Ботулотоксин як найтиповіший продукт біотехнології для естетичної косметології та вивчення суб’єктивного ставлення до його застосування серед вибірки українського населення
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-8025.2024.320781Ключові слова:
Ботулінотерапія, ставлення до ботулінотерапії, інформованість щодо ботулотоксину, населення УкраїниАнотація
Метою дослідження став аналіз ефективності ботулінотерапії в естетичній косметології та вивчення впливу різних факторів щодо рішення здійснення процедури.
Матеріали та методи. У роботі використані контент-аналіз літературних джерел, аналітичний метод, проведення онлайн-анкетування жінок та чоловіків різних поколінь щодо процедури ботулінотерапії.
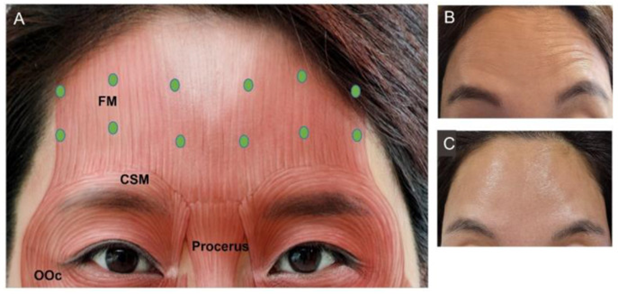
Результати та обговорення. Ботулотоксин історично спочатку використовувався для згладження глабелярних зморшок, а потім його застосування було розширено на інші ділянки обличчя. Існує сім типів ботулінічного токсину (A, B, C, D, E, F і G). Досвід використання ботулінотерапії в естетичних цілях свідчить, що клінічна неефективність трапляється вкрай рідко. Залежно від статі реакція на процедури з введенням ботулотоксину у косметичних цілях є різною. Представники жіночої статі більш обізнані про процедуру ботулінотерапію, ніж чоловіки. Ботулінотерапія найбільш поширена серед дорослих молодшого віку (25–39 років).
Висновки. Інтерес до ботулінотерапії зростає з віком. Люди, зацікавлені в ботулінотерапії, більш схильні регулярно відвідувати косметолога. Професія впливає на причетність людини до процедури ботулінотерапії. Найбільша частка респондентів, які зробили ботулінотерапію, спостерігається серед медичної та бʼюті-сфери, бізнесу та управління. Найбільше респондентів, що хочуть спробувати ботулінотерапію, є серед здобувачів освіти. Це може свідчити про відкритість молодого покоління до експериментів та розуміння важливості продовження своєї молодості в майбутньому якнайдовше. Дослідження показало, що ІМТ не впливає на причетність респондентів до процедури ботулінотерапії. Інтернет є основним джерело інформації про ботулінотерапію для значної кількості респондентів, незалежно від їх причетності до цієї процедури. Учасники ставлять на перше місце результат від ботулінотерапії, а не її вартість
Посилання
- Moriarty, K. C. (2003). Botulinum Toxin in Facial Rejuvenation. Mosby, 180. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7234-3349-1.x5002-1
- Ascher, B., Zakine, B., Kestemont, P., Baspeyras, M., Bougara, A., Santini, J. (2004). A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of efficacy and safety of 3 doses of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of glabellar lines. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 51 (2), 223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2003.11.084
- DeBoulle, K., Glogau, R., Fagien, S., Sommer, B. (2010). Treating glabellar lines with botulinum toxin type A-hemagglutinin complex: A review of the science, the clinical data, and patient satisfaction. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 5, 101–118. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s9338
- Carruthers, J. D. A., Carruthers, J. A. (1992). Treatment of Glabellar Frown Lines with C. Botulinum‐A Exotoxin. The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology, 18 (1), 17–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1992.tb03295.x
- Truong, D., Dressler, D., Hallett, M. (Eds.) (2009). Manual of Botulinum Toxin Therapy. New York: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511575761
- Dolly, J. O., Aoki, K. R. (2006). The structure and mode of action of different botulinum toxins. European Journal of Neurology, 13 (s4), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01648.x
- Arsenault, J., Cuijpers, S. A. G., Ferrari, E., Niranjan, D., Rust, A., Leese, C. et al. (2014). Botulinum protease‐cleaved SNARE fragments induce cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells. Journal of Neurochemistry, 129 (5), 781–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12645
- Pirazzini, M., Rossetto, O., Eleopra, R., Montecucco, C., Witkin, J. M. (2017). Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharmacological Reviews, 69 (2), 200–235. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.116.012658
- Wollina, U., Konrad, H., Petersen, S. (2005). Botulinum toxin in dermatology – beyond wrinkles and sweat. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 4 (4), 223–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2165.2005.00195.x
- Glogau, R. G. (2008). Botulinum toxin. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. New York: McGraw Hill, 2389–2395.
- Flynn, T. C. (2012). Advances in the use of botulinum neurotoxins in facial esthetics. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 11 (1), 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2165.2011.00593.x
- Khawaja, H. A., Hernandez‐Perez, E. (2001). Botox in dermatology. International Journal of Dermatology, 40 (5), 311–317. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-4362.2001.01176.x
- Lowe, N. J. (2010). Minimally Invasive Treatments and Procedures for Ageing Skin. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. London: Blackwell Publishing, 80.1–80.14. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444317633.ch80
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/ Last accessed: 30.04.2024
- Carruthers, J., Carruthers, A. (2007). The evolution of botulinum neurotoxin type A for cosmetic applications. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 9 (3), 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/14764170701411470
- Trindade De Almeida, A. R., Secco, L. C., Carruthers, A. (2011). Handling Botulinum Toxins. Dermatologic Surgery, 37 (11), 1553–1565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02087.x
- Kranz, G., Haubenberger, D., Voller, B., Posch, M., Schnider, P., Auff, E., Sycha, T. (2008). Respective potencies of Botox® and Dysport® in a human skin model: A randomized, double‐blind study. Movement Disorders, 24 (2), 231–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22336
- Jost, W. H., Blumel, J., Grafe, S. (2007). Botulinum neurotoxin type A free of complexing proteins (XEOMIN®) in focal dystonia. Drugs, 67 (5), 669–683. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200767050-00003
- Rieder, C. R. M., Schestatsky, P., Socal, M. P., Monte, T. L., Fricke, D., Costa, J., Picon, P. D. (2007). A Double-blind, Randomized, Crossover Study of Prosigne Versus Botox in Patients With Blepharospasm and Hemifacial Spasm. Clinical Neuropharmacology, 30 (1), 39–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wnf.0000236771.77021.3c
- Hunt, T., Clarke, K. (2008). Potency of the botulinum toxin product CNBTX-A significantly exceeds labeled units in standard potency test. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 58 (3), 517–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2007.11.015
- Spencer, J. M., Gordon, M., Goldberg, D. J. (2002). Botulinum B treatment of the glabellar and frontalis regions: a dose response analysis. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 4 (1), 19–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/14764170260030126
- Jacob, C. I. (2003). Botulinum neurotoxin type B – A rapid wrinkle reducer. Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery, 22 (2), 131–135. https://doi.org/10.1053/sder.2003.50009
- Lambros, V. (2008). Models of Facial Aging and Implications for Treatment. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 35 (3), 319–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2008.02.012
- Fagien, S., Carruthers, J. D. A. (2008). A Comprehensive Review of Patient-Reported Satisfaction with Botulinum Toxin Type A for Aesthetic Procedures. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 122 (6), 1915–1925. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0b013e31818dbfe3
- Wieder, J. M., Moy, R. L. (1998). Understanding Botulinum Toxin. Dermatologic Surgery, 24 (11), 1172–1174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.1998.tb04093.x
- Kwon, K.-H., Shin, K. S., Yeon, S. H., Kwon, D. G. (2019). Application of botulinum toxin in maxillofacial field: part I. Bruxism and square jaw. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 41 (1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-019-0218-0
- Janes, L. E., Connor, L. M., Moradi, A., Alghoul, M. (2021). Current Use of Cosmetic Toxins to Improve Facial Aesthetics. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 147 (4), 644e–657e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000007762
- Small, R. (2014). Botulinum toxin injection for facial wrinkles. American Family Physician, 90, 168–175.
- Maas, C., Kane, M. A. C., Bucay, V. W., Allen, S., Applebaum, D. J., Baumann, L. et al. (2012). Current Aesthetic Use of AbobotulinumtoxinA in Clinical Practice: An Evidence-Based Consensus Review. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 32 (1_Supplement), 8S–29S. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820x12455192
- Sundaram, H., Huang, P.-H., Hsu, N.-J., Huh, C. H., Wu, W. T. L., Wu, Y. et al. (2016). Aesthetic Applications of Botulinum Toxin A in Asians: An International, Multidisciplinary, Pan-Asian Consensus. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open, 4 (12), e872. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000000507
- Frevert, J., Ahn, K. Y., Park, M. Y., Sunga, O. (2018). Comparison of botulinum neurotoxin type A formulations in Asia. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 11, 327–331. https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.s160723
- Jaspers, G. W. C., Pijpe, J., Jansma, J. (2011). The use of botulinum toxin type A in cosmetic facial procedures. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 40 (2), 127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2010.09.014
- Kim, H.-J., Youn, K.-H., Kim, J.-S., Kim, Y. S., Hong, S. O., Na, J. (2020). US Applications in Botulinum Toxin Injection Procedures. Ultrasonographic Anatomy of the Face and Neck for Minimally Invasive Procedures. Singapore, 215–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6560-1_8
- Hong, S. O. (2023). Cosmetic Treatment Using Botulinum Toxin in the Oral and Maxillofacial Area: A Narrative Review of Esthetic Techniques. Toxins, 15 (2), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020082
- Kim, H.-J., Seo, K. K., Lee, H.-K., Kim, J. (2016). Clinical Anatomy for Botulinum Toxin Injection. Clinical Anatomy of the Face for Filler and Botulinum Toxin Injection. Singapore, 55–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0240-3_2
- Kim, H.-J., Youn, K.-H., Kim, J.-S., Kim, Y. S., Hong, S. O., Na, J. (2020). General US Anatomy of the Face and Neck. Ultrasonographic Anatomy of the Face and Neck for Minimally Invasive Procedures. Singapore, 25–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6560-1_2
- Carruthers, J., Fagien, S., Matarasso, S. L. (2004). Consensus Recommendations on the Use of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Facial Aesthetics. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 114 (Supplement), 1S-22S. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000144795.76040.d3
- Gart, M. S., Gutowski, K. A. (2016). Overview of Botulinum Toxins for Aesthetic Uses. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 43 (3), 459–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2016.03.003
- Hwang, W.-S., Hur, M.-S., Hu, K.-S., Song, W.-C., Koh, K.-S., Baik, H.-S. et al. (2009). Surface Anatomy of the Lip Elevator Muscles for the Treatment of Gummy Smile Using Botulinum Toxin. The Angle Orthodontist, 79 (1), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.2319/091407-437.1
- Rzany, B. (2007). Requirements and Rules. Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine, 21–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-34095-9_3
- de Maio, M., Wu, W. T. L., Goodman, G. J., Monheit, G. (2017). Facial Assessment and Injection Guide for Botulinum Toxin and Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Focus on the Lower Face. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 140 (3), 393e–404e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000003646
- Keaney, T. C., Alster, T. S. (2013). Botulinum toxin in men: review of relevant anatomy and clinical trial data. Dermatologic Surgery, 39 (10), 1434–1443.
- Schlessinger, J., Dover, J. S., Joseph, J., Monheit, G., Nelson, D. B., Albright, C. D. et al. (2014). Long-Term Safety of AbobotulinumtoxinA for the Treatment of Glabellar Lines: Results From a 36-Month, Multicenter, Open-Label Extension Study. Dermatologic Surgery, 40 (2), 176–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/dsu.12404
- Kundu, N., Kothari, R., Shah, N., Sandhu, S., Tripathy, D. M., Galadari, H. et al. (2022). Efficacy of botulinum toxin in masseter muscle hypertrophy for lower face contouring. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 21 (5), 1849–1856. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14858
- Kroumpouzos, G., Kassir, M., Gupta, M., Patil, A., Goldust, M. (2021). Complications of Botulinum toxin A: An update review. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 20 (6), 1585–1590. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14160
- Park, H. J., Hong, S. O., Kim, H., Oh, W., Kim, H. (2022). Positional deformation of the parotid gland: Application to minimally invasive procedures. Clinical Anatomy, 35 (8), 1147–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23941
- Teymoortash, A., Sommer, F., Mandic, R., Schulz, S., Bette, M., Aumüller, G., Werner, J. A. (2007). Intraglandular application of botulinum toxin leads to structural and functional changes in rat acinar cells. British Journal of Pharmacology, 152 (1), 161–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707375
- Ondo, W. G., Hunter, C., Moore, W. (2004). A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology, 62 (1), 37–40. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000101713.81253.4c
- Jackson, C. E., Gronseth, G., Rosenfeld, J., Barohn, R. J., Dubinsky, R., Simpson, C. B. et al. (2009). Randomized double‐blind study of botulinum toxin type B for sialorrhea in als patients. Muscle & Nerve, 39 (2), 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.21213
- Greene, P., Fahn, S., Diamond, B. (1994). Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Movement Disorders, 9 (2), 213–217. Portico. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.870090216
- Dressler, D., Tacik, P., Adib Saberi, F. (2013). Botulinum toxin therapy of cervical dystonia: comparing onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®) and incobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin®). Journal of Neural Transmission, 121 (1), 29–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1076-z
- Sethi, K. D., Rodriguez, R., Olayinka, B. (2012). Satisfaction with botulinum toxin treatment: a cross-sectional survey of patients with cervical dystonia. Journal of Medical Economics, 15 (3), 419–423. https://doi.org/10.3111/13696998.2011.653726
- Fernandez, H. H., Evidente, V. G. H., Truong, D., Brodsky, M., Hanschmann, A., Comella, C. L., Jankovic, J. (2013). Long-term treatment of blepharospasm and cervical dystonia: Incobotulinum toxin A is well tolerated when injected at flexible intervals based on patient needs. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 333, e120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2013.07.403
- Botox® (onabotulinumtoxinA) for injection, for intramuscular, intradetrusor, or intradermal use (2020). Allergan Inc. Prescribing Information. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/103000s5317lbl Last accessed: 30.04.2024
- Dressler, D., Adib Saberi, F. (2005). Botulinum Toxin: Mechanisms of Action. European Neurology, 53 (1), 3–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000083259
- Dayan, S. H., Maas, C. S. (2007). Botulinum Toxins for Facial Wrinkles: Beyond Glabellar Lines. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 15 (1), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2006.12.001
- Alam, M., Dover, J. S., Arndt, K. A. (2002). Pain Associated With Injection of Botulinum A Exotoxin Reconstituted Using Isotonic Sodium Chloride With and Without Preservative. Archives of Dermatology, 138 (4), 510. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.138.4.510
- Klein, A. W. (2003). Complications, Adverse Reactions, and Insights With the Use of Botulinum Toxin. Dermatologic Surgery, 29 (5), 549–556. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29129.x
- Thaller, S. R., Kim, S. (1998). The use of botulinum toxin to improve results in aesthetic facial surgery. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 22 (2), 141–147.
- Carruthers, J. D., Lowe, N. J., Menter, M. A., Gibson, J., Eadie, N. (2003). Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin Type A for Patients with Glabellar Lines. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 112 (4), 1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000076504.79727.62
- Dayan, S. H., Maas, C. S. (2007). Botulinum Toxins for Facial Wrinkles: Beyond Glabellar Lines. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 15 (1), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2006.12.001
- Gart, M. S., Gutowski, K. A. (2016). Overview of Botulinum Toxins for Aesthetic Uses. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 43 (3), 459–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2016.03.003
- Cula, G. O., Bargo, P. R., Nkengne, A., Kollias, N. (2012). Assessing facial wrinkles: automatic detection and quantification. Skin Research and Technology, 19 (1), 243–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0846.2012.00635.x
- Simon, C. et al. (2010). Botulinum Toxin for Cosmetic. UTMB Health, 122.
- Dayan, S. H. (2013). Complications from Toxins and Fillers in the Dermatology Clinic. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 21 (4), 663–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2013.07.008
- Alam, M., Tung, R. (2018). Injection technique in neurotoxins and fillers: Indications, products, and outcomes. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 79 (3), 423–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.01.037
- Hassouneh, B., Newman, J. P. (2013). Laser, fillers, and neurotoxins avoiding complication in the cosmetic facial practice. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, 21 (4), 585–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2013.07.002
- Bellomo, R., Harrington, L. K. (2016). Neurotoxins and Dermal Fillers: choosing the right product. Physician Assistant Clinics, 1 (2), 333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpha.2015.12.008
- Niamtu, J. (2009). Complications in Fillers and Botox. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America, 21 (1), 13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coms.2008.11.001
- Kim, K., Jeon, S., Kim, J.-K., Hwang, J. S. (2015). Effects of Kyunghee Facial Resistance Program (KFRP) on mechanical and elastic properties of skin. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 27 (2), 191–196. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2015.1056078
- Ezure, T., Hosoi, J., Amano, S., Tsuchiya, T. (2009). Sagging of the cheek is related to skin elasticity, fat mass and mimetic muscle function. Skin Research and Technology, 15 (3), 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0846.2009.00364.x
- Castillo-Garzón, M. J., Ruiz, J. R., Ortega, F. B., Gutiérrez, Á. (2006). Anti-aging therapy through fitness enhancement. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 1 (3), 213–220. https://doi.org/10.2147/ciia.2006.1.3.213
- Clark, H. M., O’Brien, K., Calleja, A., Newcomb Corrie, S. (2009). Effects of Directional Exercise on Lingual Strength. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 52 (4), 1034–1047. https://doi.org/10.1044/1092-4388(2009/08-0062)
- Plastic Surgery Statistics Report (2018). Available at: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2018/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2018.pdf Last accessed: 30.04.2024
- Schlessinger, J., Monheit, G., Kane, M. A. C., Mendelsohn, N. (2011). Time to Onset of Response of AbobotulinumtoxinA in the Treatment of Glabellar Lines: A Subset Analysis of Phase 3 Clinical Trials of a New Botulinum Toxin Type A. Dermatologic Surgery, 37 (10), 1434–1442. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02075.x
- Rappl, T., Parvizi, Wiedner, May, Kranzelbinder, Friedl, H., Wurzer, P. (2013). Onset and duration of effect of incobotulinumtoxinA, onabotulinumtoxinA, and abobotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of glabellar frown lines: a randomized, double-blind study. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 6, 211–219. https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.s41537
- Flynn, T. C. (2007). Botox in men. Dermatologic Therapy, 20 (6), 407–413. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2007.00156.x
- Flynn, T. C. (2010). Botulinum toxin: examining duration of effect in facial aesthetic applications. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 11 (3), 183–199. https://doi.org/10.2165/11530110-000000000-00000
- Fedok, F. (1996). The Aging Face. Facial Plastic Surgery, 12 (2), 107–115. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1082402
- Sundaram, H., Liew, S., Signorini, M., Vieira Braz, A., Fagien, S., Swift, A. et al. (2016). Global Aesthetics Consensus: Hyaluronic Acid Fillers and Botulinum Toxin Type A – Recommendations for Combined Treatment and Optimizing Outcomes in Diverse Patient Populations. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 137 (5), 1410–1423. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000002119
- Carruthers, J., Burgess, C., Day, D., Fabi, S. G., Goldie, K., Kerscher, M. et al. (2016). Consensus Recommendations for Combined Aesthetic Interventions in the Face Using Botulinum Toxin, Fillers, and Energy-Based Devices. Dermatologic Surgery, 42 (5), 586–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000000754
- Dover, J. S., Monheit, G., Greener, M., Pickett, A. (2018). Botulinum Toxin in Aesthetic Medicine: Myths and Realities. Dermatologic Surgery, 44 (2), 249–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000001277
- Rogozhin, A. A., Pang, K. K., Bukharaeva, E., Young, C., Slater, C. R. (2008). Recovery of mouse neuromuscular junctions from single and repeated injections of botulinum neurotoxin A. The Journal of Physiology, 586 (13), 3163–3182. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.153569
- Courtney, J., Steinbach, J. H. (1981). Age changes in neuromuscular junction morphology and acetylcholine receptor distribution on rat skeletal muscle fibres. The Journal of Physiology, 320 (1), 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013960
- Gonzalez-Freire, M., de Cabo, R., Studenski, S. A., Ferrucci, L. (2014). The Neuromuscular Junction: Aging at the Crossroad between Nerves and Muscle. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00208
- Cheng, C. M. (2007). Cosmetic use of botulinum toxin type A in the elderly. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 2 (1), 81–83. https://doi.org/10.2147/ciia.2007.2.1.81
- Yamauchi, P. (2010). Selection and preference for botulinum toxins in the management of photoaging and facial lines: patient and physician considerations. Patient Preference and Adherence, 4, 345–354. https://doi.org/10.2147/ppa.s6494
##submission.downloads##
Опубліковано
Як цитувати
Номер
Розділ
Ліцензія
Авторське право (c) 2025 Ольга Володимирівна Філіпцова, Ольга Іванівна Набока, Наталя Вікторівна Хохленкова, Катерина Юріївна Калашнік, Ольга Сергіївна Калюжная, Наталія Власівна Двінських, Аліна Володимирівна Соловйова, Андрій Вікторович Захар’єв, Людмила Станіславівна Петровська

Ця робота ліцензується відповідно до Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Наше видання використовує положення про авторські права Creative Commons CC BY для журналів відкритого доступу.
Автори, які публікуються у цьому журналі, погоджуються з наступними умовами:
1. Автори залишають за собою право на авторство своєї роботи та передають журналу право першої публікації цієї роботи на умовах ліцензії Creative Commons CC BY, котра дозволяє іншим особам вільно розповсюджувати опубліковану роботу з обов'язковим посиланням на авторів оригінальної роботи та першу публікацію роботи у цьому журналі.
2. Автори мають право укладати самостійні додаткові угоди щодо неексклюзивного розповсюдження роботи у тому вигляді, в якому вона була опублікована цим журналом (наприклад, розміщувати роботу в електронному сховищі установи або публікувати у складі монографії), за умови збереження посилання на першу публікацію роботи у цьому журналі.









