Розробка концепції задачі ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.326479Ключові слова:
інформаційна система, управління життєвим циклом системи, управління за властивостями, функція мети, обмеженняАнотація
Об’єкт дослідження – процеси функціонування та супроводження, які у сукупності визначають стадію експлуатації інформаційної системи.
Дослідження присвячено вирішенню проблеми формального управління життєвим циклом експлуатованих інформаційних систем управління підприємствами та організаціями. Дослідження в цій галузі спрямовані, переважно, на розробку моделей, методів і технологій управління матеріальними продуктами та програмними застосунками. Питання управління життєвим циклом міждисциплінарних ІТ-продуктів, таких, як інформаційні системи управління підприємствами, залишаються практично недослідженими.
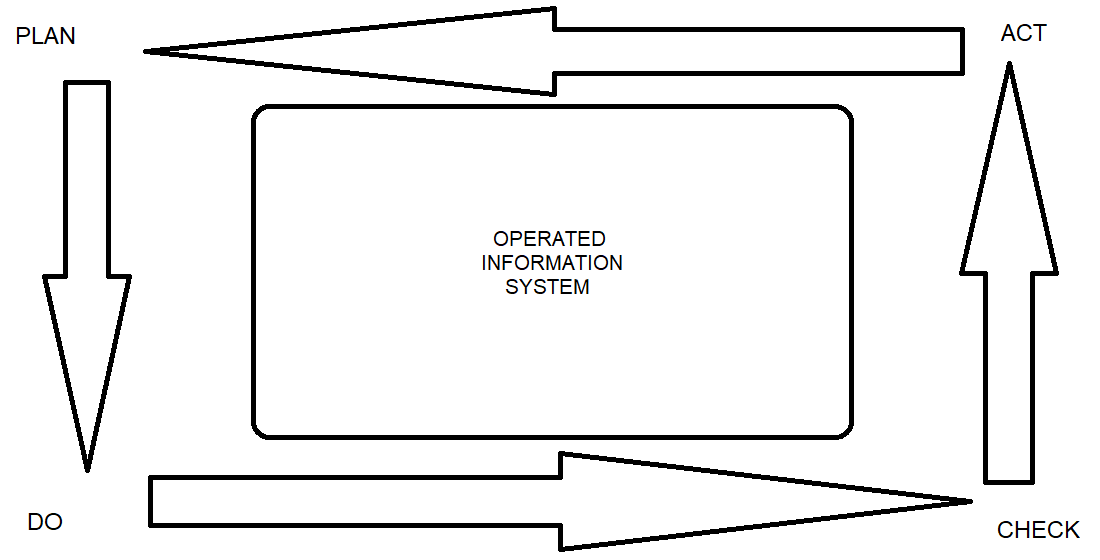
Визначено та формально описано мету та основні обмеження класичного (сталого) управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи. Як головний недолік такого управління визначено можливість значного збільшення кількості запитів на зміну, які виникають внаслідок змін у бізнес-процесах та ІТ-інфраструктурі підприємств та організацій. Тому було запропоновано перейти від концепції класичного (сталого) управління до концепції ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи. Ця концепція дозволяє формально описати задачу ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи як задачу досягнення оптимальних характеристик цієї інформаційної системи за кожною її конкретною властивістю та мінімальної ймовірності існування невирішених інцидентів та запитів на зміни під час стадії експлуатації цієї інформаційної системи. На базі положень цієї концепції розроблено формальні описи функції мети та основних обмежень задачі ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи за її окремими властивостями. Використання цієї концепції дозволяє розглядати класичне (стале) управління як частковий випадок ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи.
Практичне застосування запропонованого формального опису задачі ефективного управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи дозволяє поліпшити SLM-системи управління життєвим циклом експлуатованої інформаційної системи без глобального реінжинірингу існуючих систем і технологій зберігання та обробки даних.
Спонсор дослідження
- Дане дослідження було виконано в рамках госпдоговірної науково-дослідної роботи «Дослідження результатів моніторингу веб-базованої інформаційної системи, що експлуатується», яка виконувалася у Харківському національному університеті радіоелектроніки.
Посилання
- ISO/IEC 20000-1. Information technology – Service management – Part 1: Service management system requirements (2018). Geneva: ISO Copyright Office, 96.
- Levykin, V. M., Evlanov, M. V., Kernosov, M. A. (2014). Patterny proektirovaniia trebovanii k informatcionnym sistemam: modelirovanie i primenenie. Kharkov: OOO “Kompanіia “Smіt”, 320.
- Stark, J. (2020). Product Lifecycle Management (Volume 1). Cham: Springer International. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28864-8
- Schwaber, C. (2006). The Changing Face of Application Life-Cycle Management. Forrester Research Inc. Available at: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/13866040/download-the-changing-face-of-application-life-cycle-mks Last accessed: 07.02.2025
- Rizzo, S. (2016). Why ALM and PLM need each other. Siemens Whitepaper. Available at: https://polarion.plm.automation.siemens.com/hubfs/Docs/Whitepapers/why-alm-and-plm-need-each-other-whitepaper.pdf Last accessed: 07.02.2025
- Wyrwich, F., Kharatyan, A., Dumitrescu, R. (2024). Interdisciplinary system lifecycle management – a systematic literature review. Proceedings of the Design Society, 4, 2765–2774. https://doi.org/10.1017/pds.2024.280
- Liepert, C., Stary, C., Lamprecht, A., Zügn, D.; Elstermann, M., Lederer, M. (Eds.) (2025). Interoperable Product Change Management Within Engineering: A Digital Twin Approach. Subject-Oriented Business Process Management. Models for Designing Digital Transformations. S-BPM ONE 2024. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Vol. 2206. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72041-3_17
- Chappell, D. (2010). What is Application Lifecycle Management? David Chappell and Associates. Available at: http://davidchappell.com/writing/white_papers/What_is_ALM_v2.0--Chappell.pdf Last accessed 07.02.2025
- Eigner, M. (2021). System Lifecycle Management: Digitalisierung des Engineering. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Vieweg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-62183-7
- Binder, C., Neureiter, C., Lüder, A. (2022). Towards a domain-specific information architecture enabling the investigation and optimization of flexible production systems by utilizing artificial intelligence. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 123 (1-2), 49–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10141-2
- Colantoni, A., Berardinelli, L., Garmendia, A., Bräuer, J. (2022). Towards Blended Modeling and Simulation of DevOps Processes: the Keptn Case Study. MODELS '22: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems: Companion Proceedings, Association for Computing Machinery. New York, 784–792. https://doi.org/10.1145/3550356.3561597
- Gulzar, K., Ruusu, R., Sierla, S., Aarnio, P., Karhela, T., Vyatkin, V. (2018). Automatic Generation of a Lifecycle Analysis Model from a First Principles Industrial Process Simulation Model. 2018 IEEE 16th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN). Danvers, 741–746. https://doi.org/10.1109/indin.2018.8471980
- Calderon, N. N., Kajko-Mattsson, M., Nolan, A. J. (2015). Successful process improvement projects are no accidents. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, 27 (11), 896–911. https://doi.org/10.1002/smr.1738
- Reiff-Marganiec, S., Tilly, M. (Eds.) (2012). Handbook of Research on Service-Oriented Systems and Non-Functional Properties: Future Directions. IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-61350-432-1
- Driss, M., Aljehani, A., Boulila, W., Ghandorh, H., Al-Sarem, M. (2020). Servicing Your Requirements: An FCA and RCA-Driven Approach for Semantic Web Services Composition. IEEE Access, 8, 59326–59339. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.2982592
- Kienzle, J., Combemale, B., Mussbacher, G., Alam, O., Bordeleau, F., Burgueno, L. et al. (2022). Global Decision Making Over Deep Variability in Feedback-Driven Software Development. Proceedings of the 37th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering. New York. https://doi.org/10.1145/3551349.3559551
- Moosbauer, J., Binder, M., Schneider, L., Pfisterer, F., Becker, M., Lang, M. et al. (2022). Automated Benchmark-Driven Design and Explanation of Hyperparameter Optimizers. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 26 (6), 1336–1350. https://doi.org/10.1109/tevc.2022.3211336
- Garouani, M., Ahmad, A., Bouneffa, M., Hamlich, M., Bourguin, G., Lewandowski, A. (2022). Using meta-learning for automated algorithms selection and configuration: an experimental framework for industrial big data. Journal of Big Data, 9 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-022-00612-4
- Bush, B., Stright, D., Huggins, J., Newes, E. (2022). Simulation process and data flow for a large system dynamics model. Simulation, 98 (9), 823–833. https://doi.org/10.1177/00375497221093381
- Ebert, C. (2013). Improving engineering efficiency with PLM/ALM. Software & Systems Modeling, 12 (3), 443–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10270-013-0347-3
- Deuter, A., Imort, S. (2020). PLM/ALM Integration With The Asset Administration Shell. Procedia Manufacturing, 52, 234–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2020.11.040
- Deuter, A., Otte, A., Höllisch, D. (2017). Methodisches Vorgehen zur Entwicklung und Evaluierung von Anwendungsfällen für die PLM/ALM-Integration. Wissenschaftsforum Intelligente Technische Systeme (WInTeSys). Paderborn, 211–222. https://doi.org/10.17619/UNIPB/1-93
- Petrichenko, O. V. (2021). Improving enterprise IT-service management methodology. Management Information System and Devises, 177, 4–12. https://doi.org/10.30837/0135-1710.2021.177.004
- Kanaga Priya, P., Reethika, A.; Mishra, A., El Barachi, M., Kumar, M. (Eds.) (2024). A Review of Digital Twin Applications in Various Sectors. Transforming Industry using Digital Twin Technology. Cham: Springer, 239–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-58523-4_12
- Guinea-Cabrera, M. A., Holgado-Terriza, J. A. (2024). Digital Twins in Software Engineering – A Systematic Literature Review and Vision. Applied Sciences, 14 (3), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14030977
- Fleishman, B.; Patten, B., Jorgenson, S. (Eds). (1995). Stochastic Theory of Complex Ecological Systems. Complex Ecology. Prentice Hall PTP, Prentice Hall Inc, A. Simon & Schuster, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 07632, 166–224.
- Zimmermann, T. C., Konietzko, E., Lindow, K. (2024). Graph-based Parameter Management for Configuration Controlled Multi-level Modeling of Cyber-physical Systems. 2024 19th Annual System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), 270–274. https://doi.org/10.1109/sose62659.2024.10620964
- Katzung, S., Cinkaya, H., Kizgin, U. V., Savinov, A., Baschin, J., Vietor, T. (2024). AI-based analysis and linking of technical and organisational data using graph models as a basis for decision-making in systems engineering. Proceedings of the Design Society, 4, 2625–2634. https://doi.org/10.1017/pds.2024.265
- Rostami, K., Stammel, J., Heinrich, R., Reussner, R. (2017). Change Impact Analysis by Architecture-based Assessment and Planning. Lecture Notes in Informatics, Proceedings – Series of the Gesellschaft fur Informatik. Hannover, 267, 69–70.
- Rostami, K., Heinrich, R., Busch, A., Reussner, R. (2017). Architecture-Based Change Impact Analysis in Information Systems and Business Processes. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA). Gothenburg, 179–188. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsa.2017.17
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Viktor Levykin, Maksym Ievlanov, Ihor Levykin, Oleksandr Рetrychenko

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








