Development of a method for processing concentrates from water desalination processes to obtain aluminum coagulants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.329734Keywords:
demineralization, concentrate, reverse osmosis, ion exchange, electrolysis, electrodialysis, coagulant, aluminum chloride, membraneAbstract
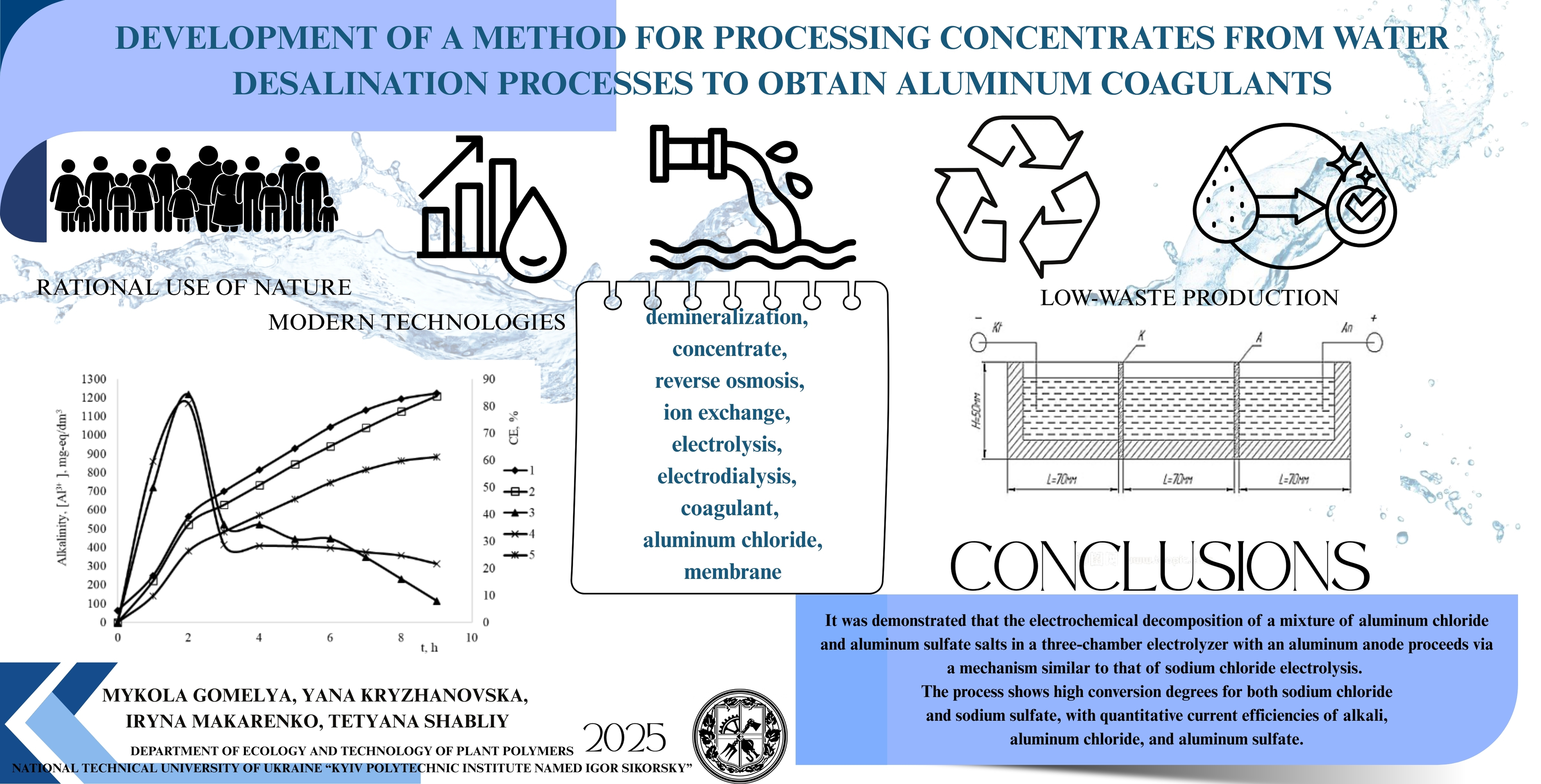
The process of processing concentrates and eluates formed during desalination of natural surface, artesian, and mine waters with increased mineralization by reverse osmosis and ion exchange methods has been studied. Specifically, this study examined the processes of processing sodium chloride solutions and mixtures of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate via electrodialysis, and obtaining alkaline and aluminum salt solutions, were examined.
Aluminum salts were produced using AD-31 aluminum anodes. A stainless-steel plate of grade 12H18N10T was used as the cathode. The process was conducted at current densities ranging from 1.67 to 8.33 A/dm² in two- and three-chamber electrolyzers using MK-40 cation-exchange membranes and MA-41 anion-exchange membranes. In all experiments, alkaline solutions were obtained in the cathode region and aluminum salt solutions in the anode region. When using a three-chamber electrolyzer, the salt solution was placed in the working chamber, separated by a cation-exchange membrane from the catholyte and an anion-exchange membrane from the anode zone. During electrolysis, alkali concentration occurred in the catholyte and aluminum salts in the anolyte. In the three-chamber electrolyzer, desalination occurred in the working chamber due to the diffusion of sodium ions through the cation-exchange membrane into the catholyte and the diffusion of anions (chlorides and sulfates) through the anion-exchange membrane into the anode area. Aluminum oxidation in the anode area resulted in the formation of Al³⁺ cations, and in the presence of chlorides, aluminum chloride was formed. Hydrolysis of aluminum chloride partially produced aluminum hydroxychlorides, predominantly forming 1/3 aluminum hydroxychloride. Before electrolysis, the anode chamber pH was adjusted to 2.5 with hydrochloric acid. During electrolysis, the pH was maintained at 2.5–3 due to electrode reactions. The salt content in the working chamber decreased to 2–20 mg-eq/dm³. In a two-chamber electrolyzer, electrolysis produced alkali in the catholyte and aluminum chloride in the anolyte. Conversion of sodium chloride in the anolyte was limited due to poisoning of the cation-exchange membrane by aluminum ions.
References
- Klimonda, A., Kowalska, I. (2021). Sequential process: membrane filtration and ion exchange as an effective method for water solution purification containing cationic surfactants. Desalination and Water Treatment, 214, 232–241. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.26663
- Tsutano, K. (2022). Application of Monolithic Ion Exchange resins for the field of Ultrapure Water. Journal of Ion Exchange, 33 (3), 51–55. https://doi.org/10.5182/jaie.33.51
- Martins, V. L., Ogden, M. D., Jones, M. R., Trowsdale, S. A., Hall, P. J., Jensen, H. S. (2020). Opportunities for coupled electrochemical and ion-exchange technologies to remove recalcitrant micropollutants in water. Separation and Purification Technology, 239, 116522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116522
- Tokui, Y., Moriguchi, H., Nishi, Y. (2014). Comprehensive environmental assessment of seawater desalination plants: Multistage flash distillation and reverse osmosis membrane types in Saudi Arabia. Desalination, 351, 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2014.07.034
- Torkian, M., Malekpour, A. (2025). Desalination of saline water and wastewater using graphene oxide mixed matrix membranes through pervaporation method. Desalination and Water Treatment, 321, 100989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dwt.2025.100989
- Nigiz, F. U., Veli, S., Hilmioglu, N. D. (2017). Deep purification of seawater using a novel zeolite 3A incorporated polyether-block-amide composite membrane. Separation and Purification Technology, 188, 90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.017
- Akhter, M., Habib, G., Qamar, S. U. (2018). Application of Electrodialysis in Waste Water Treatment and Impact of Fouling on Process Performance. Journal of Membrane Science & Technology, 8 (2). https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9589.1000182
- Al-Amshawee, S., Yunus, M. Y. B. M., Azoddein, A. A. M., Hassell, D. G., Dakhil, I. H., Hasan, H. A. (2020). Electrodialysis desalination for water and wastewater: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 380, 122231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122231
- Wang, Y., Yang, S. (2019). Thermodynamic analysis of an absorption-assisted multi-effect thermal desalination system with an extended operating temperature range. Desalination and Water Treatment, 155, 370–380. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23874
- Hu, Y., Wang, Y. (2017). Study on the dewatering process for water treatment residuals: Applicability of freezing–thawing, compression, and electro-osmotic treatment. Drying Technology, 35 (12), 1450–1459. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2016.1253021
- Liashenko, Y. V., Bila, T. A., Okhrimenko, O. V. (2017). Water purification processes. Freeze-thaw technology. Tavriiskyi Naukovyi Visnyk, 97, 236–243.
- Li, G., Liu, X., Yang, Z. (2021). Test method of seawater desalination plant based on information fusion. Desalination and Water Treatment, 241, 11–19. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27808
- Shablii, T. O., Holtvianytska, O. V., Kamaiev, V. S., Homelia, M. D. (2011). Reahentne pomiakshennia vody z vykorystanniam aliuminiivmisnykh koahuliantiv. Voda i Vodoochysni Tekhnolohii. Naukovo-Tekhnichni Visti, 2 (4), 36–41.
- Li, F., Jia, Y., Wang, M. (2024). Recovery of low-concentration waste acid by electrodialysis: Modeling and validation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 482, 144203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144203
- Mei, Y., Yao, Z., Ji, L., Toy, P. H., Tang, C. Y. (2018). Effects of hypochlorite exposure on the structure and electrochemical performance of ion exchange membranes in reverse electrodialysis. Journal of Membrane Science, 549, 295–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.016
- Campione, A., Gurreri, L., Ciofalo, M., Micale, G., Tamburini, A., Cipollina, A. (2018). Electrodialysis for water desalination: A critical assessment of recent developments on process fundamentals, models and applications. Desalination, 434, 121–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.12.044
- Shabliy, T. O. (2012). Synthesis of coagulants to intensify processes of water clarification. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 5 (6 (59)), 23–28. Available at: https://journals.uran.ua/eejet/article/view/4582
- Branovitckaia, S. V., Medvedev, R. B., Fialkov, Iu. A. (1986). Vychislitelnaia matematika v khimii i khimicheskoi tekhnologii. Kyiv: Vishcha shkola, 216.
- Gomelya, M., Kryzhanovska, Y. (2023). Concentration of sodium chloride solutions in the processing of concentrates for reverse osmotic water desalification. Proceedings of the NTUU “Igor Sikorsky KPI”. Series: Chemical Engineering, Ecology and Resource Saving, 3, 85–93. https://doi.org/10.20535/2617-9741.3.2023.288253
- Zhu, M., He, F., Feng, L., Chi, Y., Li, Y.-Y., Tian, B. (2024). Comparison of bipolar membrane electrodialysis, electrodialysis metathesis, and bipolar membrane electrodialysis multifunction for the conversion of waste Na2SO4: Process performance and economic analysis. Journal of Environmental Management, 370, 122513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122513
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mykola Gomelya, Yana Kryzhanovska, Iryna Makarenko, Tetyana Shabliy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The consolidation and conditions for the transfer of copyright (identification of authorship) is carried out in the License Agreement. In particular, the authors reserve the right to the authorship of their manuscript and transfer the first publication of this work to the journal under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY license. At the same time, they have the right to conclude on their own additional agreements concerning the non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form in which it was published by this journal, but provided that the link to the first publication of the article in this journal is preserved.







