Antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa in the presence and absence of pyocyanin pigment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-8025.2024.301416Keywords:
antibiotic resistance, P. aeruginosa, pseudomonosis of poultry, pyocyanin pigment, pigmentless strains, isolates, bacteriosis, chickens, poultry farmingAbstract
Purpose: study of antibiotic resistance of Р. aeruginosa strains in the presence and absence of pyocyanin pigment.
Materials and methods. Bacteriological studies of pathological material from "asphyxiated embryos", sick chickens and forcibly killed or dead adult birds were carried out according to generally accepted methods. Cultures from bone, brain, heart, liver, spleen, gall bladder, muscles and other organs were carried out on simple, selective and differential diagnostic nutrient media. The sensitivity of P. aeruginosa isolates to antibacterial drugs was determined by diffusion in agar according to the generally accepted method.
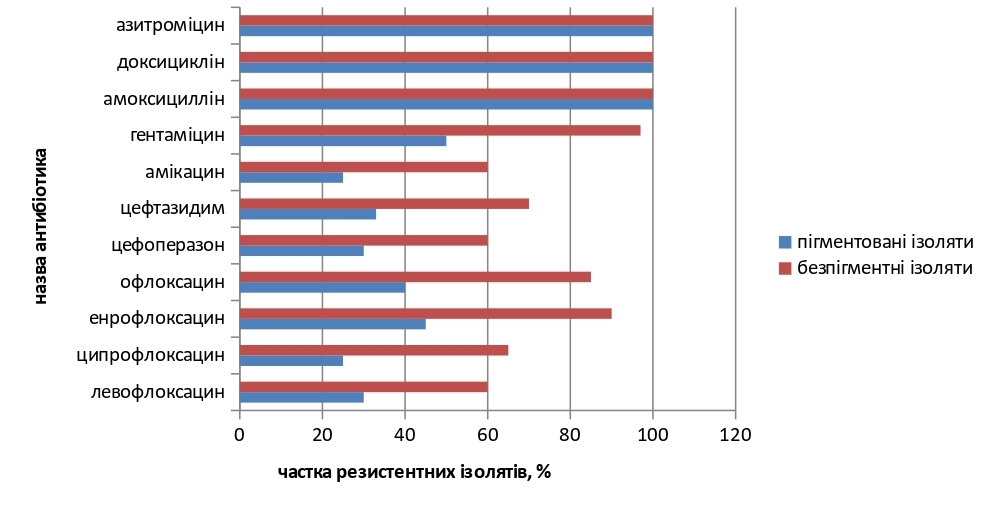
The results. The obtained results of studies by the diffusion method in agar indicate that the proportion of resistant to the studied antibiotics among non-pigmented isolates was on average 79.00 % (60-100) %, and among strains that formed pyocyanin - 51.00 % (25-100) %. 60.00 % - 90.00 % of resistant non-pigmented isolates were found to fluoroquinolones, 60.00-70.00 % to cephalosporins, 60.00-97.00 % to aminoglycosides. To representatives of semisynthetic penicillins, tetracyclines, and macrolides - 100 % of resistant isolates that did not synthesize pyocyanin were found. Among P. aeruginosa isolates that synthesized pigment, 25.00-40.00 % were resistant to fluoroquinolones, 30.00-35.00 % to cephalosporins, 25.00-50.00 % to aminoglycosides, representatives semi-synthetic penicillins, tetracyclines, macrolides - 100 % of the studied strains.
Conclusions. The absence of pigment formation in P. aeruginosa isolates, obtained in association with bacterial pathogens, is not accompanied by the absence of antibiotic resistance. 28 % more antibiotic-resistant isolates were found among non-pigmented isolates compared to isolates that synthesize pyocyanin pigment. The data presented emphasize the need for the use of differential media for the isolation of P. aeruginosa in order to identify non-pigmented strains and prescribe appropriate treatment, which, accordingly, will prevent the spread of latent forms of infection
References
- Tang, K. W. K., Millar, B. C., Moore, J. E. (2023). Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). British Journal of Biomedical Science, 80. https://doi.org/10.3389/bjbs.2023.11387
- Martinez, J. L. (2009). Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants. Environmental Pollution, 157 (11), 2893–2902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.051
- Lin, Z., Yuan, T., Zhou, L., Cheng, S., Qu, X., Lu, P., Feng, Q. (2020). Impact factors of the accumulation, migration and spread of antibiotic resistance in the environment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43 (5), 1741–1758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00759-0
- Tacconelli, E., Carrara, E., Savoldi, A., Harbarth, S., Mendelson, M., Monnet, D. L. et al. (2018). Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 18 (3), 318–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(17)30753-3
- Hall, S., McDermott, C., Anoopkumar-Dukie, S., McFarland, A., Forbes, A., Perkins, A. et al. (2016). Cellular Effects of Pyocyanin, a Secreted Virulence Factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Toxins, 8 (8), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8080236
- Zon, H. A., Vashchyk, Ye. V. (2011). Morfolohichni zminy tsentralnykh orhaniv imunnoi systemy kurchat-broileriv za psevdomonoznoi infektsii. Naukovi pratsi Poltavskoi DAA. Ser. «Veterynarna medytsyna», 2, 36–43.
- Zon, H. A., Vashchyk, Ye. V., Stets, V. V. (2011). Metodychni rekomendatsii z diahnostyky, zakhodiv borotby ta profilaktyky psevdomonozu ptytsi. Sumy.
- Lyczak, J. B., Cannon, C. L., Pier, G. B. (2000). Establishment of infection: lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes and Infection, 2 (9), 1051–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1286-4579(00)01259-4
- Gajdács, M., Baráth, Z., Kárpáti, K., Szabó, D., Usai, D., Zanetti, S., Donadu, M. G. (2021). No Correlation between Biofilm Formation, Virulence Factors, and Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Results from a Laboratory-Based In Vitro Study. Antibiotics, 10 (9), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10091134
- Bonomo, R. A., Szabo, D. (2006). Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter Species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 43 (2), S49–S56. https://doi.org/10.1086/504477
- Senobar Tahaei, S. A., Stájer, A., Barrak, I., Ostorházi, E., Szabó, D., Gajdács, M. (2021). Correlation Between Biofilm-Formation and the Antibiotic Resistant Phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates: A Laboratory-Based Study in Hungary and a Review of the Literature. Infection and Drug Resistance, 14, 1155–1168. https://doi.org/10.2147/idr.s303992
- Karballaei Mirzahosseini, H., Hadadi-Fishani, M., Morshedi, K., Khaledi, A. (2020). Meta-Analysis of Biofilm Formation, Antibiotic Resistance Pattern, and Biofilm-Related Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Clinical Samples. Microbial Drug Resistance, 26 (7), 815–824. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2019.0274
- Dietrich, L. E. P., Price‐Whelan, A., Petersen, A., Whiteley, M., Newman, D. K. (2006). The phenazine pyocyanin is a terminal signalling factor in the quorum sensing network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecular Microbiology, 61 (5), 1308–1321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05306.x
- Behzadi, P., Baráth, Z., Gajdács, M. (2021). It’s Not Easy Being Green: A Narrative Review on the Microbiology, Virulence and Therapeutic Prospects of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antibiotics, 10 (1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010042
- de Bentzmann, S., Plésiat, P. (2011). The Pseudomonas aeruginosa opportunistic pathogen and human infections. Environmental Microbiology, 13 (7), 1655–1665. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02469.x
- Kothari, A., Kumar, S. K., Singh, V., Kumar, P., Kaushal, K., Pandey, A., Jain, N., Omar, B. J. (2022). Association of multidrug resistance behavior of clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa to pigment coloration. European Journal of Medical Research, 27 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-022-00752-6
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Yevheniia Vashchyk, Olga Bobrytska, Sergiy Shtrygol', Andriy Zakhariev, Ruslan Dubin, Olga Shapovalova, Oksana Ivleva

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.
Authors, who are published in this journal, agree to the following conditions:
1. The authors reserve the right to authorship of the work and pass the first publication right of this work to the journal under the terms of a Creative Commons CC BY, which allows others to freely distribute the published research with the obligatory reference to the authors of the original work and the first publication of the work in this journal.
2. The authors have the right to conclude separate supplement agreements that relate to non-exclusive work distribution in the form in which it has been published by the journal (for example, to upload the work to the online storage of the journal or publish it as part of a monograph), provided that the reference to the first publication of the work in this journal is included.







