Ефективність перетворення енергії в електромеханічній системі з магнітним редуктором рухомого складу пасажирського електротранспорту
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.344863Ключові слова:
ефективність, магнітна передача, редуктор, демпфування, жорсткість, електротранспорт, тяговий електропривод, крутний моментАнотація
Об’єктом дослідження є електромеханічні процеси в тяговому електроприводі рухомого складу пасажирського електротранспорту при дії сильних і короткочасних моментів збурення під час розгону, руху з усталеною швидкістю та сповільнення.
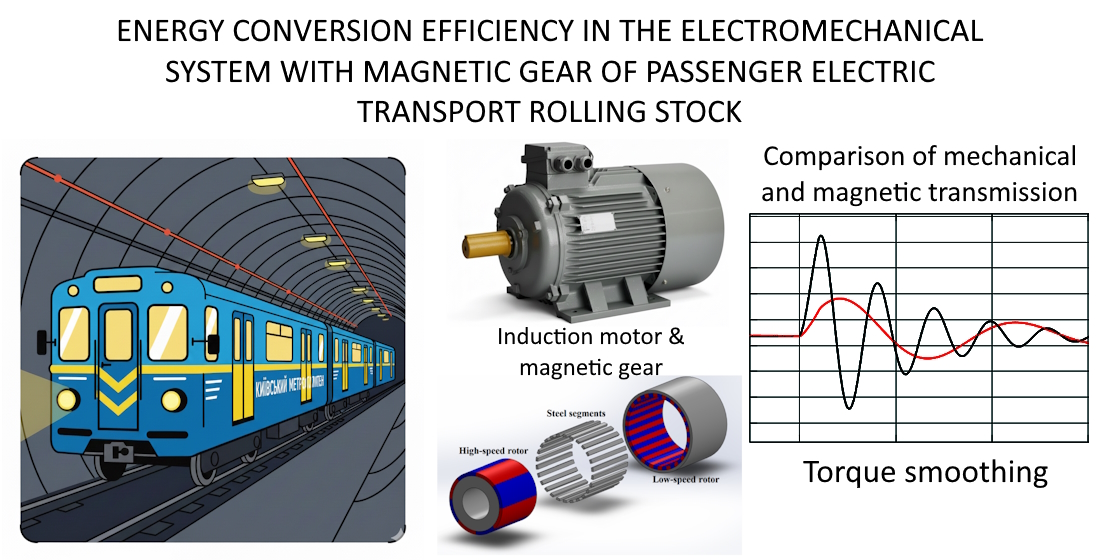
Проблема, що розглядалася, полягала в визначенні впливу параметрів магнітного редуктора на зниження дії зовнішніх збурень на електромеханічну систему рухомого складу метрополітену. Аналіз виконувався на основі порівняння типового тягового електропривода з механічним редуктором та запропонованого електропривода з магнітним редуктором. Даний редуктор передає рухомий момент до колісних пар без механічного контакту, але при цьому обумовлює пружно-в’язкий зв’язок між його вхідним та вихідним валами.
Наведено порівняння поведінки електромеханічної системи з використанням типового механічного редуктора та запропонованого магнітного редуктора. Досліджено вплив на показники ефективності перетворення енергії зміни параметрів магнітного редуктора, зокрема магнітної жорсткості та коефіцієнта демпфування. В ході досліджень виявлено відмінності у залежностях амплітуди моментів, періоду власних коливань, часу згасання перехідного процесу для двох типів редукторів. При жорсткості магнітного редуктора 5000 Нм/рад амплітуда моменту зменшилась на 59% у порівнянні з механічним редуктором. Період власних коливань зменшився на 62%, а затухання перехідного процесу збільшилося на 59%. Результати дослідження показали, що раціональний вибір параметрів магнітного редуктора дозволяє підвищити динамічну стійкість електропривода до короткочасних збурень. При цьому зменшуються ударні навантаження на вал двигуна та амплітуда коливань моменту. Це особливо актуально для тягових систем транспорту, що працюють в умовах нерівномірного опору руху.
Практична цінність результатів роботи полягає у можливості покращити ефективність перетворення енергії та показники якості керування тягового електропривода рухомого складу пасажирського електротранспорту. Це дослідження буде корисним для науковців та фірм, що спеціалізуються в області рухомого складу пасажирського електротранспорту.
Посилання
- Atallah, K., Wang, J., Calverley, S. D., Duggan, S. (2012). Design and Operation of a Magnetic Continuously Variable Transmission. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 48 (4), 1288–1295. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2012.2199451
- Tlali, P. M., Wang, R.-J., Gerber, S. (2014). Magnetic gear technologies: A review. 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM). Berlin, 544–550. https://doi.org/10.1109/icelmach.2014.6960233
- Atallah, K., Howe, D. (2001). A novel high-performance magnetic gear. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 37 (4), 2844–2846. https://doi.org/10.1109/20.951324
- Atallah, K., Rens, J., Mezani, S., Howe, D. (2008). A Novel “Pseudo” Direct-Drive Brushless Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 44 (11), 4349–4352. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmag.2008.2001509
- Jing, L., Chen, J., Huang, Z. (2019). Analysis of Magnetic Field of Magnetic Gear during Overload. 2019 4th International Conference on Intelligent Green Building and Smart Grid (IGBSG). Hubei, 557–558. https://doi.org/10.1109/igbsg.2019.8886243
- Wang, J., Atallah, K. (2009). Modeling and control of ‘pseudo’ direct-drive brushless permanent magnet machines. 2009 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference. Miami, 870–875. https://doi.org/10.1109/iemdc.2009.5075306
- Bouheraoua, M., Wang, J., Atallah, K. (2014). Speed Control for a Pseudo Direct Drive Permanent-Magnet Machine With One Position Sensor on Low-Speed Rotor. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 50 (6), 3825–3833. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2014.2322139
- O’Sullivan, T. M., Bingham, C. M., Schofield, N. (2006). High-Performance Control of Dual-Inertia Servo-Drive Systems Using Low-Cost Integrated SAW Torque Transducers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 53 (4), 1226–1237. https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2006.878311
- Zhang, G., Furusho, J. (1999). Speed control of two-inertia system by PI/PID control. Proceedings of the IEEE 1999 International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems. PEDS’99 (Cat. No.99TH8475). Hong Kong, 1, 567–572. https://doi.org/10.1109/peds.1999.794627
- Montague, R. G., Atallah, K., Bingham, C. M. (2010). Characterisation and modelling of magnetic couplings and gears for servo control systems. 5th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2010). Brighton, 232–232. https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2010.0188
- Desvaux, M., Le Goff Latimier, R., Multon, B., Sire, S., Ben Ahmed, H. (2016). Analysis of the dynamic behaviour of magnetic gear with nonlinear modelling for large wind turbines. 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM). Lausanne, 1332–1338. https://doi.org/10.1109/icelmach.2016.7732697
- PDD® High Torque Traction Motor. Available at: https://www.magnomatics.com/_files/ugd/afb904_3f9af3d122ce4f96a450da2a89a1a103.pdf
- Yang, Z., Shang, F., Brown, I. P., Krishnamurthy, M. (2015). Comparative Study of Interior Permanent Magnet, Induction, and Switched Reluctance Motor Drives for EV and HEV Applications. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 1 (3), 245–254. https://doi.org/10.1109/tte.2015.2470092
- Bozhko, S., Dymko, S., Kovbasa, S., Peresada, S. M. (2017). Maximum Torque-per-Amp Control for Traction IM Drives: Theory and Experimental Results. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 53 (1), 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2016.2608789
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Mykola Ostroverkhov, Liudmyla Spinul, Heorhii Veshchykov

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








