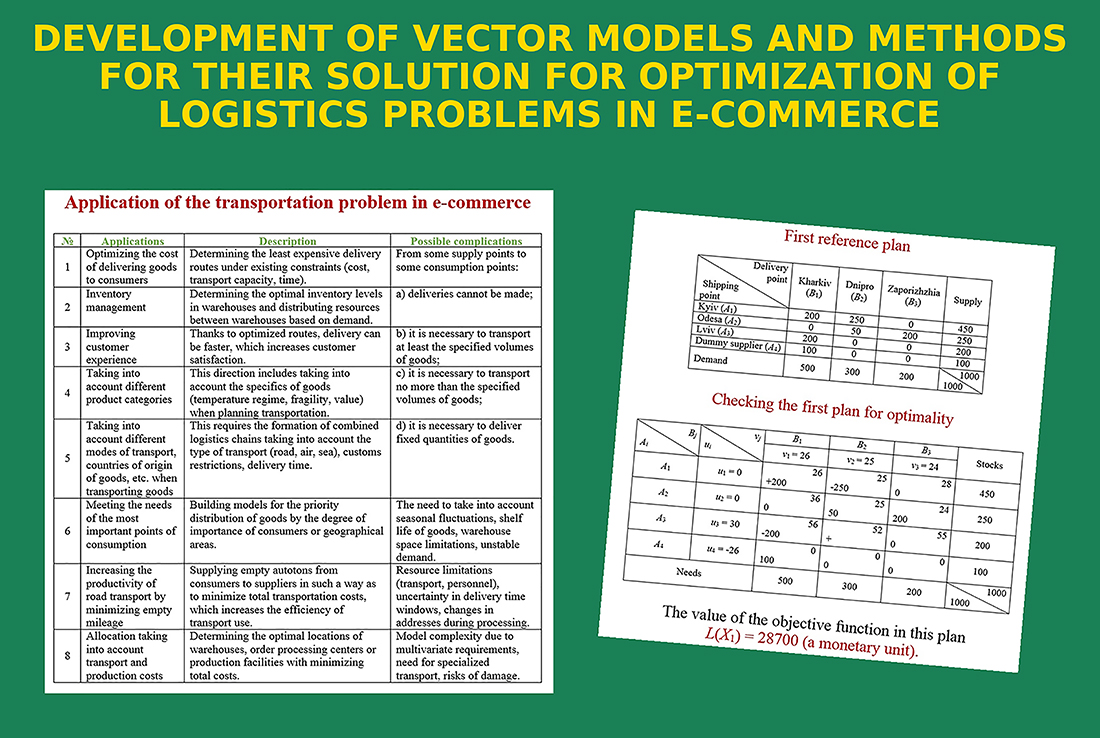
The object of research is the logistics processes of delivering goods in a digital environment (e-commerce), which require optimization using mathematical models. One of the most problematic areas is taking into account dynamic changes and unpredictable factors: seasonal and daily fluctuations in demand, delays in deliveries, fluctuations in delivery costs, changes in routes, etc. This necessitates the creation of adaptive mathematical models that can quickly respond to changing conditions and ensure high efficiency of logistics processes in real time.
The study used a comprehensive approach that includes: mathematical modeling, linear programming methods (in particular, the potential method, the simplex method), the unloading cycle method, as well as multi-criteria analysis and decision-making methods. The experiments were performed using the MATLAB and Python computing environments based on both real and synthetic data that simulate e-commerce conditions.
The main results of the study are as follows. First, it was established that classical scalar models of the transport problem (TP) are insufficient for describing multi-criteria logistics conditions in e-commerce, where it is important to simultaneously take into account several performance indicators. Second, the feasibility of using vector models that allow optimizing delivery processes according to several criteria – in particular, minimizing total costs, transportation time or loading time – was demonstrated. Such models reflect the real conditions and requirements of e-commerce much more accurately. Third, it was proven that the use of vector models allows achieving a balanced distribution of resources between competing criteria, which makes it possible to find compromise, but strategically more effective solutions at the moment. The possibility of using normalization methods, as well as methods of multi-criteria selection, was also demonstrated. As a result, two-criteria and three-criteria models of the transport problem were developed, implemented and tested, adapted to the conditions of digital logistics. It is shown that, taking into account the priorities of the criteria, these models provide a more flexible and adequate solution to optimization problems, compared to classical approaches.
References
- Lakshmi, P. T. (2018). Role of logistics in e-commerce industry. Digital Economy and Green Management: Role of Banks, Payment Gateways & Consumers: conference. Chennai. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342872143_ROLE_OF_LOGISTICS_IN_E-COMMERCE_INDUSTRY
- Padamwar, B. V., Pandey, H. (2019). Optimization techniques in operations research: a review. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 10 (1), 746–752. https://doi.org/10.61841/turcomat.v10i1.14604
- Vasilev, J., Nikolaev, R., Milkova, T. (2023). Transport Task Models with Variable Supplier Availabilities. Logistics, 7 (3), 45–48. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7030045
- Prokudin, G. S., Yerko, Ya. V., Redich, Yu. A. (2021). Solving the transport problem of the shortest path using information technology. Scientific Notes of Taurida National V. I. Vernadsky University. Series: Technical Sciences, 2 (2), 206–211. https://doi.org/10.32838/2663-5941/2021.2-2/32
- Petrunia, Yu. Ye., Litovchenko, B. V., Pasichnyk, T. O., Petrunia, V. Yu., Mormul, M. F., Tkachova, O. K. et al.; Petrunia, Yu. Ye. (Ed.) (2020). Pryiniattia upravlinskykh rishen. Dnipro: Universytet mytnoi spravy ta finansiv, 276. Available at: http://biblio.umsf.dp.ua/jspui/bitstream/123456789/4070/1/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%B9%D0%BD%D1%8F%D1%82%D1%82%D1%8F%20%D1%83%D0%BF%D1%80%20%D1%80%D1%96%D1%88%D0%B5%D0%BD%D1%8C%202020.pdf
- Skitsko, V. I., Voinikov, M. Yu. (2018). Solving a Three-Index Transportation Problem under Risk Conditions Using a Genetic Algorithm. The Problrems of Economy, 3, 246–252. Available at: https://www.problecon.com/export_pdf/problems-of-economy-2018-3_0-pages-246_252.pdf
- Hrabovska, K. A. (2023). Doslidzhennia metodiv optymizatsii transportnykh perevezen. Instytutsiinyi repozytarii Mykolaivskoho NAU, 33–35. Available at: https://dspace.mnau.edu.ua/jspui/bitstream/123456789/15837/1/zbirnyk-tez-24-03-23-men-33-35.pdf
- Chayka-Petegyrych, L. (2020). Multimodal and intermodal cargo transportation in the system of international transport logistics. Herald UNU. International Economic Relations and World Economy, 33 (2), 114–117. https://doi.org/10.32782/2413-9971/2020-33-41
- Honcharov, A. V., Mohilei, S. O. (2020). Implementation of multimodal transport tasks in different software environments. Bulletin of Cherkasy State Technological University, 3, 67–74. https://doi.org/10.24025/2306-4412.3.2020.215516
- Zabolotnii, S., Mogilei, S. (2019). Optimization of the method of constructing reference plans of multimodal transport problem. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 1 (2 (45)), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.15587/2312-8372.2019.154561
- Pasichnyk, V. I., Hrysiuk, Yu. S., Patsora, O. V. (2013). The efficiency of intermodal transport as part of providing high quality transportation services. Upravlinnia proektamy, systemnyi analiz i lohistyka. Tekhnichna seriia, 12, 125–131. Available at: http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Upsal_2013_12_16
- Аhmed, A., Dabral, S., Bahuguna, D. (2023). Artificial Intelligence’s Integration in Supply Chain Management: A Comprehensive Review. European Economics Letters, 13 (3), 1512–1527. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372965863_Artificial_Intelligence's_Integration_in_Supply_Chain_Management_A_Comprehensive_Review
- Lysenko, S., Makovoz, O., Perederii, T. (2023). Тhe impact of artificial intelligence in logistics management on sustainability development of e-business. Selected Papers of the V International Conference on European Dimensions of Sustainable Development. Kyiv, 99–109. https://doi.org/10.24263/edsd-2023-5-12
- Kotov, D., Klymenko, V., Androschuk, O., Melnyk, V., Goroshko, O., Azyzov, B. (2024). Simulation modeling of logistics processes provision based on the transport task. Social Development and Security, 14 (1), 218–228. https://doi.org/10.33445/sds.2024.14.1.18
- Back, A., Lipponen, M., Tinnilä, M. (2012). E-commerce logistics: A Literature Research Review and future research agenda. International Journal of E-Services and Mobile Applications, 4 (3), 1–22. Available at: https://ideas.repec.org/a/igg/jesma0/v4y2012i3p1-22.html
- Lavrinenko, N. M., Latynin, S. M., Fortuna, V. V., Beskrovnyi, O. I. (2010). Osnovy ekonomiko-matematychnoho modeliuvannia. Lviv: “Mahnoliia 2006”, 540. Available at: https://magnolia.lviv.ua/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Osnovy-ekonom-matem.-mod_Zmist-1.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykola Mormul, Dmytro Shchytov, Oleksandr Shchytov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







