Application of statistical tools for the formulation and optimization of carvedilol mucoadhesive buccal films by using natural polymers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.273548Keywords:
natural polymers, mucoadhesive, Carvedilol, buccal film, in vitro studiesAbstract
The aim and objective of this study was to create mucoadhesive buccal films that contained the multipurpose medical carvedilol, which has a variety of medicinal uses.
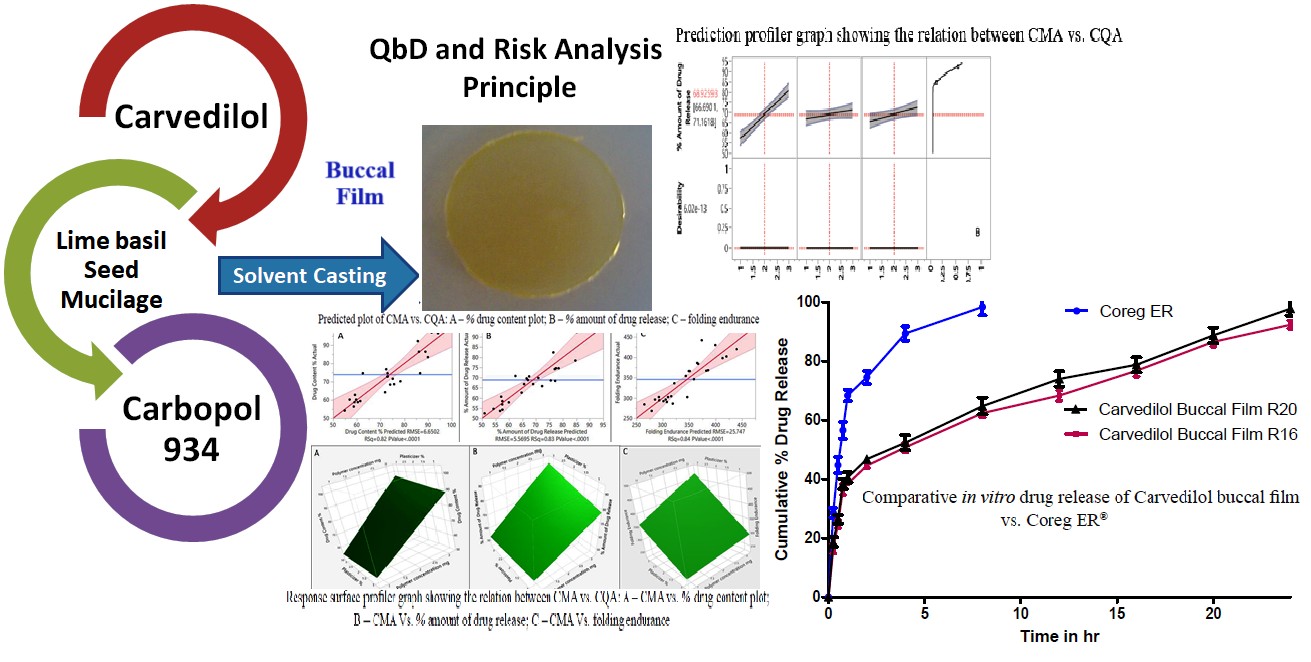
Materials and methods. The films were equipped using a solvent casting technique and concentrations of natural polymers, including Sweet basil, Lime Basil seeds and Purple basil mucilage. The influence of Carbopol 934 P, a selected natural polymer, was also investigated. The formulation variables were improved by the use of a factorial design of experiments and evaluated for their physico-chemical and in vitro evaluations.
Result. These evaluations provided crucial insights into the properties of the buccal films. To evaluate the release profile and release kinetics of carvedilol from the films, in vitro drug release experiments were carried out in a phosphate buffer solution. Ex vivo permeation tests using fresh sheep buccal mucosa were performed to evaluate the drug's permeation through the buccal membrane. Samples were taken at regular intervals, and a UV Spectrophotometer was used for analysis. With a polymer solution concentration at level "3," formulation run R20 showed the best optimized buccal formulation. This formulation shows promise for further in vivo research.
Conclusions. The results of this study offer important new evidence about the design and efficacy of mucoadhesive buccal films containing carvedilol. The optimization of formulation parameters and the assessment of physicochemical properties and drug release kinetics contribute to the progress of reproducible buccal films
References
- Hearnden, V., Sankar, V., Hull, K., Juras, D. V., Greenberg, M., Kerr, A. R. et al. (2012). New developments and opportunities in oral mucosal drug delivery for local and systemic disease. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64 (1), 16–28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2011.02.008
- Hoogstraate, J. A. J., Wertz, P. W., Wertz, P. W. (1998). Drug delivery via the buccal mucosa. Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Today, 1 (7), 309–316. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1461-5347(98)00076-5
- Mathias, N. R., Hussain, M. A. (2010). Non-invasive Systemic Drug Delivery: Developability Considerations for Alternate Routes of Administration. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 99 (1), 1–20. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21793
- Shojaei, A. H. (1998). Buccal Mucosa as a route for systemic drug delivery. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1, 15–30.
- Carvalho, F. C., Bruschi, M. L., Evangelista, R. C., Gremião, M. P. D. (2010). Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 46 (1), 1–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1984-82502010000100002
- El-Maghraby, G., Abdelzaher, M. (2015). Formulation and evaluation of simvastatin buccal film. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 5, 70–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.7324/japs.2015.50412
- Satishbabu, B., Srinivasan, B. (2008). Preparation and evaluation of buccoadhesive films of atenolol. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 70 (2), 175. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.41451
- Abouhussein, D. M. N., El-bary, A. A., Shalaby, S. H., Nabarawi, M. A. E. (2016). Chitosan mucoadhesive buccal films: effect of different casting solvents on their physicochemical properties. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 8 (9), 206–213. doi: https://doi.org/10.22159/ijpps.2016.v8i9.12999
- Singh, B., Chakkal, S. K., Ahuja, N. (2006). Formulation and optimization of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of atenolol using response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech, 7 (1), E19–E28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt070103
- Bilaskar, V. V., Indrajeet, S. P., Patil, O. A., Mandke, G. R., Mohite, S. K. (2018). Design, development and optimization of pulsatile drug delivery of antihypertensive drug. International research journal of pharmaceutical and biosciences, 4 (6), 12–19.
- Shrivastava, A., Ursekar, B., Kapadia, C. (2009). Design, Optimization, Preparation and Evaluation of Dispersion Granules of Valsartan and Formulation into Tablets. Current Drug Delivery, 6 (1), 28–37. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/156720109787048258
- Peh, K. K., Wong, C. F. (1999). Polymeric films as vehicle for buccal delivery: swelling, mechanical, and bioadhesive properties. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science, 2, 53–61.
- Perumal, V. A., Lutchman, D., Mackraj, I., Govender, T. (2008). Formulation of monolayered films with drug and polymers of opposing solubilities. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 358 (1-2), 184–191. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.03.005
- Kundu, J., Patra, C., Kundu, S. C. (2008). Design, fabrication and characterization of silk fibroin-HPMC-PEG blended films as vehicle for transmucosal delivery. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 28 (8), 1376–1380. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.03.004
- Alanazi, F. K., Abdel Rahman, A., Mahrous, G. M., Alsarra, I. A. (2007). Formulation and physicochemical characterization of buccoadhesive films containing ketorolac. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 17 (1), 1–10.
- Nafee, N. A., Boraie, N. A., Ismail, F. A., Mortada, L. M. (2003). Design and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal patches containing Cetylpyridinium chloride. Acta Pharmaceutica, 53, 199–212.
- Chun, M.-K., Kwak, B.-T., Choi, H.-K. (2003). Preparation of buccal patch composed of carbopol, poloxamer and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 26 (11), 973–978. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02980208
- Patel, R., Poddar, S. (2009). Development and Characterization of Mucoadhesive Buccal Patches of Salbutamol Sulphate. Current Drug Delivery, 6 (1), 140–144. doi: https://doi.org/10.2174/156720109787048177
- Roy, S., Pal, K., Anis, A., Pramanik, K., Prabhakar, B. (2009). Polymers in Mucoadhesive Drug-Delivery Systems: A Brief Note. Designed Monomers and Polymers, 12 (6), 483–495. doi: https://doi.org/10.1163/138577209x12478283327236
- Khurana, R., Ahuja, A., Khar, R. K. (2000). Development and evaluation of mucoadhesive films of miconazole nitrate. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 62 (6), 447–453.
- Kharenko, E. A., Larionova, N. I., Demina, N. B. (2008). Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems: Quantitative Assessment of Interaction Between Synthetic and Natural Polymer Films and Mucosa. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 42 (7), 392–399. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-008-0132-8
- Desai, K. G. H., Pramod Kumar, T. M. (2004). Preparation and evaluation of a novel buccal adhesive system. AAPS PharmSciTech, 5 (3), 1–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1208/pt050335
- Balamurugan, K., Pandit, J. K., Choudary, P. K., Balasubramaniyam, J. (2011). Systemic absorption of Propranolol Hydrochloride from buccoadhesive films. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 63 (6), 473–480.
- Hagesaether, E., Hiorth, M., Sande, S. A. (2009). Mucoadhesion and drug permeability of free mixed films of pectin and chitosan: An in vitro and ex vivo study. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 71 (2), 325–331. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.09.002
- Shidhaye, S. S., Saindane, N. S., Sutar, S., Kadam, V. (2008). Mucoadhesive Bilayered Patches for Administration of Sumatriptan Succinate. AAPS PharmSciTech, 9 (3), 909–916. doi: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9125-x
- Lewis, S., Subramanian, G., Pandey, S., Udupa, N. (2006). Design, evaluation and pharmacokinetic study of mucoadhesive buccal tablets of nicotine for smoking cessation. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 68 (6), 829–331. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474x.31030
- Kaur, A., Kaur, G. (2012). Mucoadhesive buccal patches based on interpolymer complexes of chitosan–pectin for delivery of carvedilol. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 20 (1), 21–27. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2011.04.005
- Khazaei, N., Esmaiili, M., Djomeh, Z. E., Ghasemlou, M., Jouki, M. (2014). Characterization of new biodegradable edible film made from basil seed (Ocimum basilicum L.) gum. Carbohydrate Polymers, 102, 199–206. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.062
- Trastullo, R., Abruzzo, A., Saladini, B., Gallucci, M. C., Cerchiara, T., Luppi, B., Bigucci, F. (2016). Design and evaluation of buccal films as paediatric dosage form for transmucosal delivery of ondansetron. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 105, 115–121. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.05.026
- Yamsani, V., Gannu, R., Kolli, C., Rao, M., Yamsani, M. (2007). Development and in vitro evaluation of buccoadhesive carvedilol tablets. Acta Pharmaceutica, 57 (2), 185–197. doi: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10007-007-0015-7
- Abd-Elbary, A., Makky, A. M. A., Tadros, M. I., Alaa-eldin, A. A. (2015). Development and in vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive bilayer buccal tablets of carvedilol. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 7, 172–176.
- Rajaram, D. M., Laxman, S. D. (2016). Buccal Mucoadhesive Films: A Review. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 8 (1), 31–38. doi: https://doi.org/10.5530/srp.2017.1.7
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Leela Lakshmi Vajrala, Umashankar M S, Alagusundaram M

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






