Development of a method for modeling the magnetic state and assessing the electromechanical characteristics of a vortex layer of ferromagnetic particles moving in a rotating magnetic field
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.344908Keywords:
vortex layer in RMF, electromechanical interaction FP, magnetization model VL, optimal FP concentration, VL chaos levelAbstract
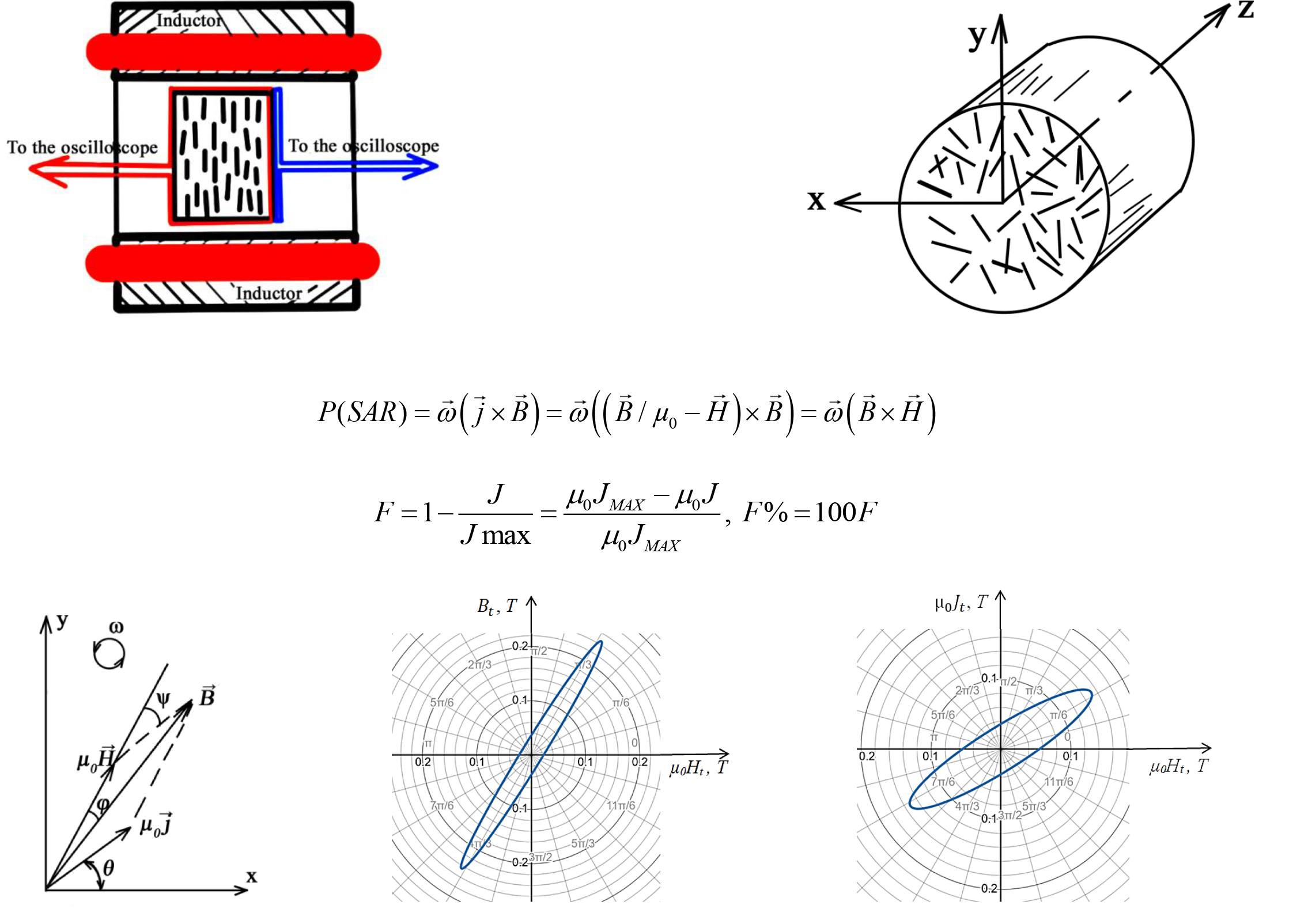
The object of this study is a vortex layer (VL) of ferromagnetic particles (FP) moving in a rotating magnetic field (RMF). Apparatuses vortex layer (AVL) devices are used to intensify energy-intensive technological processes with liquid and bulk materials that require activation, mixing, and fine grinding. External three-phase (380 V/50 Hz) two-pole inductors are used to synthesize the VL in a cylindrical AVL working chamber with a diameter of 60–330 mm. The RMFi modulus of magnetic induction at the bore center in the absence of FP is selected during design from the range of 0.12–0.25 T. Steel or nickel FPs have an elongated cylindrical shape, typically with a ratio of l/d = 8–15 (l is the FP length, d is the FP diameter) and a diameter of 0.7–2.5 mm. The magnetic and electromechanical characteristics of the VL have been insufficiently studied. This paper examines a method for estimating these characteristics of the VL by modeling its magnetic state. A real bipolar RMF existing in a working chamber with an operating VL is represented by the synchronous rotation of three plane-parallel uniform circular vector fields – field strength, induction, and magnetization H, B, J. The experimental determination of the characteristics of the model vectors H, B, J is performed using two flat frame induction coils. The simple behavior patterns of the vector field J are consistent with the relatively chaotic behavior of each individual VL particle.
A demonstration example of determining the characteristics of the model vectors H, B, J, the specific torque magnetic moment, the specific power, and the level of chaos of an industrial VL is presented.
The results of this work can be used in both academic and engineering applications related to the research and design of AVL and similar equipment.
References
- Moerland, C. P., van IJzendoorn, L. J., Prins, M. W. J. (2019). Rotating magnetic particles for lab-on-chip applications – a comprehensive review. Lab on a Chip, 19 (6), 919–933. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc01323c
- Logvinenko, D. D., Sheliakov, O. P. (1976). Intensifikatciia tekhnologicheskikh protcessov v apparatakh s vikhrevym sloem. Kyiv: Tekhnіka, 144.
- Oberemok, V. M. (2010). Elektromahnitni aparaty z feromahnitnymy robochymy elementamy. Osoblyvosti zastosuvannia. Poltava: RVV PUSKU, 201. Available at: http://dspace.puet.edu.ua/handle/123456789/6536
- GlobeCore Transformer Oil Purification Equipment, Bitumen Equipment. Available at: https://globecore.com/ Last accessed: 22.09.2023
- Ogonowski, S. (2021). On-Line Optimization of Energy Consumption in Electromagnetic Mill Installation. Energies, 14 (9), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092380
- Ibragimov, R., Korolev, E., Potapova, L., Deberdeev, T., Khasanov, A. (2022). The Influence of Physical Activation of Portland Cement in the Electromagnetic Vortex Layer on the Structure Formation of Cement Stone: The Effect of Extended Storage Period and Carbon Nanotubes Modification. Buildings, 12 (6), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12060711
- Całus, D. (2023). Experimental Research into the Efficiency of an Electromagnetic Mill. Applied Sciences, 13 (15), 8717. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13158717
- Polshchikov, H., Zhukov, P. (2023). Force effect of a circular rotating magnetic field of a cylindrical electric inductor on a ferromagnetic particle in process reactors. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 6 (1 (74)), 34–40. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2023.293005
- Polshchikov, H., Zhukov, P. (2024). Construction of a generalized mathematical model and fast calculations of plane-parallel rotating magnetic fields in process reactors with longitudinal currents of cylindrical inductors on a graphical calculator. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 5 (1 (79)), 38–49. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.313937
- Hallali, N., Rocacher, T., Crouzet, C., Béard, J., Douard, T., Khalfaoui, A. et al. (2022). Low-frequency rotating and alternating magnetic field generators for biological applications: Design details of home-made setups. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 564, 170093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.170093
- Polshchikov, G. A., Logvinenko, D. D., Zhukov, P. B. (1975). Nekotorye voprosy rascheta i proektirovaniia apparatov s vikhrevym sloem, NIIKhIMMASh. Oborudovanie s ispolzovaniem razlichnykh metodov intensifikatcii protcessov, 71, 128–141.
- Milykh, V. I., Shilkova, L. V. (2020). Characteristics of a cylindrical inductor of a rotating magnetic field for technological purposes when it is powered from the mains at a given voltage. Electrical Engineering & Electromechanics, 2, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.20998/2074-272x.2020.2.02
- Milykh, V. I., Shylkova, L. V. (2020). Experimental research of the three-phase physical model of the magnetic field inductor in the working mode when processing bulk material. Bulletin of NTU “Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute” Series: Electrical Machines and Electromechanical Energy Conversion, 3 (1357), 3–7. https://doi.org/10.20998/2409-9295.2020.3.01
- Guo, Y., Zhu, J. G., Zhong, J., Lu, H., Jin, J. X. (2008). Measurement and Modeling of Rotational Core Losses of Soft Magnetic Materials Used in Electrical Machines: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 44 (2), 279–291. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmag.2007.911250
- Prozorov, R., Kogan, V. G. (2018). Effective Demagnetizing Factors of Diamagnetic Samples of Various Shapes. Physical Review Applied, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevapplied.10.014030
- Mattei, J.-L., Floc′h, M. L. (2003). Percolative behaviour and demagnetizing effects in disordered heterostructures. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 257 (2-3), 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(02)01232-5
- Atallah, K., Howe, D. (1993). Calculation of the rotational power loss in electrical steel laminations from measured H and B. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 29 (6), 3547–3549. https://doi.org/10.1109/20.281225
- Alatawneh, N., Pillay, P. (2011). Design of a novel test fixture to measure rotational core losses in machine laminations. 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition. Phoenix, 433–440. https://doi.org/10.1109/ecce.2011.6063802
- Polshchikov, G. A., Zhukov, P. B. (1978). A.Cv. na izobretenie SU 627848 A1. Sposob kontrolia protcessov v apparate s vikhrevym sloem. Published: 15.10.78, Bul. No. 38.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Henrikh Polshchikov, Pavlo Zhukov

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







