Experimental research on the development of composition of complex action ointment based on phytocomplex
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2023.286306Keywords:
ointment base, emulsion ointment, composition, multicomponent phytoextract, tea tree essential oil, geranium essential oilAbstract
The aim of the work is to develop the composition of a complex action ointment based on active pharmaceutical ingredients of natural origin for the treatment of cheilitis of various etiologies.
Materials and methods. The development of the ointment base by selecting active pharmaceutical ingredients and auxiliary substances determined by organoleptic, physicochemical, rheological and microbiological research methods.
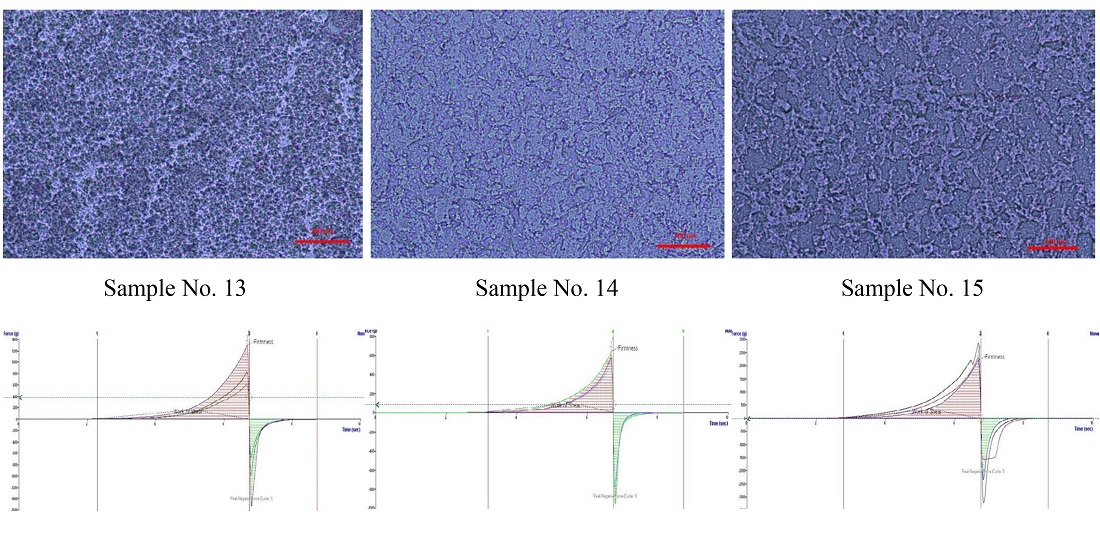
Results. Studies of the antimicrobial activity of experimental samples have established that the optimal ointment base is a water/oil emulsion, which provides better API release rates than absorption bases.
According to the results of structural and mechanical studies, the introduction of the API complex reduces the structural viscosity of the ointment base. Furthermore, the ability of the ointment to thin out with an increase in the gradient of the shear rate is shown, which will contribute to the uniform distribution of the API during the technological process and the easy application of the ointment to the skin.
The study of textural properties of the experimental ointment samples (cohesion, adhesion, and elasticity) also confirmed the satisfactory spreadability of the sample. The optimal container for its consistent properties was chosen according to the results of the ointment's structural, mechanical and textural properties.
A test of the effectiveness of antimicrobial preservatives was conducted, resulting in the minimum effective concentration of sodium benzoate in the amount of 1 % was substantiated. Furthermore, based on the results of a complex of studies, the composition of the emulsion ointment was developed, which includes vaseline (liquid paraffin) 20 %, emulsifiers glycerol monostearate 5.5 %, polysorbate-80 3.5 %, viscosity regulator of the aqueous phase hydroxyethyl cellulose 3 %, phytocomplex API "Phytol" (concentrated aqueous extract of burdock root: oak bark: pot marigold flower in the ratio 5:1:1.5, respectively) and essential oils of tea tree 1 % and geranium 1.5 %, purified water.
Conclusions. Based on organoleptic, physicochemical, rheological and microbiological studies, the composition of the ointment of complex action was developed based on active pharmaceutical ingredients of natural origin for the treatment of cheilitis of various etiologies.
References
- Rabinovich, I. M., Rabinovich, O. F., Abramova, E. S., Denisova, M. A. (2016). Clinical and pathogenetic aspects of various forms of cheilitis. Stomatologiya, 95 (1), 67–72. doi: https://doi.org/10.17116/stomat201695167-72
- Romeo, U., Rocchetti, F., Montori, A. (2019). Criticisms and Controversies in the Diagnosis of Cheilitis. The XV National and III International Congress of the Italian Society of Oral Pathology and Medicine. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019035008
- Lugović-Mihić, L., Blagec, T., Japundžić, I., Skroza, N., Delaš Adžajić, M., Mravak-Stipetić, M. (2020). Diagnostic management of cheilitis: an approach based on a recent proposal for cheilitis classification. Acta Dermatovenerologica Alpina Pannonica et Adriatica, 29 (2), 67–72. doi: https://doi.org/10.15570/actaapa.2020.16
- Khismatullina, Z. R., Bulgakova, A. I., Khamzina, G. R., Zatsepina, M. V. (2018). Treatment of vermilion zone diseases. Klinicheskaya Dermatologiya i Venerologiya, 17 (2), 81–86. doi: https://doi.org/10.17116/klinderma201817281-86
- Derzhavnyi reiestr likarskykh zasobiv. Available at: http://www.drlz.com.ua/ibp/ddsite.nsf/all/shlist?opendocument
- Smirnova, I. P., Semkina, O. A., Bondarenko, O. V. (2016). Plant Extracts in Development of Medicinal Products of Various Therapeutic Value. Antibiot Khimioter, 61, 30–34.
- Kovalenko, V. M. (2019). Kompendium 2019 – likarski preparaty. Kyiv: MORION, 2480.
- Gowher, G. (2019). Therapeutic value of arctium lappa linn – a review. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 53–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2019.v12i7.33870
- Morales, D. (2021). Oak trees (Quercus spp.) as a source of extracts with biological activities: A narrative review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 109, 116–125. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.029
- Afanasyeva, P. V., Kurkina, A. V., Kurkin, V. A., Lyamin, A. V., Zhestkov, A. V. (2016). Determination of antimicrobial activity of extracts of calendula officinalis flowers. Pharmacy & Pharmacology, 4 (2 (15)), 60–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.19163/2307-9266-2016-4-2(15)-60-70
- Al-Mijalli, S. H., Mrabti, H. N., Assaggaf, H., Attar, A. A., Hamed, M., Baaboua, A. E. et al. (2022). Chemical Profiling and Biological Activities of Pelargonium graveolens Essential Oils at Three Different Phenological Stages. Plants, 11 (17), 2226. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11172226
- Ardiana, D. (2021). Role Of Tea Tree Oil as A Skin Antimicrobial : A Literature Study. Medical and Health Science Journal, 5 (1), 26–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.33086/mhsj.v5i1.1921
- Colucci, G., Santamaria-Echart, A., Silva, S. C., Fernandes, I. P. M., Sipoli, C. C., Barreiro, M. F. (2020). Development of Water-in-Oil Emulsions as Delivery Vehicles and Testing with a Natural Antimicrobial Extract. Molecules, 25 (9), 2105. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092105
- Volianskyi, Yu. L., Hrytsenko, I. S., Shyrobokov, V. P. et al. (2004). Vyvchennia spetsyfichnoi aktyvnosti protymikrobnykh likarskykh zasobiv. Kyiv, 38.
- Roberts, M. S., Cheruvu, H. S., Mangion, S. E., Alinaghi, A., Benson, H. A. E., Mohammed, Y. et al. (2021). Topical drug delivery: History, percutaneous absorption, and product development. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 177, 113929. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.113929
- Melike Demirbolat, G., Demirel, A. (2021). The role of ointment base on stability of dexketoprofen trometamol in ointments. Journal of Research in Pharmacy, 25 (5), 674–681. doi: https://doi.org/10.29228/jrp.59
- Ghosh, P., Raney, S. G., Luke, M. C. (2022). How Does the Food and Drug Administration Approve Topical Generic Drugs Applied to the Skin? Dermatologic Clinics, 40 (3), 279–287. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2022.02.003
- Pertcev, I. M. et al. (2003). Farmatcevticheskie i biologicheskie aspekty mazei. Kharkiv: NFaU; Zolotye stranitcy, 288.
- Park, E.-K., Song, K.-W. (2010). Rheological evaluation of petroleum jelly as a base material in ointment and cream formulations: Steady shear flow behavior. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 33 (1), 141–150. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-2236-4
- McClements, D. J., Jafari, S. M. (2018). Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 251, 55–79. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2017.12.001
- Kukhtenko, H. P., Gladukh, Ye. V., Kukhtenko, O. S., Domar, N. A. (2018). Study оf Concentrated Emulsions’ Structural-Mechanical Properties Dependence From the Type and Concentration of Surfactant. Chemical Senses, 43 (9 (2)), 949–962.
- Zuikina, Y., Polovko, N., Strilets, O., Strelnikov, L. (2021). The in vitro release testing and the antimicrobial activity of semi-solid dosage forms which contain salicylic acid. Farmacia, 69 (6), 1073–1079. doi: https://doi.org/10.31925/farmacia.2021.6.8
- Derzhavna Farmakopeia Ukrainy. Vol. 1. Kharkiv: Derzhavne pidpryiemstvo «Ukrainskyi naukovyi farmakopeinyi tsentr yakosti likarskykh zasobiv», 1128.
- Thomson, K. S., Thomson, G. K., Biehle, J., Deeb, A., Crawford, J., Herrera, R. (2016). A Novel Topical Combination Ointment with Antimicrobial Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Gram-Negative Superbugs, Yeasts, and Dermatophytic Fungi. Current Therapeutic Research, 83, 8–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2016.07.001
- Yarnykh, T. G., Ivaniuk, O. I., Kovalevska, I. V., Kukhtenko, H. P., Kutsenko, S. A. (2018). Rheology-based substantiation of a gel-former choice for vaginal gel. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 10 (11), 2825–2828. Available at: http://dspace.nuph.edu.ua/handle/123456789/18553
- Strus, O., Polovko, N., Yezerska, O. (2019). Justification of technological parameters of the cream production with sapropel extract. Pharmacia, 66 (1), 19–25. doi: https://doi.org/10.3897/pharmacia.66.e35022
- Sharadha M, Gowda D V, Vishal Gupta N, Akhila A R. (2020). An overview on topical drug delivery system – Updated review. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 11 (1), 368–385. doi: https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v11i1.1831
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ksenia Matsiuk, Tetiana Kovalova, Yuliia Maslii, Nataliia Herbina, Liliia Vyshnevska, Olha Kaliuzhnaia, Oksana Tkachuk

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Our journal abides by the Creative Commons CC BY copyright rights and permissions for open access journals.






