Neurohormonal changes and intestinal barrier function disorders in irritable bowel syndrome in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and their correction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4798.2025.332826Keywords:
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic-associated fatty liver disease, irritable bowel syndrome, neurohormones (serotonin, melatonin), intestinal barrier function, neuropsychometric tests, probioticAbstract
The study of neuropsychometric disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in combination with metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) can expand the diagnostic aspects and treatment options for patients with combined pathology.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of neurohormone levels and intestinal barrier function disorders on neuropsychometric changes in patients with IBS and MAFLD, as well as their correction.
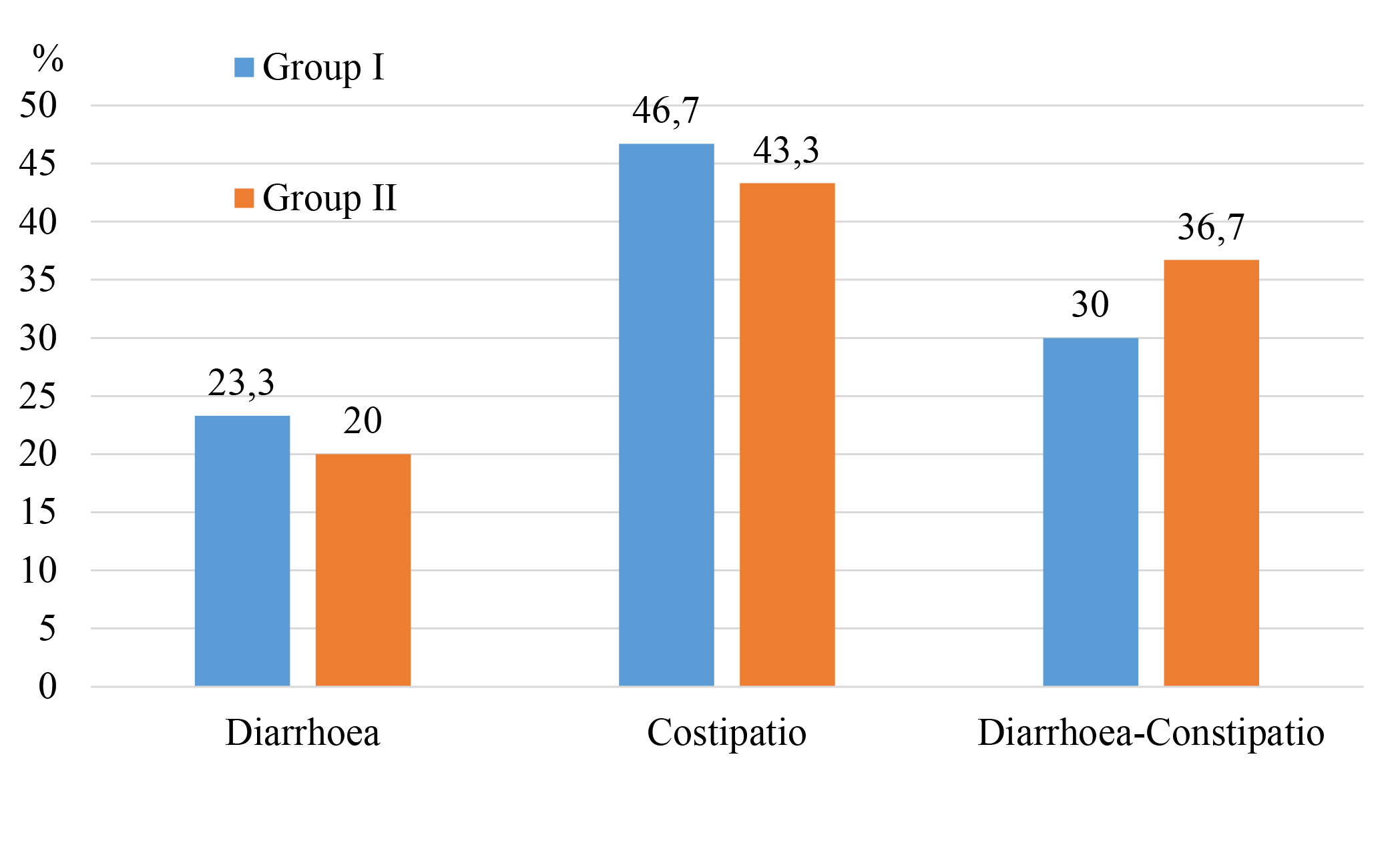
Materials and methods. We examined 60 patients with IBS in the setting of MAFLD. The level of melatonin (MT) and serotonin (ST) in the blood serum was determined. The levels of α1-antitrypsin (α1-AT) and zonulin in the blood serum and faeces of the examined patients were evaluated. Patients were divided into two groups. The first group of patients (n=30) received only basic therapy. The second group of patients (n=30), in addition to the basic treatment, received the symbiotic drug Lothardi-A. The subjects were assessed for central nervous system dysfunction (Spielberg and Khanin self-esteem scale; Beck Depression Scale; Zang scale; Toronto Alexithymic Scale).
Research results. The obtained results confirm the positive effect of Lothardi A on improving the permeability of the intestinal barrier and the level of neurohormones in the blood serum in IBS and MAFLD. Additionally, a pronounced positive dynamic in the indicators of neuropsychotrauma is observed in these patients.
Conclusions: Changes in the level of ST and MT in the blood serum, which correlate with the severity of intestinal barrier function disorders, were diagnosed in patients with IBS and MAFLD. In patients with IBS and MAFLD, neuropsychometric status disorders were found. The course prescription of Lotardi-A as part of complex therapy for patients with IBS and MAFLD is pathogenetically justified and leads not only to the improvement of clinical symptoms but also contributes to the improvement of dysbiotic changes, impaired intestinal barrier function, normalization of serum levels of ST, MT, which is a prerequisite for improving the mental status of these patients
References
- Shaikh, S. D., Sun, N., Canakis, A., Park, W. Y., Weber, H. C. (2023). Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Gut Microbiome: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12 (7), 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072558
- Sperber, A. D., Bangdiwala, S. I., Drossman, D. A., Ghoshal, U. C., Simren, M., Tack, J. et al. (2021). Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology, 160 (1), 99–114.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.014
- Sperber, A. D., Dumitrascu, D., Fukudo, S., Gerson, C., Ghoshal, U. C., Gwee, K. A., Hungin, A. P. S. et al. (2016). The global prevalence of IBS in adults remains elusive due to the heterogeneity of studies: a Rome Foundation working team literature review. Gut, 66 (6), 1075–1082. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311240
- Purssell, H., Whorwell, P. J., Athwal, V. S., Vasant, D. H. (2021). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in irritable bowel syndrome: More than a coincidence? World Journal of Hepatology, 13 (12), 1816–1827. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1816
- Oka, P., Parr, H., Barberio, B., Black, C. J., Savarino, E. V., Ford, A. C. (2020). Global prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to Rome III or IV criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 5 (10), 908–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(20)30217-x
- Staudacher, H. M., Black, C. J., Teasdale, S. B., Mikocka-Walus, A., Keefer, L. (2023). Irritable bowel syndrome and mental health comorbidity – approach to multidisciplinary management. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 20 (9), 582–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-023-00794-z
- Zamani, M., Alizadeh‐Tabari, S., Zamani, V. (2019). Systematic review with meta‐analysis: the prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 50 (2), 132–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.15325
- Liu, Q., He, H., Yang, J., Feng, X., Zhao, F., Lyu, J. (2020). Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 126, 134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2019.08.002
- Black, C. J., Ford, A. C. (2020). Global burden of irritable bowel syndrome: trends, predictions and risk factors. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 17 (8), 473–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-020-0286-8
- Younossi, Z. M., Golabi, P., Paik, J. M., Henry, A., Van Dongen, C., Henry, L. (2023). The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology, 77 (4), 1335–1347. https://doi.org/10.1097/hep.0000000000000004
- Tinajero, M. G., Malik, V. S. (2021). An Update on the Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 50 (3), 337–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2021.05.013
- Lin, X., Xu, Y., Pan, X., Xu, J., Ding, Y., Sun, X. (2020). Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: an analysis from 1990 to 2025. Scientific Reports, 10 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71908-9
- Golabi, P., Otgonsuren, M., de Avila, L., Sayiner, M., Rafiq, N., Younossi, Z. M. (2018). Components of metabolic syndrome increase the risk of mortality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Medicine, 97 (13), e0214. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000010214
- Powell, E. E., Wong, V. W.-S., Rinella, M. (2021). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The Lancet, 397 (10290), 2212–2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32511-3
- Xiong, R.-G., Li, J., Cheng, J., Zhou, D.-D., Wu, S.-X., Huang, S.-Y. et al. (2023). The Role of Gut Microbiota in Anxiety, Depression, and Other Mental Disorders as Well as the Protective Effects of Dietary Components. Nutrients, 15 (14), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143258
- Fasano, A. (2020). All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research, 9, 69. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20510.1
- Mörkl, S., Lackner, S., Meinitzer, A., Mangge, H., Lehofer, M., Halwachs, B. et al. (2018). Gut microbiota, dietary intakes and intestinal permeability reflected by serum zonulin in women. European Journal of Nutrition, 57 (8), 2985–2997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1784-0
- Kwon, J., Lee, H. G., Seo, K., Kim, H. (2018). Combination of Whole Grapeseed Flour and Newly Isolated Kefir Lactic Acid Bacteria Reduces High‐Fat‐Induced Hepatic Steatosis. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 63(4). Portico. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201801040
- Ohlsson, B., Orho-Melander, M., Nilsson, P. (2017). Higher Levels of Serum Zonulin May Rather Be Associated with Increased Risk of Obesity and Hyperlipidemia, Than with Gastrointestinal Symptoms or Disease Manifestations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18 (3), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030582
- Barbaro, M. R., Cremon, C., Morselli-Labate, A. M., Di Sabatino, A., Giuffrida, P., Corazza, G. R. et al. (2020). Serum zonulin and its diagnostic performance in non-coeliac gluten sensitivity. Gut, 69 (11), 1966–1974. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319281
- Singh, P., Silvester, J., Chen, X., Xu, H., Sawhney, V., Rangan, V., Iturrino, J. et al. (2019). Serum zonulin is elevated in IBS and correlates with stool frequency in IBS‐D. United European Gastroenterology Journal, 7 (5), 709–715. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640619826419
- Asmar, R. E., Panigrahi, P., Bamford, P., Berti, I., Not, T., Coppa, G. V. et al. (2002). Host-dependent zonulin secretion causes the impairment of the small intestine barrier function after bacterial exposure. Gastroenterology, 123 (5), 1607–1615. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.36578
- Ko, M., Kamimura, K., Owaki, T., Nagoya, T., Sakai, N., Nagayama, I. et al. (2021). Modulation of serotonin in the gut-liver neural axis ameliorates the fatty and fibrotic changes in non-alcoholic fatty liver. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 14 (3). https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.048922
- Namkung, J., Shong, K. E., Kim, H., Oh, C.-M., Park, S., Kim, H. (2018). Inhibition of Serotonin Synthesis Induces Negative Hepatic Lipid Balance. Diabetes & Metabolism Journal, 42 (3), 233–243. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0084
- Atallah, M. A. A., Elaidy, S. M., Tawfik, M. K. (2018). Assessment of the possible roles of SB-269970 versus ketanserin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Oxidative stress/TGF-β 1 -induced HSCs activation pathway. Pharmacological Reports, 70 (3), 509–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.11.017
- Ford, A. C., Sperber, A. D., Corsetti, M., Camilleri, M. (2020). Irritable bowel syndrome. The Lancet, 396 (10263), 1675–1688. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31548-8
- Gros, M., Gros, B., Mesonero, J. E., Latorre, E. (2021). Neurotransmitter Dysfunction in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Emerging Approaches for Management. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10 (15), 3429. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153429
- Kumar, A., Pramanik, J., Goyal, N., Chauhan, D., Sivamaruthi, B. S., Prajapati, B. G., Chaiyasut, C. (2023). Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression: Unveiling the Relationships and Management Options. Pharmaceuticals, 16 (4), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040565
- Nobis, A., Zalewski, D., Waszkiewicz, N. (2020). Peripheral Markers of Depression. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9 (12), 3793. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123793
- Beaglehole, B., Mulder, R. T., Frampton, C. M., Boden, J. M., Newton-Howes, G., Bell, C. J. (2018). Psychological distress and psychiatric disorder after natural disasters: systematic review and meta-analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 213 (6), 716–722. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.2018.210
- Chaves, C., Castellanos, T., Abrams, M., Vazquez, C. (2018). The impact of economic recessions on depression and individual and social well-being: the case of Spain (2006–2013). Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 53 (9), 977–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-018-1558-2
- Bear, T. L. K., Dalziel, J. E., Coad, J., Roy, N. C., Butts, C. A., Gopal, P. K. (2020). The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Dietary Interventions for Depression and Anxiety. Advances in Nutrition, 11 (4), 890–907. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmaa016
- Shabbir, M. A., Mehak, F., Khan, Z. M., Ahmed, W., Haq, S. M. A. U., Khan, M. R. et al. (2022). Delving the role of nutritional psychiatry to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic induced stress, anxiety and depression. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 120, 25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.12.035
- Álvarez, S. A., Rocha-Guzmán, N. E., González-Laredo, R. F., Gallegos-Infante, J. A., Moreno-Jiménez, M. R., Bravo-Muñoz, M. (2022). Ancestral Food Sources Rich in Polyphenols, Their Metabolism, and the Potential Influence of Gut Microbiota in the Management of Depression and Anxiety. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 70 (4), 944–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06151
- Zhang, B., Chen, T., Cao, M., Yuan, C., Reiter, R. J., Zhao, Z. et al. (2022). Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Induced by Decreasing Endogenous Melatonin Mediates the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Obesity. Frontiers in Immunology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.900132
- Rothschild, D., Weissbrod, O., Barkan, E., Kurilshikov, A., Korem, T., Zeevi, D. et al. (2018). Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature, 555 (7695), 210–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25973
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yelyzaveta Sirchak

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.
Authors, who are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. The authors reserve the right to authorship of the work and pass the first publication right of this work to the journal under the terms of a Creative Commons CC BY, which allows others to freely distribute the published research with the obligatory reference to the authors of the original work and the first publication of the work in this journal.
2. The authors have the right to conclude separate supplement agreements that relate to non-exclusive work distribution in the form in which it has been published by the journal (for example, to upload the work to the online storage of the journal or publish it as part of a monograph), provided that the reference to the first publication of the work in this journal is included.








