Оцінка вмісту флавоноїдів у борошні зеленої гречки
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2025.341092Ключові слова:
зелена гречка, борошно зеленої гречки, флавоноїди, рутин, кверцетин, функціональне харчуванняАнотація
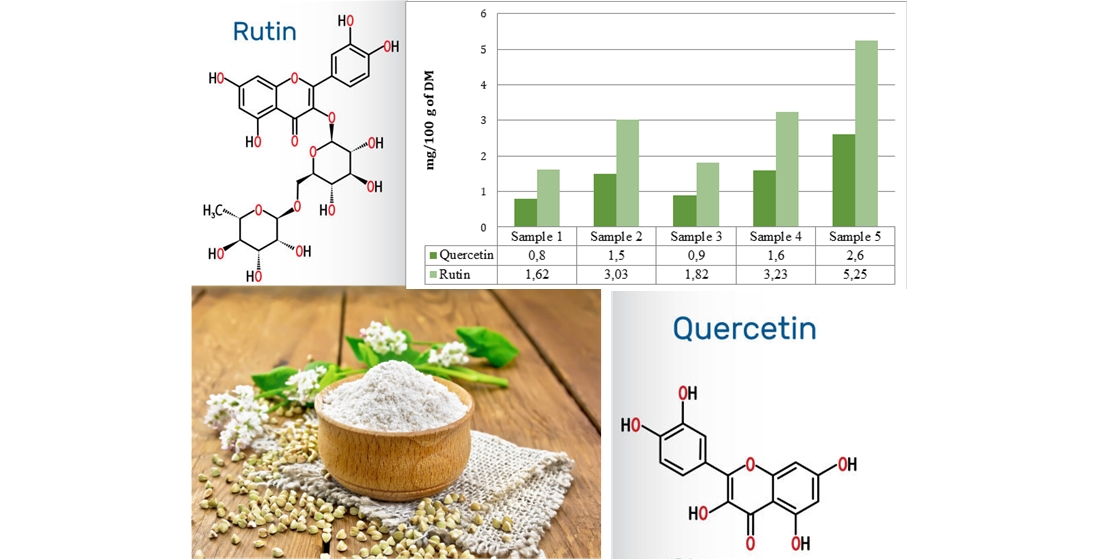
Об'єктом дослідження є борошно із зеленої гречки (БЗГ) різних торгових марок «Екород», ТМ «Екоорганік», ТМ «Ms. Tally», ТМ «Ecosmak», ТМ «Ahimsa», яке розглядається як перспективна сировина для виробництва функціональних харчових продуктів.
Одним з найбільш проблемних аспектів у вивченні даної сировини є недостатня кількість даних щодо кількісного вмісту окремих флавоноїдних сполук, зокрема кверцетину та рутина, а також відсутність системного порівняння цих показників між зразками різних виробників. Це обмежує можливості цілеспрямованого використання БЗГ як джерела біологічно активних речовин для створення продуктів із підвищеною антиоксидантною активністю.
В ході дослідження використовувалися методи абсорбційної спектрофотометрії на основі утворення хелатних комплексів із хлоридом алюмінію (AlCl₃), що дало змогу визначити сумарний вміст флавоноїдів з подальшим перерахунком результатів у вміст кверцетину та рутина. Такий підхід дозволяє кількісно оцінити біоактивний потенціал досліджуваної сировини та виявити варіабельність показників залежно від торгової марки.
Отримано дані, які свідчать про значну концентрацію флавоноїдів у БЗГ: вміст кверцетину у досліджених зразках становив 0,8–2,6 мг/100 г сухої речовини (СР), а вміст рутина – 1,62–5,25 мг/100 г СР. Це пов’язано з тим, що зелена гречка, на відміну від термічно обробленої, зберігає природну ферментну активність та фітохімічний комплекс, серед яких флавоноїди відіграють провідну роль. Запропонований підхід до аналізу дає можливість більш обґрунтовано оцінити функціональну цінність зерна та борошна зеленої гречки, що має безпосереднє практичне значення для харчової промисловості.
Завдяки цьому забезпечується можливість ідентифікації та кількісної оцінки біологічно активних речовин, що формують антиоксидантний потенціал БЗГ. У порівнянні з аналогічними відомими дослідженнями, отримані результати підтверджують перспективність використання зеленої гречки як безглютенового інгредієнта для розробки функціональних харчових продуктів, що сприятимуть зниженню ризиків розвитку оксидативного стресу та хронічних неінфекційних захворювань.
Посилання
- Tungmunnithum, D., Thongboonyou, A., Pholboon, A., Yangsabai, A. (2018). Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants for Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects: An Overview. Medicines, 5 (3), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030093
- Kuljarusnont, S., Iwakami, S., Iwashina, T., Tungmunnithum, D. (2024). Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds for Physiological Roles, Plant Species Delimitation, and Medical Benefits: A Promising View. Molecules, 29 (22), 5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29225351
- Rice-Evans, C. A., Miller, N. J., Paganga, G. (1996). Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 20 (7), 933–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(95)02227-9
- Kumar, S., Pandey, A. K. (2013). Chemistry and Biological Activities of Flavonoids: An Overview. The Scientific World Journal, 2013 (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/162750
- Kim, Y. W., Kang, H. E., Lee, M. G., Hwang, S. J., Kim, S. C., Lee, C. H. et al. (2009). Liquiritigenin, a flavonoid aglycone from licorice, has a choleretic effect and the ability to induce hepatic transporters and phase-II enzymes. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 296 (2), 372–381. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.90524.2008
- Sebastian, R. S., Goldman, J. D., Moshfegh, A. J. (2023). Dietary intake and sources of flavonoids by adults in the U.S. What We Eat in America, NHANES 2017–2018. Food Surveys Research Group Dietary Data Brief, 49. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK603802
- Schoenlechner, R., Bender, D. (2020). Pseudocereals for global food production. Cereal Foods World, 65 (2). https://doi.org/10.1094/CFW-65-2-0014
- Skřivan, P., Chrpová, D., Klitschová, B., Švec, I., Sluková, M. (2023). Buckwheat Flour (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) – A Contemporary View on the Problems of Its Production for Human Nutrition. Foods, 12 (16), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163055
- Dębski, H., Wiczkowski, W., Szawara-Nowak, D., Horbowicz, M. (2021). Elicitation with Sodium Silicate and Iron Chelate Affects the Contents of Phenolic Compounds and Minerals in Buckwheat Sprouts. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, 71 (1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.31883/pjfns/131061
- Jha, R., Zhang, K., He, Y., Mendler-Drienyovszki, N., Magyar-Tábori, K., Quinet, M. et al. (2024). Global nutritional challenges and opportunities: Buckwheat, a potential bridge between nutrient deficiency and food security. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 145, 104365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104365
- Kreft, I., Germ, M., Golob, A., Vombergar, B., Bonafaccia, F., Luthar, Z. (2022). Impact of Rutin and Other Phenolic Substances on the Digestibility of Buckwheat Grain Metabolites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (7), 3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073923
- Mirza, M. A., Mahmood, S., Hilles, A. R., Ali, A., Khan, M. Z., Zaidi, S. A. A. et al. (2023). Quercetin as a therapeutic product: Evaluation of its pharmacological action and clinical applications – a review. Pharmaceuticals, 16 (11), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111631
- Semwal, R., Joshi, S. K., Semwal, R. B., Semwal, D. K. (2021). Health benefits and limitations of rutin – a natural flavonoid with high nutraceutical value. Phytochemistry Letters, 46, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2021.10.006
- Yang, H., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Lv, J., Ni, H. (2019). Rutin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in myocardial cells by up-regulating SIRT1 expression. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 297, 44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.10.016
- Ganeshpurkar, A., Saluja, A. K. (2017). The Pharmacological Potential of Rutin. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 25 (2), 149–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2016.04.025
- Patel, K., Patel, D. K. (2019). The beneficial role of rutin, a naturally occurring flavonoid in health promotion and disease prevention: A systematic review and update. Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases, 457–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813820-5.00026-x
- Singh, S., Singh, D. K., Meena, A., Dubey, V., Masood, N., Luqman, S. (2019). Rutin protects t‑butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative impairment via modulating the Nrf2 and iNOS activity. Phytomedicine, 55, 92–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2018.07.009
- Pedriali, C. A., Fernandes, A. U., Bernusso, L. de C., Polakiewicz, B. (2008). The synthesis of a water-soluble derivative of rutin as an antiradical agent. Química Nova, 31 (8), 2147–2151. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422008000800039
- Giménez-Bastida, J. A., Zieliński, H. (2015). Buckwheat as a Functional Food and Its Effects on Health. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 63 (36), 7896–7913. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02498
- Pivec, T., Kargl, R., Maver, U., Bračič, M., Elschner, T., Žagar, E., Gradišnik, L., Stana Kleinschek, K. (2019). Chemical Structure–Antioxidant Activity Relationship of Water–Based Enzymatic Polymerized Rutin and Its Wound Healing Potential. Polymers, 11 (10), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11101566
- Ge, X., Jing, L., Zhao, K., Su, C., Zhang, B., Zhang, Q., Han, L., Yu, X., Li, W. (2021). The phenolic compounds profile, quantitative analysis and antioxidant activity of four naked barley grains with different color. Food Chemistry, 335, 127655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127655
- Kreft, I., Germ, M., Golob, A., Vombergar, B., Bonafaccia, F., Luthar, Z. (2022). Impact of Rutin and Other Phenolic Substances on the Digestibility of Buckwheat Grain Metabolites. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (7), 3923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073923
- Luthar, Z., Germ, M., Likar, M., Golob, A., Vogel-Mikuš, K., Pongrac, P., Kušar, A., Pravst, I., Kreft, I. (2020). Breeding Buckwheat for Increased Levels of Rutin, Quercetin and Other Bioactive Compounds with Potential Antiviral Effects. Plants, 9 (12), 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121638
- Kreft, I., Golob, A., Vombergar, B., Germ, M. (2023). Tartary Buckwheat Grain as a Source of Bioactive Compounds in Husked Groats. Plants, 12 (5), 1122. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12051122
- Li, D., Li, X., Ding, X., Park, K.-H. (2008). A process for preventing enzymatic degradation of rutin in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn) flour. Food Science and Biotechnology, 17, 118–122. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282054353_A_process_for_preventing_enzymatic_degradation_of_rutin_in_tartary_buckwheat_Fagopyrum_tataricum_Gaertn_flour
- Jiang, P., Burczynski, F., Campbell, C., Pierce, G., Austria, J. A., Briggs, C. J. (2007). Rutin and flavonoid contents in three buckwheat species Fagopyrum esculentum, F. tataricum, and F. homotropicum and their protective effects against lipid peroxidation. Food Research International, 40 (3), 356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2006.10.009
- Ma, H., Bian, Z., Wang, S. (2020). Effects of Different Treatments on the Germination, Enzyme Activity, and Nutrient Content of Buckwheat. Food Science and Technology Research, 26 (3), 319–328. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.26.319
- Živković, A., Polak, T., Cigić, B., Požrl, T. (2021). Germinated Buckwheat: Effects of Dehulling on Phenolics Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Buckwheat Seeds. Foods, 10 (4), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040740
- Gao, Y., Xia, W., Shao, P., Wu, W., Chen, H., Fang, X. et al. (2022). Impact of thermal processing on dietary flavonoids. Current Opinion in Food Science, 48, 100915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100915
- Lesjak, M., Beara, I., Simin, N., Pintać, D., Majkić, T., Bekvalac, K. et al. (2018). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin and its derivatives. Journal of Functional Foods, 40, 68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.10.047
- Boots, A. W., Haenen, G. R. M. M., Bast, A. (2008). Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. European Journal of Pharmacology, 585 (2–3), 325–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.03.008
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Olha Sereda, Yevheniia Demydova, Olena Koshel, Valeriia Ponomarenko, Oleksandr Voronin, Inha Kuznietsova, Liudmyla Zaichuk

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Закріплення та умови передачі авторських прав (ідентифікація авторства) здійснюється у Ліцензійному договорі. Зокрема, автори залишають за собою право на авторство свого рукопису та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY. При цьому вони мають право укладати самостійно додаткові угоди, що стосуються неексклюзивного поширення роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом, але за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію статті в цьому журналі.








