Study of aqueous solutions of poloxamers by rotational viscometry and spin probe method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.285933Keywords:
poloxamer, solution, gel, viscosity, micelle, spin probe, EPR spectrum, spectrum parametersAbstract
The aim. To study aqueous solutions of different poloxamers by spin probe method and rotational viscometry depending on the temperature and poloxamer content.
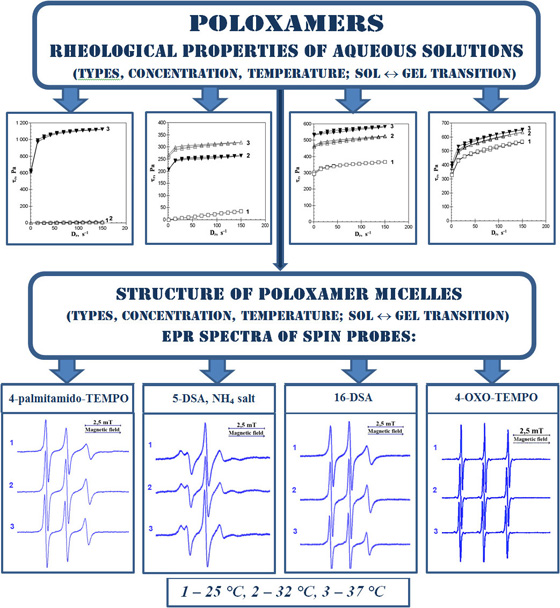
Materials and methods. The aqueous solutions of poloxamers 188, 237, 338 and 407 were studied. The solutions were studied by rotational viscometry at different temperatures; the flow behaviour, yield stress (t0), and dynamic or apparent viscosity (η) were determined. Five spin probes differing in molecular structure, solubility, and radical localisation were introduced into the solutions. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra were obtained. The EPR spectra were used to determine their type and to calculate parameters.
Results. Three factors are important for gel formation: the poloxamer type, its concentration in aqueous solution, and temperature. As the temperature of aqueous solutions of poloxamers 237, 338, and 407 increases, the rotational correlation times of fatty acid-based spin probes and the order parameters of their EPR spectra decrease. This indicates a decrease in the packing density and orderliness of the polypropylene oxide (PPO) chains in the non-polar part of the poloxamer associates, leading to an increase in the volume fraction of micelles/mesophases and promoting the formation of gels. As the temperature decreases, the opposite processes occur, leading to a gel → sol transition. At 37 °C, non-polar micelle cores could be characterised as two-dimensionally liquid and one-dimensionally solid. The rotational correlation times of the hydrophilic spin probe 4-OXO-TEMPO in 25 % aqueous solutions of poloxamers 338 and 407 are approximately constant or increasing despite an increase in the temperature. This indicates that in the polar part of the poloxamer associates, where this probe is partially localised, structural rearrangements occur with increasing temperature, which probably prevents hydrophobic hydration of the PPO chains.
Conclusions. The rheological properties of aqueous solutions of poloxamers depend on their type, concentration, and temperature. According to the parameters of the EPR spectra of fatty acid-based spin probes, it was found that with increasing temperature, the packing density and the orderliness of the PPO chains in the non-polar part of the poloxamer associates decrease, probably leading to an increase in the volume of the micelles and causing a sol → gel transition
References
- The European Pharmacopoeia (2019). European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare of the Council of Europe, Strasbourg, 5224.
- Sheskey, P. J., Hancock, B. C., Moss, G. P., Goldfarb, D. J. (Eds.) (2020). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. London: Pharm. Press, 1296.
- Bodratti, A., Alexandridis, P. (2018). Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 9 (1), 11. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9010011
- Bodratti, A. M., Sarkar, B., Alexandridis, P. (2017). Adsorption of poly(ethylene oxide)-containing amphiphilic polymers on solid-liquid interfaces: Fundamentals and applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 244, 132–163. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2016.09.003
- Mortensen, K., Talmon, Y. (1995). Cryo-TEM and SANS Microstructural Study of Pluronic Polymer Solutions. Macromolecules, 28 (26), 8829–8834. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00130a016
- Alexandridis, P., lan Hatton, T. (1995). Poly(ethylene oxide) poly(propylene oxide) poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 96 (1-2), 1–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7757(94)03028-x
- Alexandridis, P., Athanassiou, V., Fukuda, S., Hatton, T. A. (1994). Surface Activity of Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-Poly(propylene oxide)-block-Poly(ethylene oxide) Copolymers. Langmuir, 10 (8), 2604–2612. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/la00020a019
- Alexandridis, P., Holzwarth, J. F., Hatton, T. A. (1994). Micellization of Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(propylene oxide)-Poly(ethylene oxide) Triblock Copolymers in Aqueous Solutions: Thermodynamics of Copolymer Association. Macromolecules, 27 (9), 2414–2425. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00087a009
- Raval, A., Pillai, S. A., Bahadur, A., Bahadur, P. (2017). Systematic characterization of Pluronic® micelles and their application for solubilization and in vitro release of some hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 230, 473–481. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.01.065
- Cabana, A., Aı̈t-Kadi, A., Juhász, J. (1997). Study of the Gelation Process of Polyethylene Oxidea–Polypropylene Oxideb–Polyethylene OxideaCopolymer (Poloxamer 407) Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 190 (2), 307–312. doi: https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1997.4880
- Prud’homme, R. K., Wu, G., Schneider, D. K. (1996). Structure and Rheology Studies of Poly(oxyethylene−oxypropylene−oxyethylene) Aqueous Solution. Langmuir, 12 (20), 4651–4659. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/la951506b
- Soliman, K. A., Ullah, K., Shah, A., Jones, D. S., Singh, T. R. R. (2019). Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications. Drug Discovery Today, 24 (8), 1575–1586. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2019.05.036
- Cook, M. T., Brown, M. B. (2018). Polymeric gels for intravaginal drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 270, 145–157. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.004
- Russo, J., Fiegel, J., Brogden, N. K. (2020). Rheological and Drug Delivery Characteristics of Poloxamer-Based Diclofenac Sodium Formulations for Chronic Wound Site Analgesia. Pharmaceutics, 12 (12), 1214. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12121214
- Russo, E., Villa, C. (2019). Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics, 11 (12), 671. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120671
- Zhang, T., Chen, S., Dou, H., Liu, Q., Shu, G., Lin, J. et al. (2021). Novel glucosamine-loaded thermosensitive hydrogels based on poloxamers for osteoarthritis therapy by intra-articular injection. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 118, 111352. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111352
- Abdeltawab, H., Svirskis, D., Sharma, M. (2020). Formulation strategies to modulate drug release from poloxamer based in situ gelling systems. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 17 (4), 495–509. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2020.1731469
- Wanka, G., Hoffmann, H., Ulbricht, W. (1990). The aggregation behavior of poly-(oxyethylene)-poly-(oxypropylene)-poly-(oxyethylene)-block-copolymers in aqueous solution. Colloid & Polymer Science, 268 (2), 101–117. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01513189
- Alexandridis, P., Zhou, D., Khan, A. (1996). Lyotropic Liquid Crystallinity in Amphiphilic Block Copolymers: Temperature Effects on Phase Behavior and Structure for Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) Copolymers of Different Composition. Langmuir, 12 (11), 2690–2700. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/la951025s
- Alexandridis, P., Olsson, U., Lindman, B. (1998). A Record Nine Different Phases (Four Cubic, Two Hexagonal, and One Lamellar Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline and Two Micellar Solutions) in a Ternary Isothermal System of an Amphiphilic Block Copolymer and Selective Solvents (Water and Oil). Langmuir, 14 (10), 2627–2638. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/la971117c
- Sarkar, B., Venugopal, V., Bodratti, A. M., Tsianou, M., Alexandridis, P. (2013). Nanoparticle surface modification by amphiphilic polymers in aqueous media: Role of polar organic solvents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 397, 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.01.034
- Valero, M., Castiglione, F., Mele, A., da Silva, M. A., Grillo, I., González-Gaitano, G., Dreiss, C. A. (2016). Competitive and Synergistic Interactions between Polymer Micelles, Drugs, and Cyclodextrins: The Importance of Drug Solubilization Locus. Langmuir, 32 (49), 13174–13186. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03367
- Cook, M. T., Abou-Shamat, M. A., Stair, J. L., Calvo-Castro, J. (2022). Raman spectroscopy coupled to computational approaches towards understanding self-assembly in thermoreversible poloxamer gels. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 351, 118660. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118660
- Berliner, L. (Ed.). (1979). Metod spinovyih metok. Teoriya i primenenie. Moscow: Mir, 635.
- Georgieva, E. R. (2017). Nanoscale lipid membrane mimetics in spin-labeling and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of protein structure and function. Nanotechnology Reviews, 6 (1), 75–92. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2016-0080
- Sahu, I. D., Lorigan, G. A. (2021). Probing Structural Dynamics of Membrane Proteins Using Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Techniques. Biophysica, 1 (2), 106–125. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica1020009
- Camargos, H. S., Alonso, A. (2013). Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectral components of spin-labeled lipids in saturated phospholipid bilayers: effect of cholesterol. Química Nova, 36 (6), 815–821. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-40422013000600013
- Catte, A., White, G. F., Wilson, M. R., Oganesyan, V. S. (2018). Direct Prediction of EPR Spectra from Lipid Bilayers: Understanding Structure and Dynamics in Biological Membranes. ChemPhysChem, 19 (17), 2183–2193. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201800386
- Farafonov, V. S., Lebed, A. V. (2020). Nitroxyl spin probe in ionic micelles: A molecular dynamics study. Kharkiv University Bulletin. Chemical Series, 34 (57), 57–64. doi: https://doi.org/10.26565/2220-637x-2020-34-02
- Bezuglaya, E., Lyapunov, N., Lysokobylka, O., Liapunov, O., Klochkov, V., Grygorova, H., Liapunova, A. (2021). Interaction of surfactants with poloxamers 338 and its effect on some properties of cream base. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 6 (34), 4–19. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2021.249312
- Bezuglaya, E., Lyapunov, N., Chebanov, V., Liapunov, O. (2022). Study of the formation of micelles and their structure by the spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (38), 4–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.263054
- Rusanov, A. I., Shchyokin, A. K. (2016). Micelloobrazovanie v rastvorah poverhnostno-aktivnyh veshchestv. Saint-Peterburg: OOO «Izdatel'stvo «Lan'», 612.
- Markus, F., Dreher, F., Laschat, S., Baudis, S., Tovar, G. E. M., Southan, A. (2017). Physically and chemically gelling hydrogel formulations based on poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and Poloxamer 407. Polymer, 108, 21–28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.11.039
- Lykhtenshtein, G. I. (1974). Metod spinovykh zondov v molekuliarnoi biologii, Moscow: Nauka, 256.
- Kuznecov, A. N. (1976). Metod spinovogo zonda (Osnovy i primenenie), Moscow: Nauka, 210.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Nikolay Lyapunov, Elena Bezuglaya, Oleksii Liapunov, Oleksii Lysokobylka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






