Investigation of drill string dynamics using probabilistic methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.296725Keywords:
drill string, drill string dynamics, impact on rock, nature of oscillations, probabilistic methodsAbstract
The object of research is a drill string. The work is directed to the study of the drill string dynamics and its influence on the rock, which is drilled using probabilistic methods.
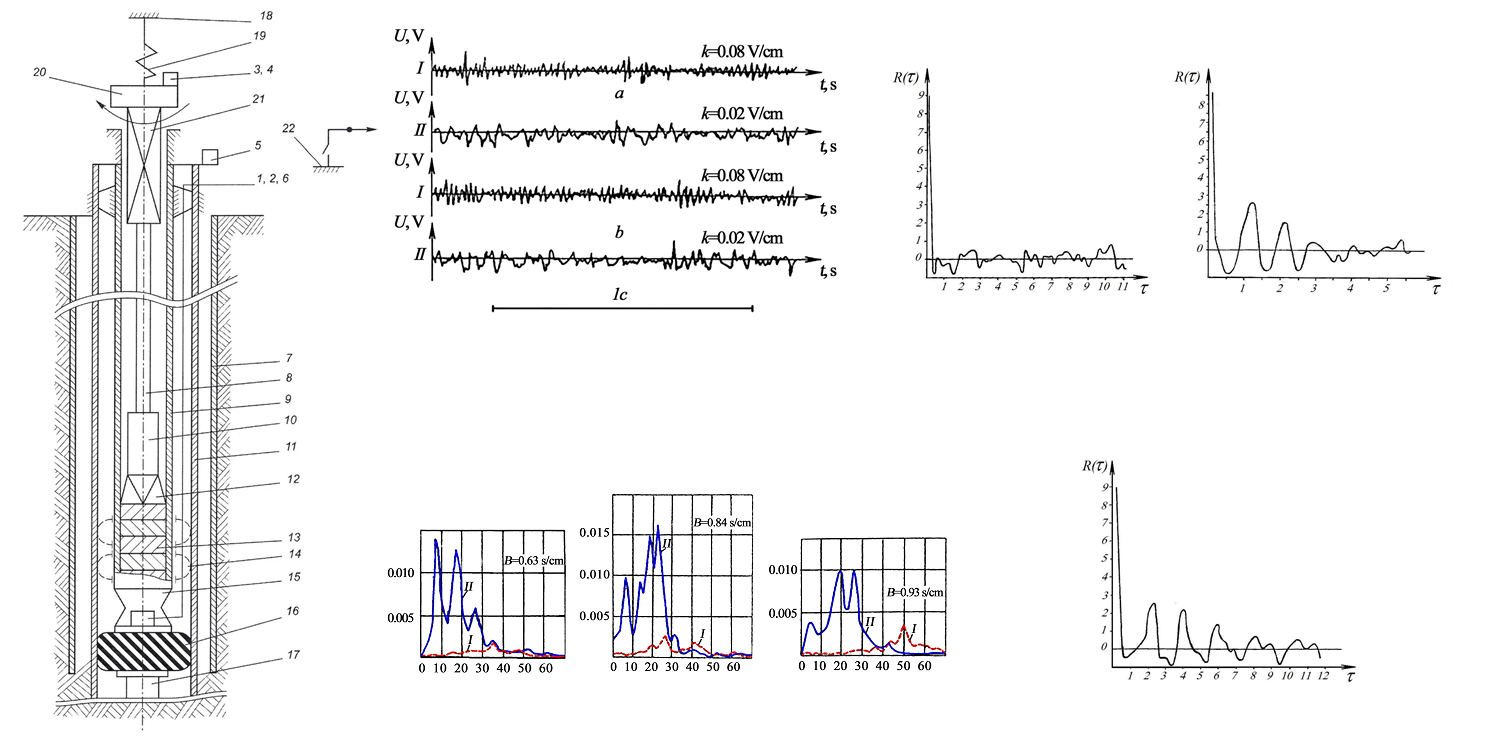
It is shown that the nature of the vibrations of the top of the drill string and the downhole signals are different and have a stationary random character. It is proved that the process at the output of the drill string, taking into account random disturbances, is narrow-band (quasi-harmonic) or close to it. It is found that the energy composition of the spectrum sections and the appearance of resonance peaks and their displacement is directly determined by the physical and mechanical properties of the rocks being drilled, as one of the factors that determines the vibration state of the drill string. Graphs of the spectral density of the power of pitting vibrations are given, showing their amplification at frequencies of 30–40 Hz as the hardness of the rocks being drilled increases. The maximum of the power density bending curve shifts towards low frequencies. There is a «mutual convergence» of the maxima of the power spectral density of the oscillations of the top and bottom of the drill string. It is shown that an important feature of drill string vibrations in the process of drilling with ball bits is that the intensity of vibrations of the top of the drill string passes with frequencies close to low frequencies, and the vibrations of the bottom of the string – to high frequencies.
It is determined that the process at the output of the drill string, taking into account random disturbances, is narrow-band (quasi-harmonic) or close to it. As a result, the assumption of a narrow band at the output of the system, which is the basis of theoretical research, is justified. It is proven that the drill string, as a system with liquid filling under pressure, is more stable compared to a hollow structure. The washing liquid, in this case, plays the role of a dynamic absorber.
References
- Ogorodnikov, P. I. (1991). Ulravlenie uglubleniia skvazhin na baze izucheniia dinamicheskikh protcesov v burilnoi kolone. MINKhiGP im akad. Gubkina I. P., 421.
- Ullah, F. K., Duarte, F., Bohn, C. (2016). A Novel Backstepping Approach for the Attenuation of Torsional Oscillations in Drill Strings. Solid State Phenomena, 248, 85–92. doi: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.248.85
- Iunin, E. K., Khegai, V. K. (2017). Dinamika glubokogo bureniia. Nedra, 285.
- Nikolaenko, H. A. (1967). Veroiatnostnye metody dinamicheskogo rascheta mashinostroitelnykh konstruktcіi. Mashinostroenie, 368.
- Mendil, K., Kiddush, M., Dogman, M. Z. (2020). Modeling of hydrocarbon rotary drilling systems under torsional vibration conditions: a review. Artificial Intelligence and Renewable Energy Towards the Energy Transition. ICAIRES 2020. Cham: Springer, 174, 243–251. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63846-7_24
- Nikolaenko, N. A., Ulianov, C. B. (1977). Statisticheskaia dinamika mashinostroitelnikh konstruktcіi. Mashinostroenie, 368.
- ASTM Standard E756-05, Standard test method for measuring vibration-damping properties of materials (2010). ASTM International.
- Kreuzer, E., Steidl, M. (2011). Controlling torsional vibrations of drill strings via decomposition of traveling waves. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 82 (4), 515–531. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-011-0570-8
- Samarin, A. A. (1979). Vibratcii truboprovodov energeticheskikh ustanovok i metody ikh ustraneniia. Energiia, 266.
- Saadeldin, R., Gamal, H., Elkatatny, S., Abdulraheem, A. (2021). Intelligent Model for Predicting Downhole Vibrations Using Surface Drilling Data During Horizontal Drilling. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 144 (8). doi: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4052794
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Viktor Svitlytskyi, Sergii Iagodovskyi, Iryna Boshkova

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







