Selection of the base for a topical pharmaceutical form for stump care after prosthetic fitting
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.313142Keywords:
amputation, prosthetics, complications, therapy, prevention, semi-solid medicine, technology, structural and mechanical propertiesAbstract
The aim of the work. Rehabilitation of patients with amputation of the lower limbs is an urgent task of society. Currently, the pharmaceutical market of Ukraine lacks medicinal products for stump care of domestic production. Therefore, the aim of this work was to research the selection of the basis of soft medicine for the care of stumps after prosthetics.
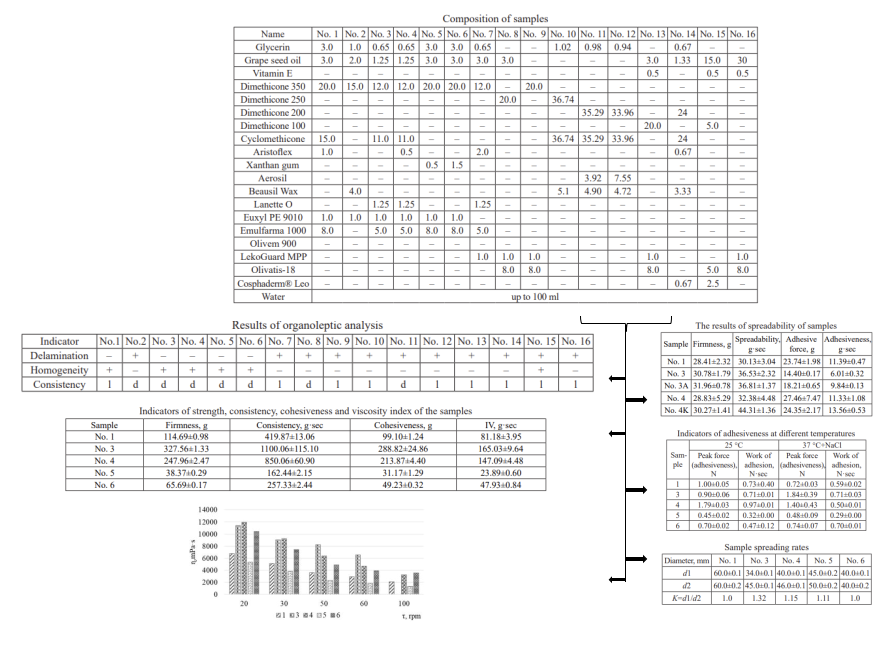
Materials and methods. The objects of the study were samples of a soft medicinal product on an emulsion basis. Gelling agents (aristoflex, xanthan gum, aerosil) were used as regulators of the structural and mechanical parameters of soft medicine. Research was conducted using a set of studies to determine organoleptic and structural-mechanical indicators.
Results. According to the results of the organoleptic analysis, according to the indicators of homogeneity, the presence of delamination, samples were selected for further research, where aristoflex and xanthan gum were used as a thickener. According to the results of structural and mechanical studies, it was established that the samples with xanthan gum have a satisfactory degree of spreading and adhesiveness, which increases with increasing exposure to mechanical forces. The determined values of static and dynamic coefficients of friction testify to the sliding properties of samples with xanthan gum.
Conclusion. It was established that the addition of xanthan gum to the composition of the base would provide all the necessary characteristics for a soft medicine that is planned to be used in the care of the stump after prosthetics
Supporting Agency
- State budget of Ukraine within the framework of the budget program KPKVK2301020 "Research, scientific and scientific and technical developments, implementation of works under state target programs and state orders, training and advanced training of scientific personnel in the field of health care, financial support for the development of scientific infrastructure and objects constituting the national heritage" related to the topic 0124U001991 "Development of soft drugs to improve the functional state of the stump during prosthetics".
References
- Denysiuk, M. V., Dubrov, S., Cherniaiev, S., Sereda, S., Zaikin, Yu. M. (2022). Structure of Traumatic Injuries and Experience in the Treatment of the Wounded Patients, as a Result of Hostilities in the First Days of Russia’s Attack on Ukraine. Pain, Anaesthesia & Intensive Care, 1 (98), 7–12. https://doi.org/10.25284/2519-2078.1(98).2022.256092
- Khomenko, I. P., Korol, S. O., Khalik, S. V., Shapovalov, V. Yu., Yenin, R. V., Нerasimenko, O. S., Tertyshnyі, S. V. (2021). Clinical and Epidemiological analysis of the structure of combat surgical injury during Antiterrorist operation / Joint Forces Operation. Ukrainian Journal of Military Medicine, 2 (2), 5–13. https://doi.org/10.46847/ujmm.2021.2(2)-005
- WSJ: cherez viinu 50 tysiach ukraintsiv vtratyly ruky chy nohy (2023). Available at: https://www.radiosvoboda.org/a/news-wsj-50-tysyach-ukrajincivamputacija/32530520.html
- Šupolová, K., Barkasi, D. (2022). The importance of rehabilitation in patients with bilateral transfemoral amputation. Ukraine. Nation’s Health, 2, 99–102. https://doi.org/10.32782/2077-6594.2.1.2022.258920
- Cordella, F., Ciancio, A. L., Sacchetti, R., Davalli, A., Cutti, A. G., Guglielmelli, E., Zollo, L. (2016). Literature Review on Needs of Upper Limb Prosthesis Users. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00209
- Guriev, S., Kravtsov, D., Titova, Y. (2022). Clinical and pathomorphological characteristics of modern combat injury. Trauma, 18 (5), 50–53. https://doi.org/10.22141/1608-1706.5.18.2017.114117
- Bespalenko, А. А., Shchehlіuk, O. I., Kikh, A. Y., Buryanov, О. А., Volyansky, O. M., Korchenok, V. V., Myhailovska, M. (2020). Algorithm for rehabilitation of combat-related patients with limb amputations based on multiprofessional and individual approach. Ukrainian Journal of Military Medicine, 1 (1), 64–72. https://doi.org/10.46847/ujmm.2020.1(1)-064
- McIntosh, J., Earnshaw, J. J. (2009). Antibiotic Prophylaxis for the Prevention of Infection after Major Limb Amputation. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 37 (6), 696–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2009.01.013
- Kooijman, C. M., Dijkstra, P. U., Geertzen, J. H. B., Elzinga, A., van der Schans, C. P. (2000). Phantom pain and phantom sensations in upper limb amputees: an epidemiological study. Pain, 87 (1), 33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00264-5
- MacIver, K., Lloyd, D. M., Kelly, S., Roberts, N., Nurmikko, T. (2008). Phantom limb pain, cortical reorganization and the therapeutic effect of mental imagery. Brain, 131 (8), 2181–2191. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn124
- Le Feuvre, P., Aldington, D. (2013). Know Pain Know Gain: proposing a treatment approach for phantom limb pain. Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps, 160 (1), 16–21. https://doi.org/10.1136/jramc-2013-000141
- Pasquina, P. F., Miller, M., Carvalho, A. J., Corcoran, M., Vandersea, J., Johnson, E., Chen, Y.-T. (2014). Special Considerations for Multiple Limb Amputation. Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports, 2 (4), 273–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40141-014-0067-9
- Coulston, J. E., Tuff, V., Twine, C. P., Chester, J. F., Eyers, P. S., Stewart, A. H. R. (2012). Surgical Factors in the Prevention of Infection Following Major Lower Limb Amputation. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 43(5), 556–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2012.01.029
- Schober, T.-L., Abrahamsen, C. (2022). Patient perspectives on major lower limb amputation – A qualitative systematic review. International Journal of Orthopaedic and Trauma Nursing, 46, 100958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijotn.2022.100958
- Gerasimenko, O. S., Mukhin, V. M. (2016). Prerequisites for the development of a comprehensive program of physical rehabilitation of persons with amputations of the lower limbs at the level of the leg. Bulletin of the Carpathian University. Series: Physical culture, 23, 50–59.
- Burban, K., Kukhtenko, H., Kriukova, A., Yakovenko, V., Matsiuk, K., Slipchenko, H., Vyshnevska, L. (2023). Research by choice of excipients ingredients of the gel for the therapy of radiation lesions of the skin based on rheological studies. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 5 (45), 44–52. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.290004
- Baranova, I. I., Kovalenko, I. S. M., Khokhlenkova, N. V., Martyniuk, T. V., Kutsenko, S. A. (2017). Prospects of using synthetic and semi-synthetic gelling substances in development of medicinal and cosmetic gels. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics, 11 (2), 302–307.
- Velia, M., Ruban, O. (2022). Research on the selection of emulgel preservative with thick extract of feverfew. Annals of Mechnikov Institute, 2, 68–72. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6634854
- Matsiuk, K., Kovalova, T., Maslii, Y., Herbina, N., Vyshnevska, L., Kaliuzhnaia, O., Tkachuk, O. (2023). Experimental research on the development of composition of complex action ointment based on phytocomplex. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (44), 19–27. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.286306
- Ruban, O., Al Sayasneh, M., Kovalevska, I., Grudko, V., Lytkin, D., Dunaіevska, O. (2023). Study of the influence of ingredients on biopharmaceutical factors and pharmacological activity of a medicinal product with carrot extract and rutin. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 2 (42), 20–28. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.277562
- Maslii, Yu., Ruban, O., Levachkova, Yu., Gureyeva, S., Kolisnyk, T. (2020). Choice of mucosal adhesive in the composition of a new dental gel. Pharmakeftiki, 32 (1), 40–49. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351614507
- Borko, Y., Inna, K., Grudko, V., Kononenko, N., Velya, M. (2022). Comprehensive study for the development of rectal suppositories with diosmin and hesperidin. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (35), 14–21. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.253518
- Mudryk, K., Hutsol, T., Wrobel, M., Jewiarz, M., Dziedzic, B. (2019). Determination of friction coefficients of fast-growing tree biomass. Engineering for Rural Development, 1568–1573.https://doi.org/10.22616/erdev2019.18.n506
- Sobral-Souza, D. F., Gouveia, T. H. N., Condeles, A. L., Junior, J. C. T., Muniz, B. V., Franz-Montan, M. et al. (2022). Effect of accelerated stability on the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of experimental bleaching gels containing different bioadhesive polymers. Clinical Oral Investigations, 26 (3), 3261–3271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04308-6
- Lemaitre‐Aghazarian, V., Piccerelle, P., Reynier, J. P., Joachim, J., Phan‐Tan‐Luu, R., Sergent, M. (2004). Texture Optimization of Water‐in‐Oil Emulsions. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 9 (2), 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1081/pdt-120027424
- Andrade, F. F., Santos, O. D. H., Oliveira, W. P., Rocha‐Filho, P. A. (2007). Influence of PEG‐12 Dimethicone addition on stability and formation of emulsions containing liquid crystal. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 29 (3), 211–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2494.2007.00374.x
- Djekic, L., Martinović, M., Dobričić, V., Čalija, B., Medarević, Đ., Primorac, M. (2019). Comparison of the Effect of Bioadhesive Polymers on Stability and Drug Release Kinetics of Biocompatible Hydrogels for Topical Application of Ibuprofen. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 108 (3), 1326–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.10.054
- Waters, M. G. J., Jagger, R. G., Polyzois, G. L. (1999). Wettability of silicone rubber maxillofacial prosthetic materials. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 81 (4), 439–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3913(99)80011-0
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Inna Kovalevska, Halyna Slipchenko, Yuliia Maslii, Nataliia Herbina, Olena Ruban, Olena Ivaniuk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






