Study of the effect of propylene glycol on the properties of poloxamer 338 solutions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.313294Keywords:
poloxamer 338 (Р338), propylene glycol (PG), solution, gel, viscosity, micelle, spin probe, EPR spectrum, spectrum parametersAbstract
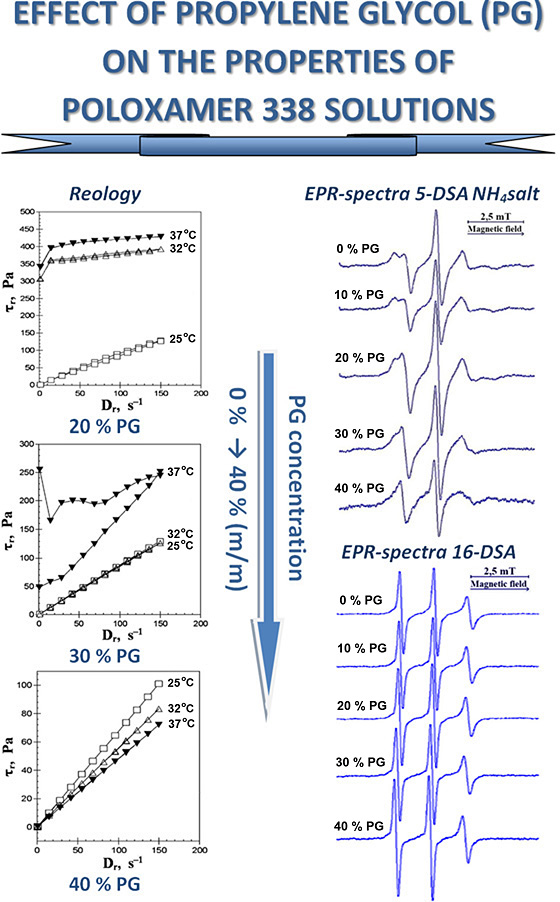
The aim. Study of the characteristics of 20 % solutions of poloxamer 338 (P338) in water and mixed solvents water – propylene glycol (PG) at various temperatures using rotational viscometry and the spin probe method.
Materials and methods. 20 % m/m solutions of P338 in water and water – PG mixtures were the objects of research. The solutions were studied by rotational viscometry at 25 °С, 32 °С і 37 °С; the flow behaviour, low-yield stress (t0), hysteresis area (SN) and dynamic or apparent viscosity (η) were determined. Spin probes based on fatty acids, which differ in molecular structure, solubility, and radical localisation, were added to the solutions. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra was obtained to determine their type and parameters.
Results. Depending on the content, PG affects the rheological properties of 20 % P338 solution. The ability of this solution to undergo thermally induced sol-gel transitions, resulting in the formation of gels with plastic flow behaviour at temperatures of 32 °C and 37 °C, is maintained at PG content of up to 20 %. At 37 °C and a 30 % PG content, an atypical thixotropic gel is formed. The rheological characteristics of gels containing 10-20 % PG at 32 °C and 37 °C are higher than those of gels without PG. The increase in the PG concentration from 0 to 40 % generally has little effect on the rotational correlation times (τ) and values of the order parameter (S) of the spin probes. In the case of the ammonium salt of 5-doxylstearic acid (5-DSA NH4 salt), the anisotropic EPR spectra at a PG concentration of 40 % undergoes a transformation, becoming a triplet. This coincides with the loss of the ability of 20 % P338 solutions to thermally induced sol ↔ gel transitions. An increase in the concentration of PG (in contrast to ethanol) does not lead to the solvation of P338 micelle cores by the dispersion medium. The transformation of the EPR spectrum of the 5-DSA NH4 salt into a triplet is probably the result of the interaction between PG and the hydrophilic shell of micelles through the formation of hydrogen bonds.
Conclusions. The rheological properties of 20 % P338 solution are affected by the PG, depending on its content. The P338 solutions can undergo a thermally induced sol ↔ gel transition, provided that the PG content does not exceed 30 %. A correlation has been identified between alterations in the rheological properties of 20 % P338 solution and the corresponding change in the types of EPR spectra observed for the 5-DSA NH4 salt, namely a transition from anisotropic spectra to triplet. As the PG content in the P338 solution increases up to 40 %, the solvation of micelle cores by the dispersion medium does not occur. It may be posited that the alteration in the structure of P338 micelles is a consequence of the interaction between PG and their hydrophilic shell
Supporting Agency
- National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine within the framework of the project «Study of dispersed systems as bases-vehicles for development of medicinal products» (0124U003095).
References
- The European Pharmacopoeia (2022). European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare of the Council of Europe. Strasbourg: Sedex, 6105.
- Sheskey, P. J., Hancock, B. C., Moss, G. P., Goldfarb, D. J. (Eds.) (2020). Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients. London: Pharm. Press, 1296.
- Bodratti, A., Alexandridis, P. (2018). Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 9 (1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9010011
- Alexandridis, P., Hatton, T. A. (1994). Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 96 (1-2), 1–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-7757(94)03028-x
- Alexandridis, P., Holzwarth, J. F., Hatton, T. A. (1994). Micellization of Poly(ethylene oxide)-Poly(propylene oxide)-Poly(ethylene oxide) Triblock Copolymers in Aqueous Solutions: Thermodynamics of Copolymer Association. Macromolecules, 27 (9), 2414–2425. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00087a009
- Cabana, A., Aı̈t-Kadi, A., Juhász, J. (1997). Study of the Gelation Process of Polyethylene Oxidea–Polypropylene Oxideb–Polyethylene OxideaCopolymer (Poloxamer 407) Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 190 (2), 307–312. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1997.4880
- Prud’homme, R. K., Wu, G., Schneider, D. K. (1996). Structure and Rheology Studies of Poly(oxyethylene−oxypropylene−oxyethylene) Aqueous Solution. Langmuir, 12 (20), 4651–4659. https://doi.org/10.1021/la951506b
- Lyapunov, N., Bezuglaya, E., Liapunov, O., Lysokobylka, O. (2023). Study of aqueous solutions of poloxamers by rotational viscometry and spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (44), 4–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.285933
- Cook, M. T., Brown, M. B. (2018). Polymeric gels for intravaginal drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 270, 145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.004
- Russo, E., Villa, C. (2019). Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics, 11 (12), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120671
- Zhang, T., Chen, S., Dou, H., Liu, Q., Shu, G., Lin, J. et al. (2021). Novel glucosamine-loaded thermosensitive hydrogels based on poloxamers for osteoarthritis therapy by intra-articular injection. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 118, 111352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111352
- Soliman, K. A., Ullah, K., Shah, A., Jones, D. S., Singh, T. R. R. (2019). Poloxamer-based in situ gelling thermoresponsive systems for ocular drug delivery applications. Drug Discovery Today, 24 (8), 1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2019.05.036
- Ivanova, R., Alexandridis, P., Lindman, B. (2001). Interaction of poloxamer block copolymers with cosolvents and surfactants. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 183–185, 41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0927-7757(01)00538-6
- Ivanova, R., Lindman, B., Alexandridis, P. (2002). Effect of Pharmaceutically Acceptable Glycols on the Stability of the Liquid Crystalline Gels Formed by Poloxamer 407 in Water. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 252 (1), 226–235. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2002.8417
- Liapunov, O., Bezuglaya, E., Liapunova, A., Lysokobylka, O. (2024). Study of the effect of ethanol on the properties of poloxamer 338 solutions by rotational viscometry and spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 3 (49), 13–26. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.306365
- Bezuglaya, E. P., Lyapunova, A. N., Krasnoperova, A. P. (2013). Water–Hexylene Glycol System as a Potential Medicinal Base. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 47 (5), 281–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-013-0943-0
- Khattab, I. S., Bandarkar, F., Khoubnasabjafari, M., Jouyban, A. (2017). Density, viscosity, surface tension, and molar volume of propylene glycol + water mixtures from 293 to 323 K and correlations by the Jouyban–Acree model. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 10, S71–S75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.07.012
- Bielawska, M., Chodzińska, A., Jańczuk, B., Zdziennicka, A. (2013). Determination of CTAB CMC in mixed water+short-chain alcohol solvent by surface tension, conductivity, density and viscosity measurements. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 424, 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.017
- Makarov, D. M., Egorov, G. I., Kolker, A. M. (2016). Temperature and composition dependences of volumetric properties of (water + 1,2-propanediol) binary system. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 222, 656–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.07.095
- Prajapati, P. M., Pandit, T. R., Vankar, H. P., Rana, V. A. (2021). Physical and acoustical properties of paracetamol in binary mixtures of water + propylene glycol. Materials Today: Proceedings, 47, 632–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.756
- George, J., Sastry, N. V. (2003). Densities, Dynamic Viscosities, Speeds of Sound, and Relative Permittivities for Water + Alkanediols (Propane-1,2- and -1,3-diol and Butane-1,2-, -1,3-, -1,4-, and -2,3-Diol) at Different Temperatures. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 48 (6), 1529–1539. https://doi.org/10.1021/je0340755
- Sun, T., Teja, A. S. (2004). Density, Viscosity and Thermal Conductivity of Aqueous Solutions of Propylene Glycol, Dipropylene Glycol, and Tripropylene Glycol between 290 K and 460 K. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 49 (5), 1311–1317. https://doi.org/10.1021/je049960h
- Zhou, Y., Hu, K., Shen, J., Wu, X., Cheng, G. (2009). Microstructure variations with concentration of propylene glycol–water solution probed by NMR. Journal of Molecular Structure, 921 (1-3), 150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.12.050
- Xu, Y., Xing, L., Cao, X., Li, D., Men, Z., Li, Z. et al. (2023). Hydrogen bonding network dynamics of 1,2-propanediol-water binary solutions by Raman spectroscopy and stimulated Raman scattering. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 284, 121825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2022.121825
- Bezuhlaia, E. P., Melnykova, E. N., Zhemerova, E. H., Liapunov, A. N., Zynchenko, Y. A. (2016). Efficacy of antimicrobial preservation of certain hydrophilic non-aqueous solvents in aqueous solutions and gels. Farmakom, 1, 51–59.
- Bendas, B., Schmalfuβ, U., Neubert, R. (1995). Influence of propylene glycol as cosolvent on mechanisms of drug transport from hydrogels. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 116 (1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(94)00267-9
- Wiegand, T. J. (2024). Propylene glycol. Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 981–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-824315-2.01179-9
- Bezugla, O. P., Lyapunov, M. O., Zinchenko, I. O., Lisokobilka, O. A., Liapunova, A. M. (2022). Modeling of processes of solvent diffusion from ointment bases using in vitro experiments. Functional materials, 29 (4), 553–558. https://doi.org/10.15407/fm29.04.553
- Nemati, A., Rezaei, H., Poturcu, K., Hanaee, J., Jouyban, A., Zhao, H., Rahimpour, E. (2023). Effect of temperature and propylene glycol as a cosolvent on dissolution of clotrimazole. Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises, 81 (2), 258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharma.2022.10.001
- García, O. E., Martínez, F., Peña, Á., Jouyban, A., Acree, W. E. (2024). Solubility of atenolol in aqueous propylene glycol mixtures revisited: IKBI preferential solvation analysis. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 62 (5), 527–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319104.2024.2329917
- Zeng, A.-G., Pang, X.-L., Wu, N., Wang, D., Nan, G.-J., Yang, G.-D., Bian, X.-L. (2014). Solubility of daidzein in propylene glycol plus water cosolvent mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 366, 127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2013.12.024
- Fathi-Azarjbayjani, A., Mabhoot, A., Martínez, F., Jouyban, A. (2016). Modeling, solubility, and thermodynamic aspects of sodium phenytoin in propylene glycol–water mixtures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 219, 68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.02.089
- Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V., Rahimpour, E., Hemmati, S., Martinez, F., Jouyban, A. (2020). Mesalazine solubility in propylene glycol and water mixtures at various temperatures using a laser monitoring technique. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 299, 112136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112136
- Muñoz, M. M., Rodríguez, C. J., Delgado, D. R., Peña, M. Á., Jouyban, A., Martínez, F. (2015). Solubility and saturation apparent specific volume of some sodium sulfonamides in propylene glycol + water mixtures at 298.15 K. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 211, 192–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.07.016
- del Mar Muñoz, M., Delgado, D. R., Peña, M. Á., Jouyban, A., Martínez, F. (2015). Solubility and preferential solvation of sulfadiazine, sulfamerazine and sulfamethazine in propylene glycol+water mixtures at 298.15K. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 204, 132–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.01.047
- Assis, G. P., Derenzo, S., Bernardo, A. (2022). Solid-liquid equilibrium of nicotinamide in water-ethanol and water-propylene glycol mixtures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 345, 117799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117799
- Assis, G. P., Garcia, R. H. L., Derenzo, S., Bernardo, A. (2021). Solid-liquid equilibrium of paracetamol in water-ethanol and water-propylene glycol mixtures. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 323, 114617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114617
- Pirhayati, F. H., Shayanfar, A., Rahimpour, E., Barzegar-Jalali, M., Martinez, F., Jouyban, A. (2017). Solubility of sildenafil citrate in propylene glycol + water mixtures at various temperatures. Physics and Chemistry of Liquids, 56 (4), 508–517. https://doi.org/10.1080/00319104.2017.1354376
- Alkilani, A., McCrudden, M. T., Donnelly, R. (2015). Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the Stratum Corneum. Pharmaceutics, 7 (4), 438–470. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7040438
- Berliner, L. (Ed.) (1979). Metod spinovykh metok. Teoriia i primenenie. Moscow: Mir, 635.
- Likhtenshtein, G. I. (1974). Metod spinovykh zondov v molekuliarnoi biologii. Moscow: Nauka, 256.
- Kuznetcov, A. N. (1976). Metod spinovogo zonda (Osnovy i primenenie). Moscow: Nauka, 210.
- Bezuglaya, E., Lyapunov, N., Chebanov, V., Liapunov, O. (2022). Study of the formation of micelles and their structure by the spin probe method. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 4 (38), 4–18. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2022.263054
- Bezuglaya, E., Krasnopyorova, A., Liapunova, A., Zinchenko, I., Lyapunov, N., Sytnik, O. (2023). Influence of physicochemical properties and structure of mixed solvents propylene glycol – macrogol 400 on their in vitro release. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, 1 (41), 4–13. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.274468
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oleksii Liapunov, Olena Bezugla, Nikolay Lyapunov, Oleksii Lysokobylka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






