Аналіз та розподіл поліхлорованих біфенілів (ПХБ) у відкладах уздовж лиману Шатт-ель-Араб, Ірак
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.310819Ключові слова:
відкладення, лиман Шатт-ель-Араб, поліхлоровані біфеніли, ПХБ, сезонні коливання, газова хромато-мас-спектрометріяАнотація
Об’єктом цього дослідження є поліхлоровані біфеніли (ПХБ) у відкладеннях уздовж лиману Шатт-ель-Араб, Ірак. Проведене дослідження розглядає проблему річкового забруднення ПХБ. Вплив ПХБ на людину включає рак, порушення репродукції, вплив на розвиток нервової системи у немовлят, імунотоксичність та ендокринні порушення. ПХБ призводять до пошкодження печінки та стимулює зміни в послідовності ДНК. Лиман Шатт-ель-Араба утворюється на півдні Іраку біля міста Аль-Курна після злиття річок Тигр і Євфрат. Регіон лиману Шатт-ель-Араб ділиться між Іраком та Іраном. Лиман отримує забруднюючі речовини, коли він проходить через райони міста Басра, через промислову, сільськогосподарську та людську діяльність, яка скидає забруднювачі в лиман без очищення.
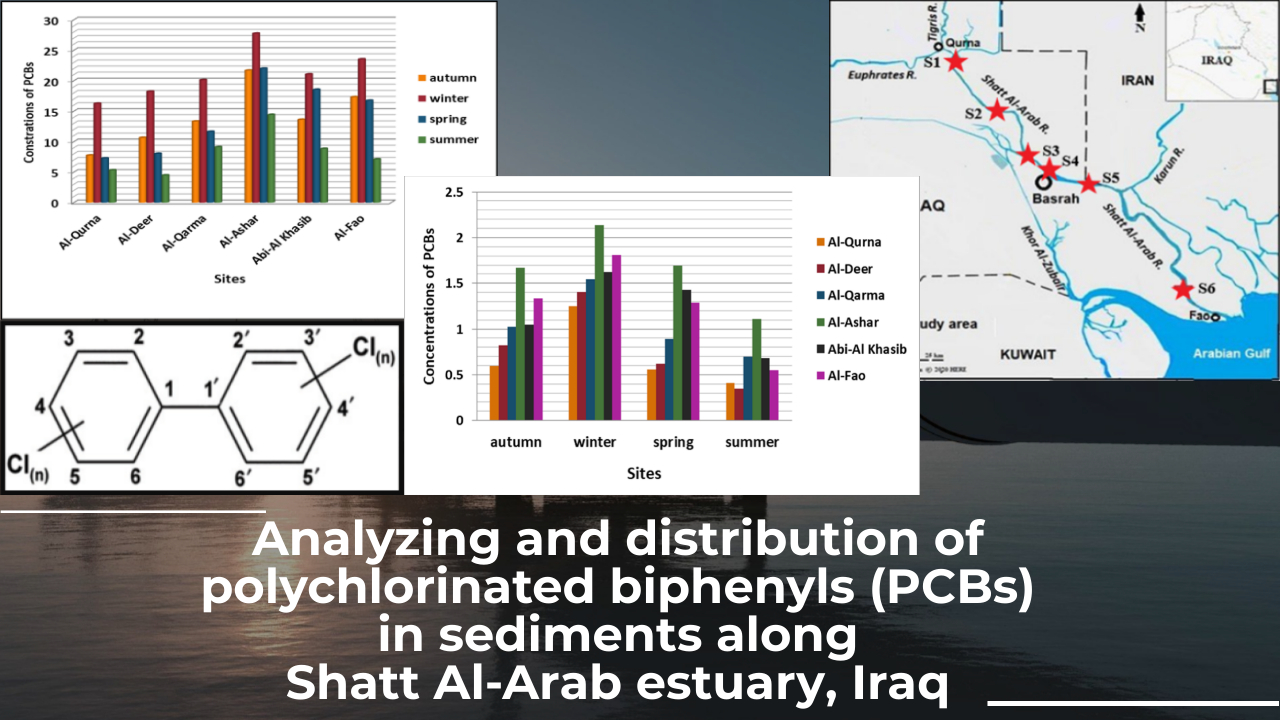
Концентрації сполуки Σ13 ПХБ у зразках осаду визначали та аналізували на кожній ділянці за допомогою газової хромато-мас-спектрометрії (GC-MS, Agilent). Шість місць було обрано вздовж лиману Шатт-ель-Араб. Це Аль-Курна (S1), Аль-Дір (S2), Аль-Карма (S3), Аль-Ашар (S4), Абі Аль-Хасіб (S5) і Аль-Фао (S6), у місті Басра, на півдні Іраку. Зразки осаду збирали сезонно, починаючи з осіннього сезону вересня 2019 року до літнього сезону липня 2020 року. Концентрації сполуки Σ13 (ПХБ-141, ПХБ-149, ПХБ-138, ПХБ-153, ПХБ-189 і ПХБ-194) у зразках опадів коливалися від 4,48 нг/г на ділянці Аль-Дір протягом літнього сезону до 27,75 нг/г на території Аль-Ашар протягом зимового сезону для всіх обраних ділянок. Було виявлено, що на ділянці Аль-Дір середнє значення ПХБ було найнижчим – 0,345 нг/г, а на ділянці Аль-Ашар – найвище середнє значення ПХБ – 2,135 нг/г. Концентрація ПХБ у пробах донних відкладень в осінній, зимовий, весняний та літній періоди коливалась від 7,75 до 21,68 нг/г, від 16,25 до27,75 нг/г, від 7,28 до 22,01 нг/г та від 4,48 до 14,41 нг/г, відповідно. Структури розподілу конгенерів у цих зразках вказують на домінування високохлорованих конгенерів (три- та гекса-ПХБ) у порівнянні з іншими конгенерами ПХБ. Цей проєкт є першим у своєму роді в Басрі та в усьому Іраку, який повідомляє про концентрації ПХБ у регіоні, і вважається базовим дослідженням і може бути використаний для наступних досліджень.
Посилання
- Wang, Y., Luo, C.-L., Li, J., Yin, H., Li, X.-D., Zhang, G. (2011). Characterization and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and vegetations near an electronic waste recycling site, South China. Chemosphere, 85 (3), 344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.096
- Cocco, E., Guignard, C., Hoffmann, L., Bohn, T. (2011). Rapid analysis of polychlorinated biphenyls in fish by pressurised liquid extraction with in-cell cleanup and GC-MS. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 91 (4), 333–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2010.496048
- Kucklick, J. R., Baker, J. E. (1998). Organochlorines in Lake Superior’s Food Web. Environmental Science & Technology, 32 (9), 1192–1198. https://doi.org/10.1021/es970794q
- Jiang, J.-J., Lee, C.-L., Fang, M.-D., Ko, F.-C., Baker, J. E. (2011). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of southwest Taiwan: Regional characteristics and potential sources. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62 (4), 815–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.12.019
- Li, Q., Luo, Z., Yan, C., Zhang, X. (2011). Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Contamination in Sediment and Organism from Xiamen Offshore Area, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87 (4), 372–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0385-x
- Barakat, A. O., Khairy, M., Aukaily, I. (2013). Persistent organochlorine pesticide and PCB residues in surface sediments of Lake Qarun, a protected area of Egypt. Chemosphere, 90 (9), 2467–2476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.012
- Klaren, W. D., Gadupudi, G. S., Wels, B., Simmons, D. L., Olivier, A. K., Robertson, L. W. (2015). Progression of micronutrient alteration and hepatotoxicity following acute PCB126 exposure. Toxicology, 338, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2015.09.004
- Ludewig, G., Robertson, L. W. (2013). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as initiating agents in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Letters, 334 (1), 46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2012.11.041
- Frame, G. M., Robertson, L. W., Hansen, L. G. (2001). The current state-of-the-art of comprehensive, quantitative, congener-specific PCB analysis, and what we now know about the distributions of individual congeners in commercial Aroclor mixtures. PCBs: Recent Advances in Environmental Toxicology and Health Effects, 3–9.
- Mai, B., Zeng, E. Y., Luo, X., Yang, Q., Zhang, G., Li, X., Sheng, G., and Fu, J. (2004). Abundances, Depositional Fluxes, and Homologue Patterns of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Dated Sediment Cores from the Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Science & Technology, 39 (1), 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049015d
- PCB Transformers and Capacitors From Management to Reclassification and Disposal (2002). United Nation Environment Programme UNEP Chemicals.
- Rahuman, M., Pistone, L., Trifirò, F., Miertus, S. (2000). Destruction technologies for polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Proceedings of Expert Group Meetings on POPs and Pesticides Contamination, 16 (6), 405–423.
- Al-Saad, H. T., Alhello, A. A., Al-Kazaeh, D. K., Al-Hello, M. A., Hassan, W. F., Mahdi, S. (2015). Analysis of Water Quality Using Physico-Chemical Parameters in the Shatt AL-Arab Estuary, Iraq. International Journal of Marine Science. https://doi.org/10.5376/ijms.2015.05.0049
- Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater (2005). APHA, American Public Health Association. Washington, 1193.
- Aganbi, E., Iwegbue, C. M. A., Martincigh, B. S. (2019). Concentrations and risks of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in transformer oils and the environment of a power plant in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Toxicology Reports, 6, 933–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.08.008
- Al-Khatib, F. M. H. (1998). Distribution of hydrocarbons compound and their sources in sediment cores from Shatt Al-Arab Estuary and NW Arabian Gulf. M.Sc. thesis. University of Basrah.
- Zhou, J. L., Hong, H., Zhang, Z., Maskaoui, K., Chen, W. (2000). Multi-phase distribution of organic micropollutants in Xiamen Harbour, China. Water Research, 34 (7), 2132–2150. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(99)00360-7
- Arfaeinia, H., Asadgol, Z., Ahmadi, E., Seifi, M., Moradi, M., Dobaradaran, S. (2017). Characteristics, distribution and sources of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in coastal sediments from the heavily industrialized area of Asalouyeh, Iran. Water Science and Technology, 76 (12), 3340–3350. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.500
- Gómez-Gutiérrez, A., Garnacho, E., Bayona, J. M., Albaigés, J. (2007). Screening ecological risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants in Mediterranean sea sediments. Environment International, 33 (7), 867–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.04.002
- Abdel-Dayem, S. (1994). Water quality issues in Egypt. Proceedings of the Italian-Egyptian Study-Days on the Environment (IESDE’94), 81–92.
- Konat, J., Kowalewska, G. (2001). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments of the southern Baltic Sea – trends and fate. The Science of the Total Environment, 280 (1-3), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00785-9
- Al-Hejuje, M. M. (2014). Application of water quality and pollution indices to evaluate the water and sediments status in the middle part of Shatt Al-Arab River. PhD Thesis. University of Basrah.
- Johnson, G. W., Hamilton, M. C., Forensics, E. (2006). Polychlorinated Biphenyl. Environmental Forensics.
- Gao, J., Shi, H., Dai, Z., Mei, X., Zong, H., Yang, H. et al. (2018). Linkages between the spatial toxicity of sediments and sediment dynamics in the Yangtze River Estuary and neighboring East China Sea. Environmental Pollution, 233, 1138–1146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.023
- Sakai, N., Dayana, E., Abu Bakar, A., Yoneda, M., Nik Sulaiman, N. M., Ali Mohd, M. (2016). Occurrence, distribution, and dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls and health risk assessment in Selangor River basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188 (10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5595-6
- Lyons, B. P., Barber, J. L., Rumney, H. S., Bolam, T. P. C., Bersuder, P., Law, R. J. et al. (2015). Baseline survey of marine sediments collected from the State of Kuwait: PAHs, PCBs, brominated flame retardants and metal contamination. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100 (2), 629–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.08.014
- El-Aziz El-Maradny, A. A., Turki, A. J., Shaban, Y. A., Sultan, K. M. (2015). Levels and Distribution of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Jeddah Coastal Sediments, Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Journal of the Chemical Society of Pakistan, 37 (3), 599–611.
- Hassan, J., NejatKhah Manavi, P., Darabi, E. (2013). Polychlorinated biphenyls hot and cold seasons distribution in see water, sediment, and fish samples in the Khour-e-Mousa (Mah-Shahr), Iran. Chemosphere, 90 (9), 2477–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.006
- El-Kady, A. A., Abdel-Wahhab, M. A., Henkelmann, B., Belal, M. H., Morsi, M. K. S., Galal, S. M., Schramm, K.-W. (2007). Polychlorinated biphenyl, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and polychlorinated dibenzofuran residues in sediments and fish of the River Nile in the Cairo region. Chemosphere, 68 (9), 1660–1668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.03.066
- Barhoumi, B., LeMenach, K., Dévier, M.-H., El megdiche, Y., Hammami, B., Ameur, W. B. et al. (2013). Distribution and ecological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in surface sediments from the Bizerte lagoon, Tunisia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21 (10), 6290–6302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1709-7
- Iwegbue, C. (2016). Distribution and ecological risks of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in surface sediment of the Forcados River, Niger Delta, Nigeria. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 41 (1), 51–56. https://doi.org/10.2989/16085914.2016.1138926
- Zhang, R., Zhang, F., Zhang, T., Yan, H., Shao, W., Zhou, L., Tong, H. (2014). Historical sediment record and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from tidal flats of Haizhou Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 89 (1-2), 487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.09.001
- Bazzanti, M., Chiavarini, S., Cremisini, C., Soldati, P. (1997). Distribution of PCB congeners in aquatic ecosystems: A case study. Environment International, 23 (6), 799–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0160-4120(97)00092-5
- Wenning, R. J., Bonnevie, N. L., Huntley, S. L. (1994). Accumulation of metals, polychlorinated biphenyls, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the lower Passaic River, New Jersey. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 27 (1), 64–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00203890
- Ssebugere, P., Sillanpää, M., Kiremire, B. T., Kasozi, G. N., Wang, P., Sojinu, S. O. et al. (2014). Polychlorinated biphenyls and hexachlorocyclohexanes in sediments and fish species from the Napoleon Gulf of Lake Victoria, Uganda. Science of The Total Environment, 481, 55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.039
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2024 Rafid A. Al-Zabad, Ayad H. Al-Khafaji, Hamid T. AL-Saad

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








