Залежність каталітичної активності цеолітних каталізаторів від типу модифікування в процесі низькотемпературного крекінгу полістиролу
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.323963Ключові слова:
полістирол, каталітичний крекінг, каталітичний піроліз, кліноптилоліт, кислотна активація, оксиди металівАнотація
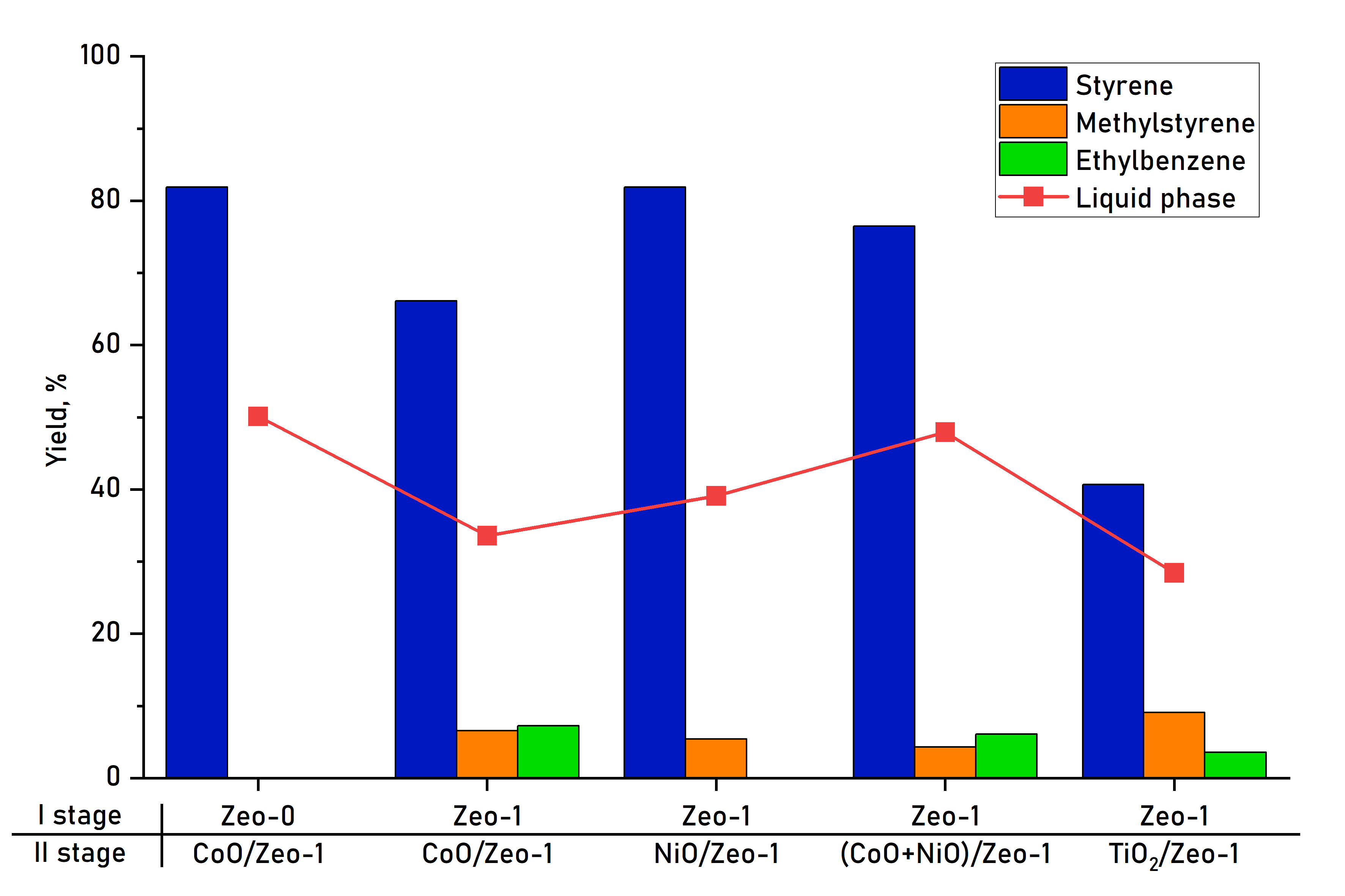
Об’єктом дослідження є каталітичний крекінг полістиролу у водневому середовищі у присутності каталізаторів на основі природного цеоліту. Каталізатори синтезовано шляхом кислотної активації цеоліту та подальшого його модифікування нікель (ІІ) оксидом, кобальт (ІІ) оксидом та титан (IV) оксидом. Одним із найбільш проблемних місць є те, що поряд зі швидким накопиченням відходів пластику у довкіллі, зокрема полістиролу, досі відсутні діючі низьковартісні та ефективні промислові технології його переробки у цінні продукти. Сучасні методи переробки пластику часто потребують високих температур і значних енергетичних витрат, що знижує їх економічну та екологічну доцільність. Тому розробка технологій з використанням дешевих природних матеріалів для створення каталізаторів крекінгу пластику досі залишається актуальною та затребуваною. Отримано низьковартісні каталізатори на основі природного кліноптилоліту українського родовища, площа поверхні яких після кислотної активації значно збільшувалась, але суттєвого впливу активації на вихід рідкої фази та селективність за стиролом не було виявлено. Таким чином, природний кліноптилоліт сам по собі проявив каталітичну активність, співрозмірну з активністю його кислотно-активованої форми. Подальше модифікування зразків каталізаторів оксидами металів (NiO, CoO, TiO2) суттєво збільшило їх каталітичну активність, що підтверджено методом газової хроматографії. Результати дослідження демонструють вихід рідкої фази у діапазоні від 40 % до 80 % з високою селективністю за стиролом, яка в окремих випадках перевищувала 80 %. Це пов’язано з тим, що запропонований метод синтезу каталізаторів має ряд особливостей: кислотна активація дозволяє видалити природні домішки та збільшити поверхневу площу контакту фаз реагентів, що є важливим в процесах гетерогенного каталізу, а модифікування оксидами металів забезпечує утворення додаткових каталітичних центрів. Завдяки тому, що вартість синтезованих каталізаторів зменшується через використання дешевих природних цеолітів українського походження і значно знижує температуру крекінгу, запропонований спосіб переробки полістиролу може бути перспективним і економічно доцільним для впровадження в промислові процеси. Також забезпечується отримання стиролу з високою селективністю, це дозволяє значно знизити витрати на енергію та матеріали у порівнянні з традиційними технологіями. У порівнянні з аналогічними відомими технологіями переробки полімерів, використання природного кліноптилоліту як бази для синтезу каталізаторів крекінгу дозволяє запропонувати ефективну і «зелену» технологію утилізації пластикових відходів.
Посилання
- Yanushevska, O., Dontsova, T., Krymets, G., Kyrii, S., Krasuliak, O., Dorozhko, K.; Fesenko, O., Yatsenko, L. (Eds.) (2023). Prospects for the Catalytic Conversion of Plastic Waste. Nanooptics and Photonics. Nanochemistry and Nanobiotechnology, and Their Applications. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18104-7_5
- Gonzalez-Aguilar, A. M., Pérez-García, V., Riesco-Ávila, J. M. (2023). A Thermo-Catalytic Pyrolysis of Polystyrene Waste Review: A Systematic, Statistical, and Bibliometric Approach. Polymers, 15 (6), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061582
- Kik, K., Bukowska, B., Sicińska, P. (2020). Polystyrene nanoparticles: Sources, occurrence in the environment, distribution in tissues, accumulation and toxicity to various organisms. Environmental Pollution, 262, 114297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114297
- Kyrii, S., Dontsova, T., Karaschuk, O., Yanushevska, O.; Fesenko, O., Yatsenko, L. (Eds.) (2023). State of the Art of Microplastic and Nanoplastic Pollution: Origin and Removal Methods. Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites, Nanostructure Surfaces, and Their Applications. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 229–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-18096-5_12
- Tokiwa, Y., Calabia, B. P., Ugwu, C. U., Aiba, S. (2009). Biodegradability of Plastics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 10 (9), 3722–3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093722
- Rehan, M., Miandad, R., Barakat, M. A., Ismail, I. M. I., Almeelbi, T., Gardy, J. et al. (2017). Effect of zeolite catalysts on pyrolysis liquid oil. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 119, 162–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.11.015
- Polystyrene waste or scrap (HS: 391520) Product Trade, Exporters and Importers. The Observatory of Economic Complexity. Available at: https://oec.world/en/profile/hs/polystyrene-waste-or-scrap
- Zhang, X., Xu, S., Tang, J., Fu, L., Karimi-Maleh, H. (2022). Sustainably Recycling and Upcycling of Single-Use Plastic Wastes through Heterogeneous Catalysis. Catalysts, 12 (8), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12080818
- Inayat, A., Fasolini, A., Basile, F., Fridrichova, D., Lestinsky, P. (2022). Chemical recycling of waste polystyrene by thermo-catalytic pyrolysis: A description for different feedstocks, catalysts and operation modes. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 201, 109981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109981
- Dewangga, P. B., Rochmadi, Purnomo, C. W. (2020). Styrene Recovery from the Pyrolysis of Polystyrene Waste Using Bentonite and Natural Zeolite Catalyst. Key Engineering Materials, 849, 84–89. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.849.84
- Yanushevska, O. I., Dontsova, T. A., Aleksyk, A. I., Vlasenko, N. V., Didenko, O. Z., Nypadymka, A. S. (2020). Surface and Structural Properties of Clay Materials Based on Natural Saponite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 68 (5), 465–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42860-020-00088-4
- Maafa, I. (2021). Pyrolysis of Polystyrene Waste: A Review. Polymers, 13 (2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020225
- Miandad, R., Barakat, M. A., Rehan, M., Aburiazaiza, A. S., Ismail, I. M. I., Nizami, A. S. (2017). Plastic waste to liquid oil through catalytic pyrolysis using natural and synthetic zeolite catalysts. Waste Management, 69, 66–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.032
- Verma, A., Sharma, S., Pramanik, H. (2021). Pyrolysis of waste expanded polystyrene and reduction of styrene via in-situ multiphase pyrolysis of product oil for the production of fuel range hydrocarbons. Waste Management, 120, 330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.11.035
- Lee, S. Y., Yoon, J. H., Kim, J. R., Park, D. W. (2001). Catalytic degradation of polystyrene over natural clinoptilolite zeolite. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 74 (2), 297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0141-3910(01)00162-8
- Montalvo, S., Guerrero, L., Borja, R., Sánchez, E., Milán, Z., Cortés, I., Angeles de la la Rubia, M. (2012). Application of natural zeolites in anaerobic digestion processes: A review. Applied Clay Science, 58, 125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.01.013
- Pal, P.; Pal, P. (Ed.) (2017). Nanotechnology in Water Treatment. Industrial Water Treatment Process Technology. Butterworth-Heinemann, 513–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-810391-3.00007-2
- Tran, Y. T., Lee, J., Kumar, P., Kim, K.-H., Lee, S. S. (2019). Natural zeolite and its application in concrete composite production. Composites Part B: Engineering, 165, 354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.084
- Sokyrnytskyi tseolitovyi zavod TZOV. Available at: https://zeolite.ub.ua/
- Ivanenko, O. I., Nosachova, Yu. V., Krysenko, T. V. (2020). Comprehensive use of natural clinoptylolite in environmental protection technologies. Proceedings of the NTUU “Igor Sikorsky KPI”. Series: Chemical Engineering, Ecology and Resource Saving, 4, 66–82. https://doi.org/10.20535/2617-9741.4.2020.219786
- Pavlovskyi, D. O., Krymets, H. V., Yanushevska, O. I., Levandovskyi, I. A., Dontsova, T. O. (2024). Perspectives of low-temperature atmospheric pressure catalytic decomposition of polystyrene. Journal of Chemistry and Technologies, 32 (2), 276–283. https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i2.286999
- Field, L. D., Sternhell, S., Kalman, J. R. (2013). Organic Structures from Spectra. Wiley, 510.
- Thommes, M., Kaneko, K., Neimark, A. V., Olivier, J. P., Rodriguez-Reinoso, F., Rouquerol, J., Sing, K. S. W. (2015). Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 87 (9-10), 1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Viktor Kurylenko, Olena Yanushevska, Tetiana Dontsova

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








