Justification of the optimal option and transportation parameters for export supplies using marine transport
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2023.277804Keywords:
vessel deadweight, sea transportation, transport support, export production, sales logisticsAbstract
The object of this research is transport provision of supplies using sea transport. The problem of increasing the efficiency of transportation of bulk cargo by bulk carriers or universal destination by optimizing the option and parameters of transport equipment is considered.
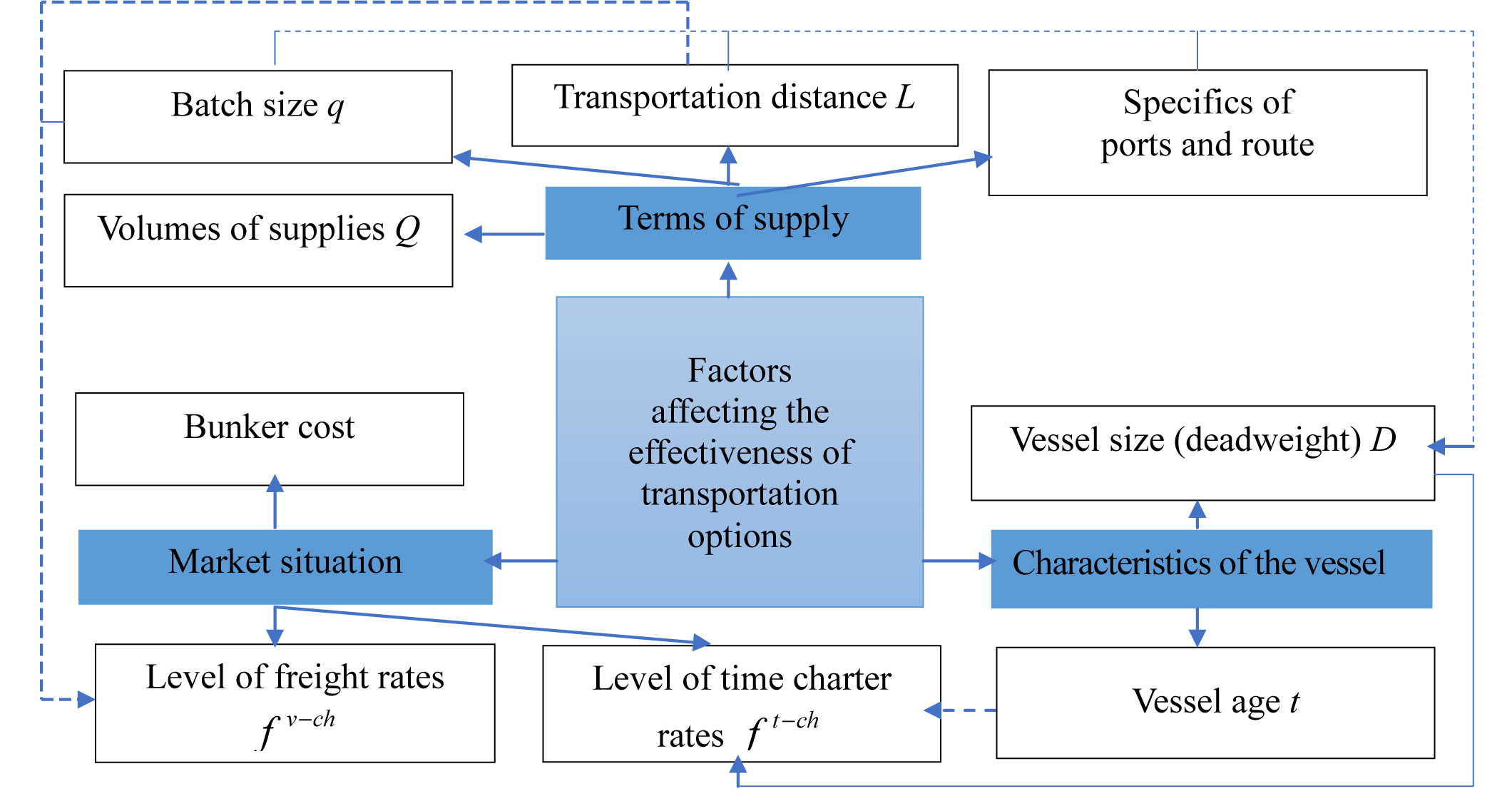
For categories of goods that are exported using sea transport, it is possible to use not only different options for transport equipment – own or leased (for vessels – time charter), but also different options from the point of view of the parameters of the vehicles. In this paper, the parameters are understood as the characteristics of sea vessels, on which the main economic indicators depend – deadweight, which reflects the size of the vessel and its carrying capacity for bulk carriers; as well as the age of the courts, which determines the cost of their rent and the level of operational costs.
The result of the research is an optimization model that allows to determine for each market a variant of transport equipment and its parameters. Model not only distributes deliveries according to transport options, but also determines which vessels of what size and age (for time charter) should carry out transportation. These results are focused on the exporter's decision-making process about sales markets in combination with decisions on transport provision before concluding contracts. Varying the size and age of the vessels makes it possible to consider a wider range of options from the point of view of parameters.
The practical use of the model allows the exporter at the stage of preparation (before the conclusion of contracts) depending on the volume of supplies and the market situation, including the freight one, to make decisions about options for transport support, which is taken into account when formulating transport conditions of contracts. Integral consideration of commercial (volumes of deliveries, transport terms of contracts), economic (price levels, freight rates, costs) and technological (size of vessels and their age) factors within the framework of the model allows taking into account the multifaceted nature of the problem of transport provision.
References
- Rusanova, S., Piterska, V., Onyshchenko, S. (2021). Modelling the project transport support optimal option. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 1 (2 (57)), 43–48. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2021.225288
- Datsko, M. V., Tsvir, L. R. (2016). Construction of transport routes in logistics. Naukovyi visnyk Khersonskoho derzhavnoho universytetu. Seriia: Ekonomichni nauky, 16 (4), 152–155.
- Shramenko, N. Yu. (2015). Effect of process-dependent parameters of the handling-and-storage facility operation on the cargo handling cost. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (3 (77)), 43–47. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2015.51396
- Christiansen, M., Fagerholt, K., Nygreen, B., Ronen, D. (2013). Ship routing and scheduling in the new millennium. European Journal of Operational Research, 228 (3), 467–483. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2012.12.002
- Pečený, L., Meško, P., Kampf, R., Gašparík, J. (2020). Optimisation in Transport and Logistic Processes. Transportation Research Procedia, 44, 15–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2020.02.003
- Juan, A. A., Kelton, W. D., Currie, C. S., Faulin, J. (2018). Simheuristics applications: Dealing with uncertainty in logistics, transportation, and other supply chain areas. Proceedings of the 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC). Gothenburg, 3048–3059. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/wsc.2018.8632464
- Castaneda, J., Ghorbani, E., Ammouriova, M., Panadero, J., Juan, A. A. (2022). Optimizing Transport Logistics under Uncertainty with Simheuristics: Concepts, Review and Trends. Logistics, 6 (3), 42. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics6030042
- Yan, Q., Zhang, Q. (2015). The Optimization of Transportation Costs in Logistics Enterprises with Time-Window Constraints. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2015, 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/365367
- Danchuk, V. D., Svatko, V. V. (2010). Optymizatsiia poshuku shliakhiv po hrafu v zadachakh lohistyky metodom modyfikovanoho murashynoho alhorytmu. Visnyk Natsionalnoho transportnoho universytetu, 20, 109–114.
- Vyshnevskyi, D., Vyshnevska, O., Onyshchenko, S. (2019). Modeling of the distribution of the vessels' time budget under long-term freight contracts within conditions of uncertainty. Development of Management and Entrepreneurship Methods on Transport, 69 (4), 15–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.31375/2226-1915-2019-4-15-25
- Koskina, Yu. O. (2019). Set-theory Approach to Modelling of the Structure of Cargoes Delivery Systems. Visnyk of Vinnytsia Politechnical Institute, 146 (5), 62–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.31649/1997-9266-2019-146-5-62-74
- Plomaritou, E., Papadopoulos, A. (2017). Shipbroking and Chartering Practice. Lloyd’s Practical Shipping Guide. Lloyd’s Shipping Law Library. Abingdon: Routledge, 770. doi: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315689609
- Rusanova, S. (2020). Modeling the costs of project transportation maintenance. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 6 (2 (56)), 19–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2020.221137
- Kovalova, M. (2022). Transport support of foreign trade operations: principles and selection criteria. Economy and Society, 38. doi: https://doi.org/10.32782/2524-0072/2022-38-42
- Onyshchenko, S., Onyshchenko, A. (2022). Dry bulk freight market research based on correlation and regression analysis. Development of management and entrepreneurship methods on transport, 2 (79), 5–17. doi: http://doi.org/10.31375/2226-1915-2022-2-5-17
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Svitlana Onyshchenko, Olha Vyshnevska, Dmytro Vyshnevskyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







